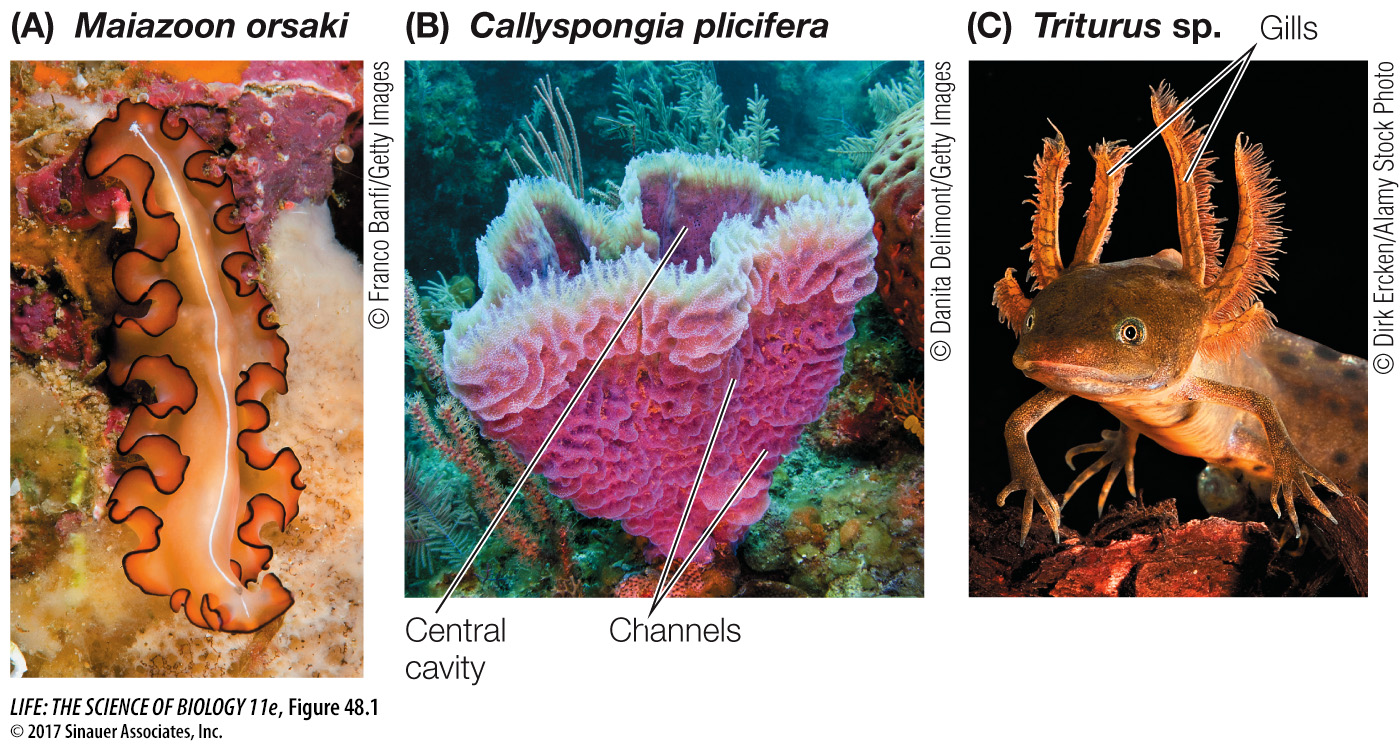
Figure 48.1 Keeping in Touch with the Medium (A) No cell in the leaflike body of this marine flatworm is more than a millimeter away from seawater. (B) Sponges have body walls perforated by many channels, which allow water to flow between the outside world and a central cavity. No cell in the sponge is more than a millimeter away from seawater. (C) A feathery fringe of gills on this aquatic salamander provides a large surface area for gas exchange. Blood circulating through the gills comes into close contact with the respiratory medium.