PROBLEMS
Question 7.15
The United States imposes an excise tax on the sale of domestic airline tickets. Let’s assume that in 2013 the total excise tax was $6.10 per airline ticket (consisting of the $3.60 flight segment tax plus the $2.50 September 11 fee). According to data from the Bureau of Transportation Statistics, in 2013, 643 million passengers traveled on domestic airline trips at an average price of $380 per trip. The accompanying table shows the supply and demand schedules for airline trips. The quantity demanded at the average price of $380 is actual data; the rest is hypothetical.
Price of trip
Quantity of trips demanded (millions)
Quantity of trips supplied (millions)
$380.02
642
699
380.00
643
698
378.00
693
693
373.90
793
643
373.82
913
642
What is the government tax revenue in 2013 from the excise tax?
On January 1, 2014, the total excise tax increased to $6.20 per ticket. What is the quantity of tickets transacted now? What is the average ticket price now? What is the 2014 government tax revenue?
Does this increase in the excise tax increase or decrease government tax revenue?
Question 7.16
The U.S. government would like to help the American auto industry compete against foreign automakers that sell trucks in the United States. It can do this by imposing an excise tax on each foreign truck sold in the United States. The hypothetical pre-
tax demand and supply schedules for imported trucks are given in the accompanying table. Quantity of imported trucks (thousands)
Price of imported truck
Quantity demanded
Quantity supplied
$32,000
100
400
31,000
200
350
30,000
300
300
29,000
400
250
28,000
500
200
27,000
600
150
In the absence of government interference, what is the equilibrium price of an imported truck? The equilibrium quantity? Illustrate with a diagram.
Assume that the government imposes an excise tax of $3,000 per imported truck. Illustrate the effect of this excise tax in your diagram from part a. How many imported trucks are now purchased and at what price? How much does the foreign automaker receive per truck?
Calculate the government revenue raised by the excise tax in part b. Illustrate it on your diagram.
How does the excise tax on imported trucks benefit American automakers? Whom does it hurt? How does inefficiency arise from this government policy?
Question 7.17
In 1990, the United States began to levy a tax on sales of luxury cars. For simplicity, assume that the tax was an excise tax of $6,000 per car. The accompanying figure shows hypothetical demand and supply curves for luxury cars.
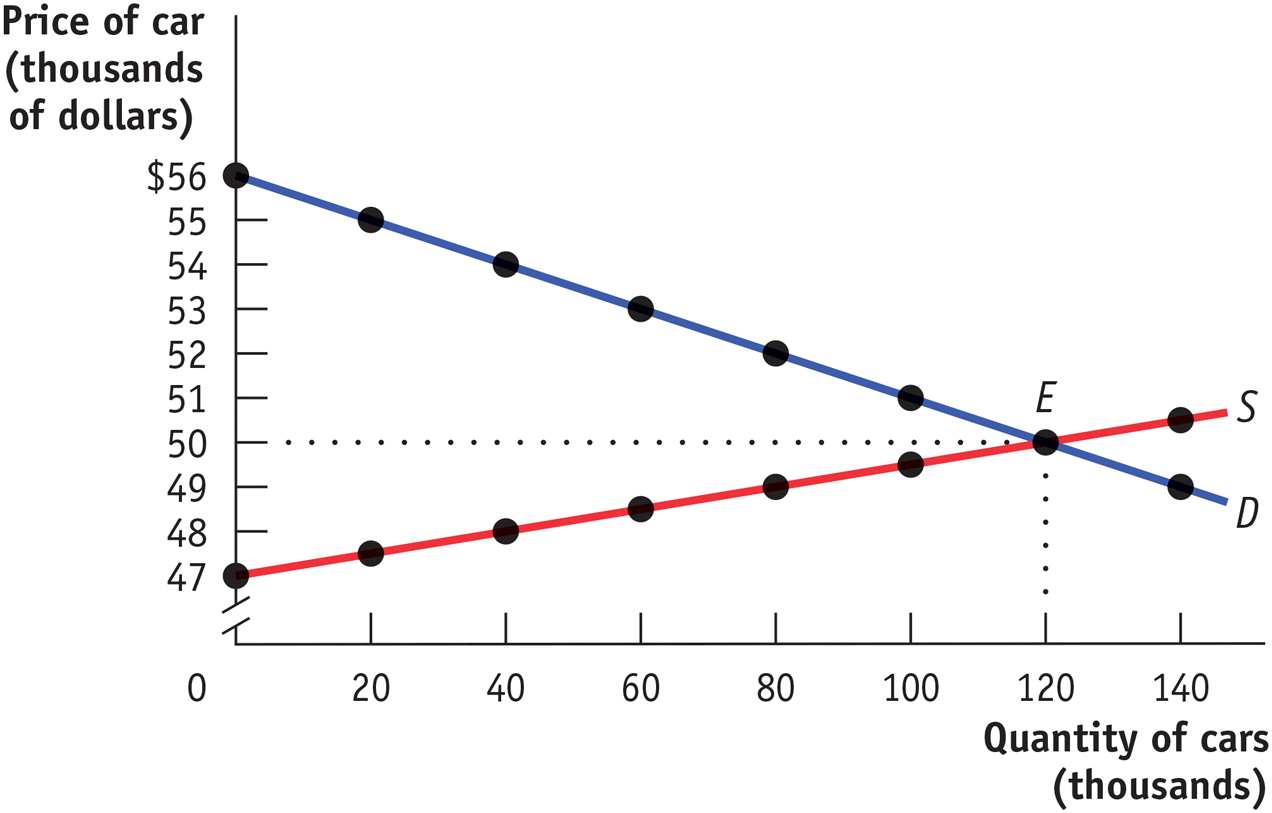
Under the tax, what is the price paid by consumers? What is the price received by producers? What is the government tax revenue from the excise tax?
Over time, the tax on luxury automobiles was slowly phased out (and completely eliminated in 2002). Suppose that the excise tax falls from $6,000 per car to $4,500 per car.
After the reduction in the excise tax from $6,000 to $4,500 per car, what is the price paid by consumers? What is the price received by producers? What is tax revenue now?
Compare the tax revenue created by the taxes in parts a and b. What accounts for the change in tax revenue from the reduction in the excise tax?
Question 7.18
All states impose excise taxes on gasoline. According to data from the Federal Highway Administration, the state of California imposes an excise tax of $0.40 per gallon of gasoline. In 2013, gasoline sales in California totaled 18.4 billion gallons. What was California’s tax revenue from the gasoline excise tax? If California doubled the excise tax, would tax revenue double? Why or why not?
Question 7.19
In the United States, each state government can impose its own excise tax on the sale of cigarettes. Suppose that in the state of North Texarkana, the state government imposes a tax of $2.00 per pack sold within the state. In contrast, the neighboring state of South Texarkana imposes no excise tax on cigarettes. Assume that in both states the pre-
tax price of a pack of cigarettes is $1.00. Assume that the total cost to a resident of North Texarkana to smuggle a pack of cigarettes from South Texarkana is $1.85 per pack. (This includes the cost of time, gasoline, and so on.) Assume that the supply curve for cigarettes is neither perfectly elastic nor perfectly inelastic. Draw a diagram of the supply and demand curves for cigarettes in North Texarkana showing a situation in which it makes economic sense for a North Texarkanan to smuggle a pack of cigarettes from South Texarkana to North Texarkana. Explain your diagram.
Draw a corresponding diagram showing a situation in which it does not make economic sense for a North Texarkanan to smuggle a pack of cigarettes from South Texarkana to North Texarkana. Explain your diagram.
Suppose the demand for cigarettes in North Texarkana is perfectly inelastic. How high could the cost of smuggling a pack of cigarettes go until a North Texarkanan no longer found it profitable to smuggle?
Still assume that demand for cigarettes in North Texarkana is perfectly inelastic and that all smokers in North Texarkana are smuggling their cigarettes at a cost of $1.85 per pack, so no tax is paid. Is there any inefficiency in this situation? If so, how much per pack? Suppose chip-
embedded cigarette packaging makes it impossible to smuggle cigarettes across the state border. Is there any inefficiency in this situation? If so, how much per pack?
Question 7.20
In each of the following cases involving taxes, explain: (i) whether the incidence of the tax falls more heavily on consumers or producers, (ii) why government revenue raised from the tax is not a good indicator of the true cost of the tax, and (iii) how deadweight loss arises as a result of the tax.
The government imposes an excise tax on the sale of all college textbooks. Before the tax was imposed, 1 million textbooks were sold every year at a price of $50. After the tax is imposed, 600,000 books are sold yearly; students pay $55 per book, $30 of which publishers receive.
The government imposes an excise tax on the sale of all airline tickets. Before the tax was imposed, 3 million airline tickets were sold every year at a price of $500. After the tax is imposed, 1.5 million tickets are sold yearly; travelers pay $550 per ticket, $450 of which the airlines receive.
The government imposes an excise tax on the sale of all toothbrushes. Before the tax, 2 million toothbrushes were sold every year at a price of $1.50. After the tax is imposed, 800,000 toothbrushes are sold every year; consumers pay $2 per toothbrush, $1.25 of which producers receive.
Question 7.21
The accompanying diagram shows the market for cigarettes. The current equilibrium price per pack is $4, and every day 40 million packs of cigarettes are sold. In order to recover some of the health care costs associated with smoking, the government imposes a tax of $2 per pack. This will raise the equilibrium price to $5 per pack and reduce the equilibrium quantity to 30 million packs.
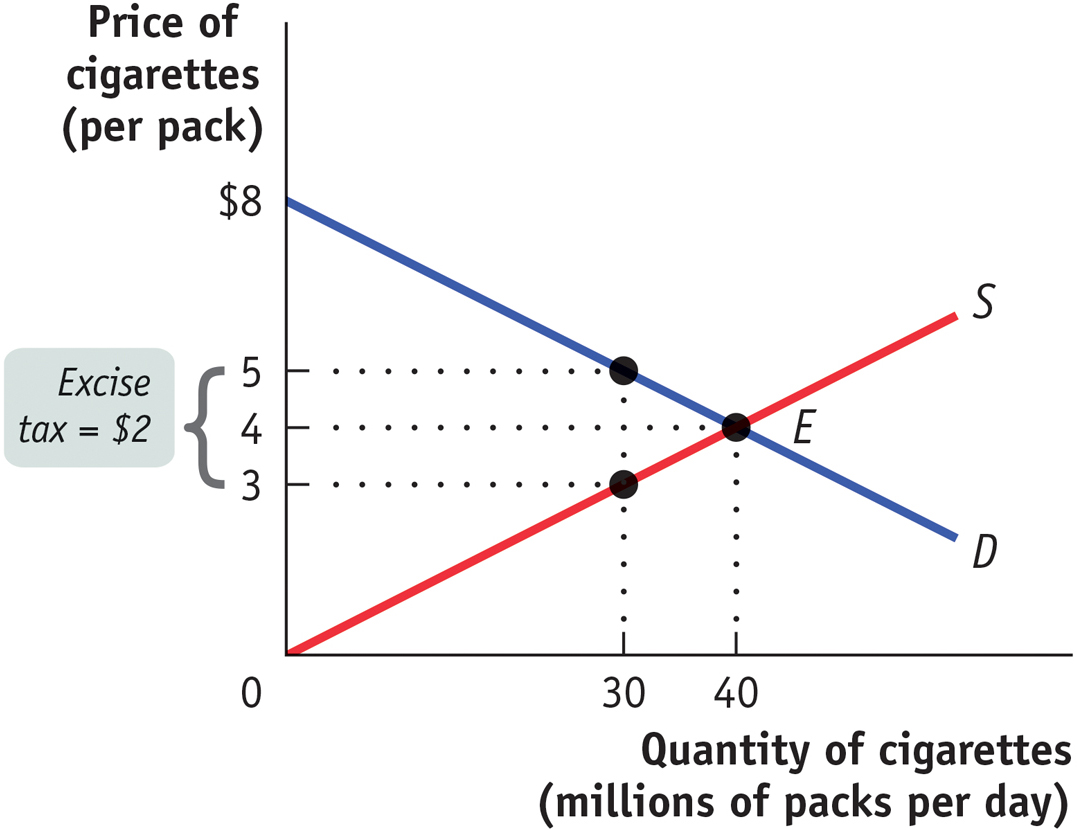
The economist working for the tobacco lobby claims that this tax will reduce consumer surplus for smokers by $40 million per day, since 40 million packs now cost $1 more per pack. The economist working for the lobby for sufferers of second-
hand smoke argues that this is an enormous overestimate and that the reduction in consumer surplus will be only $30 million per day, since after the imposition of the tax only 30 million packs of cigarettes will be bought and each of these packs will now cost $1 more. They are both wrong. Why? Question 7.22
Consider the original market for pizza in Collegetown, illustrated in the accompanying table. Collegetown officials decide to impose an excise tax on pizza of $4 per pizza.
Price of pizza
Quantity of pizza demanded
Quantity of pizza supplied
$10
0
6
9
1
5
8
2
4
7
3
3
6
4
2
5
5
1
4
6
0
3
7
0
2
8
0
1
9
0
What is the quantity of pizza bought and sold after the imposition of the tax? What is the price paid by consumers? What is the price received by producers?
Calculate the consumer surplus and the producer surplus after the imposition of the tax. By how much has the imposition of the tax reduced consumer surplus? By how much has it reduced producer surplus?
How much tax revenue does Collegetown earn from this tax?
Calculate the deadweight loss from this tax.
Question 7.23
The state needs to raise money, and the governor has a choice of imposing an excise tax of the same amount on one of two previously untaxed goods: the state can tax sales of either restaurant meals or gasoline. Both the demand for and the supply of restaurant meals are more elastic than the demand for and the supply of gasoline. If the governor wants to minimize the deadweight loss caused by the tax, which good should be taxed? For each good, draw a diagram that illustrates the deadweight loss from taxation.
Question 7.24
Assume that the demand for gasoline is inelastic and supply is relatively elastic. The government imposes a sales tax on gasoline. The tax revenue is used to fund research into clean fuel alternatives to gasoline, which will improve the air we all breathe.
Who bears more of the burden of this tax, consumers or producers? Show in a diagram who bears how much of the burden.
Is this tax based on the benefits principle or the ability-
to- pay principle? Explain.
Question 7.25
Assess the following four tax policies in terms of the benefits principle versus the ability-
to- pay principle. A tax on gasoline that finances maintenance of state roads
An 8% tax on imported goods valued in excess of $800 per household brought in on passenger flights
Airline-
flight landing fees that pay for air traffic control A reduction in the amount of income tax paid based on the number of dependent children in the household.
Question 7.26
You are advising the government on how to pay for national defense. There are two proposals for a tax system to fund national defense. Under both proposals, the tax base is an individual’s income. Under proposal A, all citizens pay exactly the same lump-
sum tax, regardless of income. Under proposal B, individuals with higher incomes pay a greater proportion of their income in taxes. Is the tax in proposal A progressive, proportional, or regressive? What about the tax in proposal B?
Is the tax in proposal A based on the ability-
to- pay principle or on the benefits principle? What about the tax in proposal B? In terms of efficiency, which tax is better? Explain.
Question 7.27
Each of the following tax proposals has income as the tax base. In each case, calculate the marginal tax rate for each level of income. Then calculate the percentage of income paid in taxes for an individual with a pre-
tax income of $5,000 and for an individual with a pre- tax income of $40,000. Classify the tax as being proportional, progressive, or regressive. (Hint: You can calculate the marginal tax rate as the percentage of an additional $1 in income that is taxed away.) All income is taxed at 20%.
All income up to $10,000 is tax-
free. All income above $10,000 is taxed at a constant rate of 20%. All income between $0 and $10,000 is taxed at 10%. All income between $10,000 and $20,000 is taxed at 20%. All income higher than $20,000 is taxed at 30%.
Each individual who earns more than $10,000 pays a lump-
sum tax of $10,000. If the individual’s income is less than $10,000, that individual pays in taxes exactly what his or her income is. Of the four tax policies, which is likely to cause the worst incentive problems? Explain.
Question 7.28
In Transylvania the basic income tax system is fairly simple. The first 40,000 sylvers (the official currency of Transylvania) earned each year are free of income tax. Any additional income is taxed at a rate of 25%. In addition, every individual pays a social security tax, which is calculated as follows: all income up to 80,000 sylvers is taxed at an additional 20%, but there is no additional social security tax on income above 80,000 sylvers.
Calculate the marginal tax rates (including income tax and social security tax) for Transylvanians with the following levels of income: 20,000 sylvers, 40,000 sylvers, and 80,000 sylvers. (Hint: You can calculate the marginal tax rate as the percentage of an additional 1 sylver in income that is taxed away.)
Is the income tax in Transylvania progressive, regressive, or proportional? Is the social security tax progressive, regressive, or proportional?
Which income group’s incentives are most adversely affected by the combined income and social security tax systems?
WORK IT OUT
For interactive, step-
Question 7.29
15. You work for the Council of Economic Advisers, providing economic advice to the White House. The president wants to overhaul the income tax system and asks your advice. Suppose that the current income tax system consists of a proportional tax of 10% on all income and that there is one person in the country who earns $110 million; everyone else earns less than $100 million. The president proposes a tax cut targeted at the very rich so that the new tax system would consist of a proportional tax of 10% on all income up to $100 million and a marginal tax rate of 0% (no tax) on income above $100 million. You are asked to evaluate this tax proposal.
For incomes of $100 million or less, is this proposed tax system progressive, regressive, or proportional? For incomes of more than $100 million? Explain.
Would this tax system create more or less tax revenue, other things equal? Is this tax system more or less efficient than the current tax system? Explain.