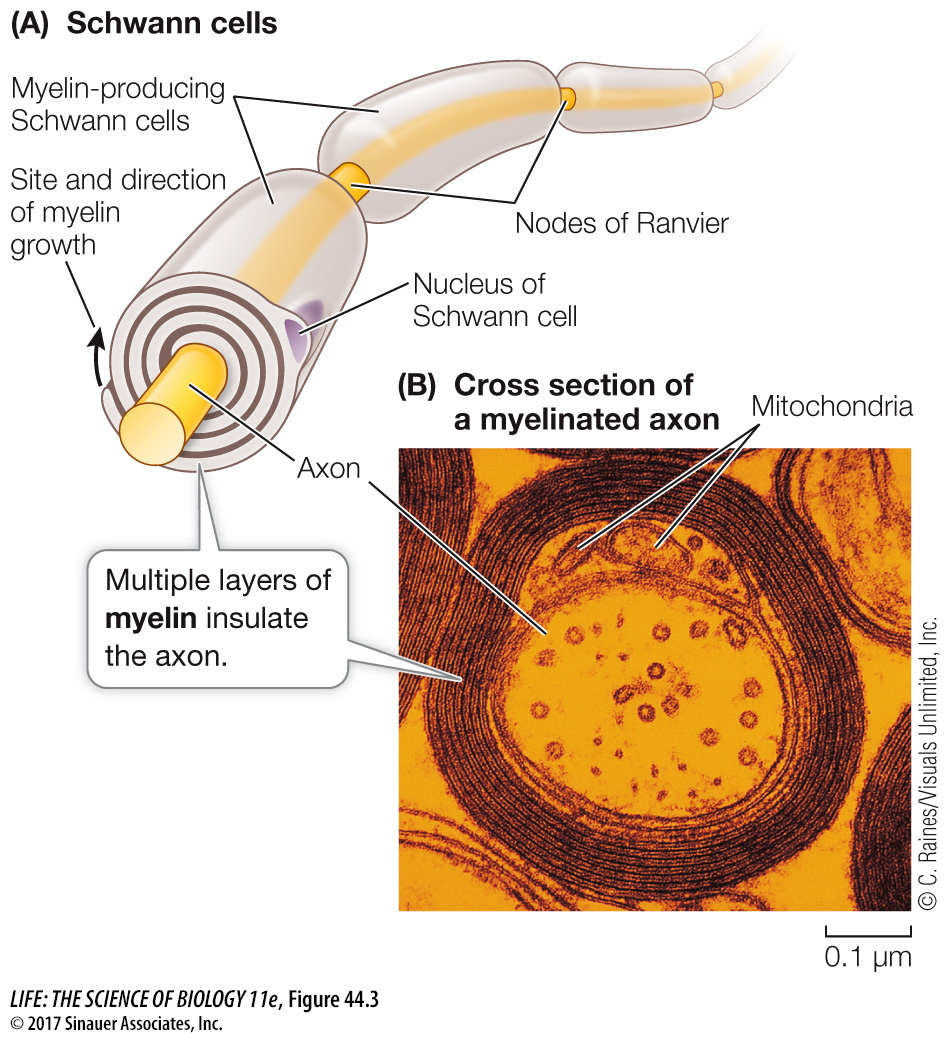
Figure 44.3 Glial Cells Insulate Axons (A) Schwann cells produce layers of myelin, a type of cell membrane that provides electrical insulation to the axon. At the intervals between Schwann cells— r—