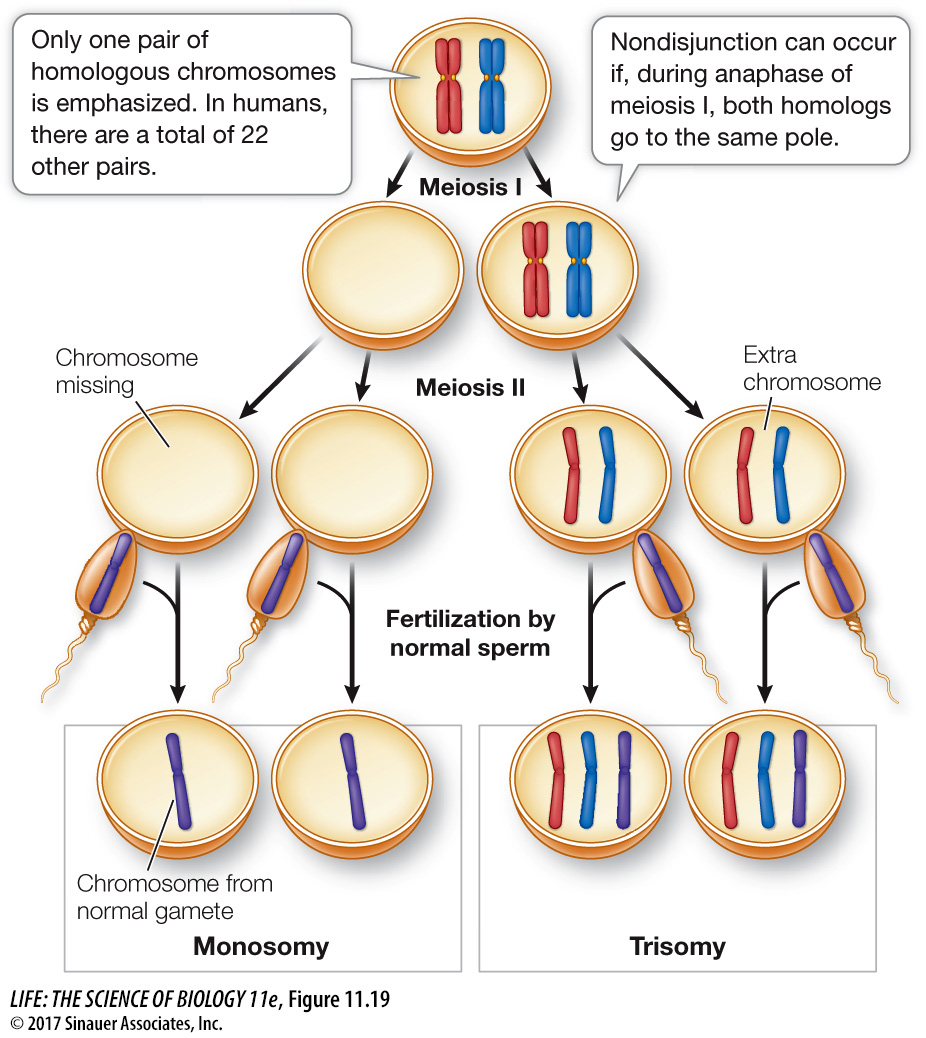
Figure 11.19 Nondisjunction Leads to Aneuploidy Nondisjunction occurs if homologous chromosomes fail to separate during meiosis I, as illustrated here, or if chromatids fail to separate during mitosis or meiosis II. The first case is shown here. The result is aneuploidy: one or more chromosomes are either lacking or present in excess. Generally, aneuploidy is lethal to the developing embryo.