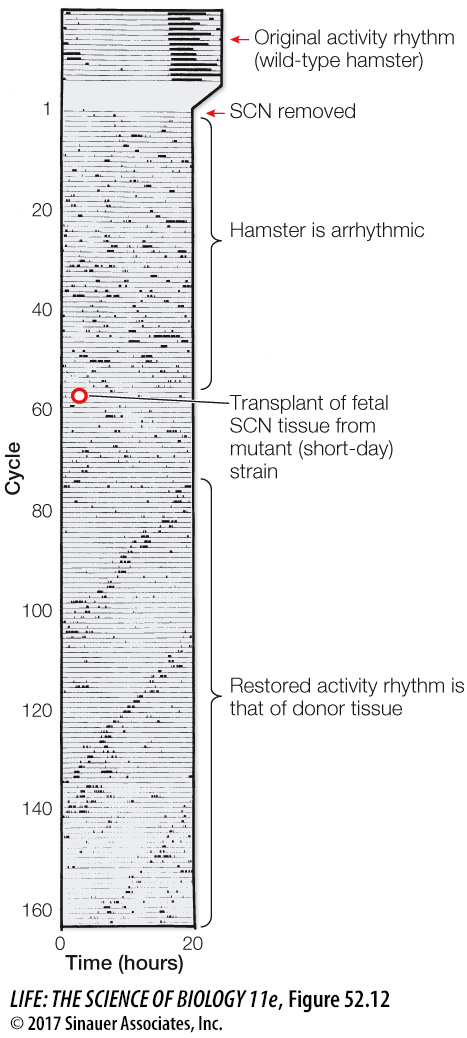
Figure 52.12 The Brain Clock Can Be Transplanted In this experiment, the activity rhythm of a wild- t- 9- d-