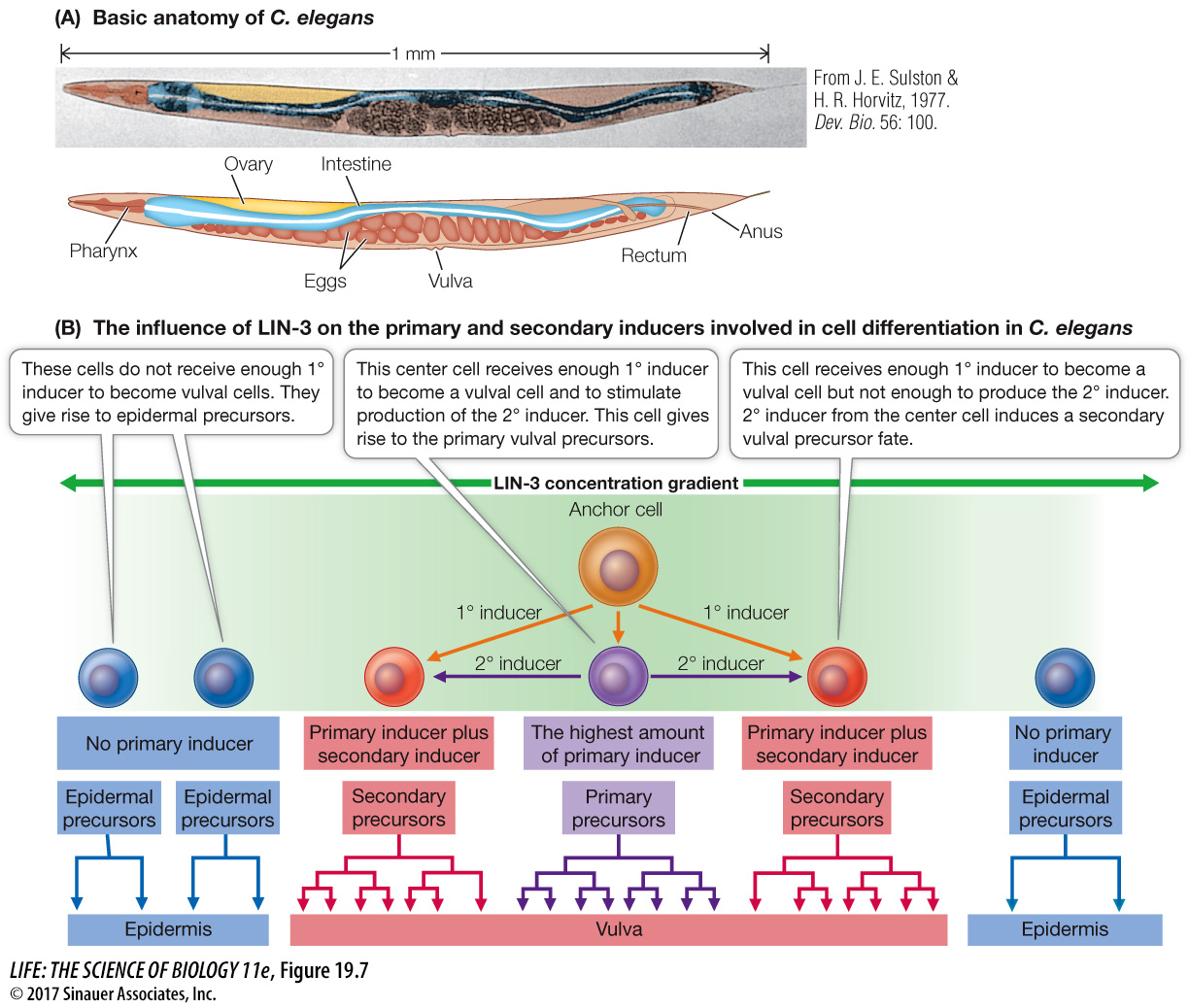
Figure 19.7 Induction during Vulval Development in Caenorhabditis elegans (A) In the nematode C. elegans (shown in false color here), it is possible to follow all of the cell divisions from the fertilized egg to the 959 somatic cells found in the adult. (B) During vulval development, a molecule secreted by the anchor cell (the LIN- N-