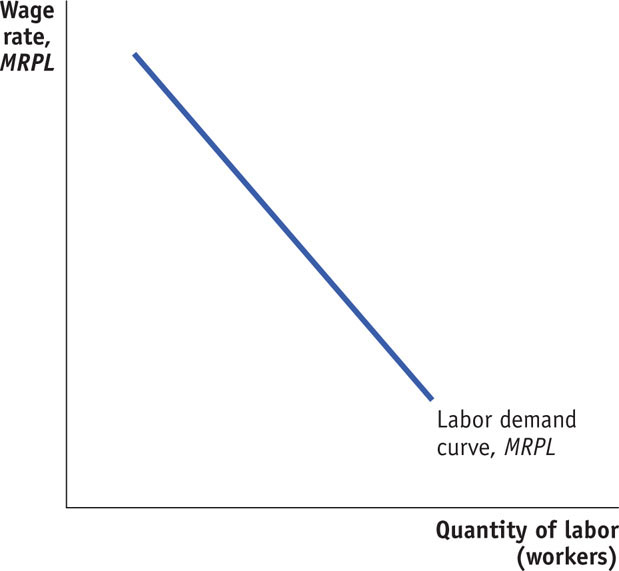
A firm’s labor demand curve is the marginal revenue product of labor curve, which differs from the value of the marginal product of labor curve when there is imperfect competition in the product market (as with a monopoly, for example). With perfect competition, the marginal revenue product of labor (MPL × MR) and the value of the marginal product of labor (MPL × P) are the same because MR = P.