Microscopes reveal the features of cells
Most cells are too small to be seen with the unaided eye. Microscopes allow cells and details within them to be seen. The property that allows detail to be seen is called resolution. Formally defined, resolution is the minimum distance two objects can be apart and still be seen as two objects. Resolution for the human eye is about 0.2 mm (200 µm). Most cells are much smaller than 200 µm and thus are invisible to the human eye. Microscopes magnify and increase resolution so that cells and their internal structures can be seen clearly (Figure 5.3).
research tools

Note that the images in most cases are flat, two-
Activity 5.2 Know Your Techniques
www.life11e.com/
There are two basic types of microscopes—
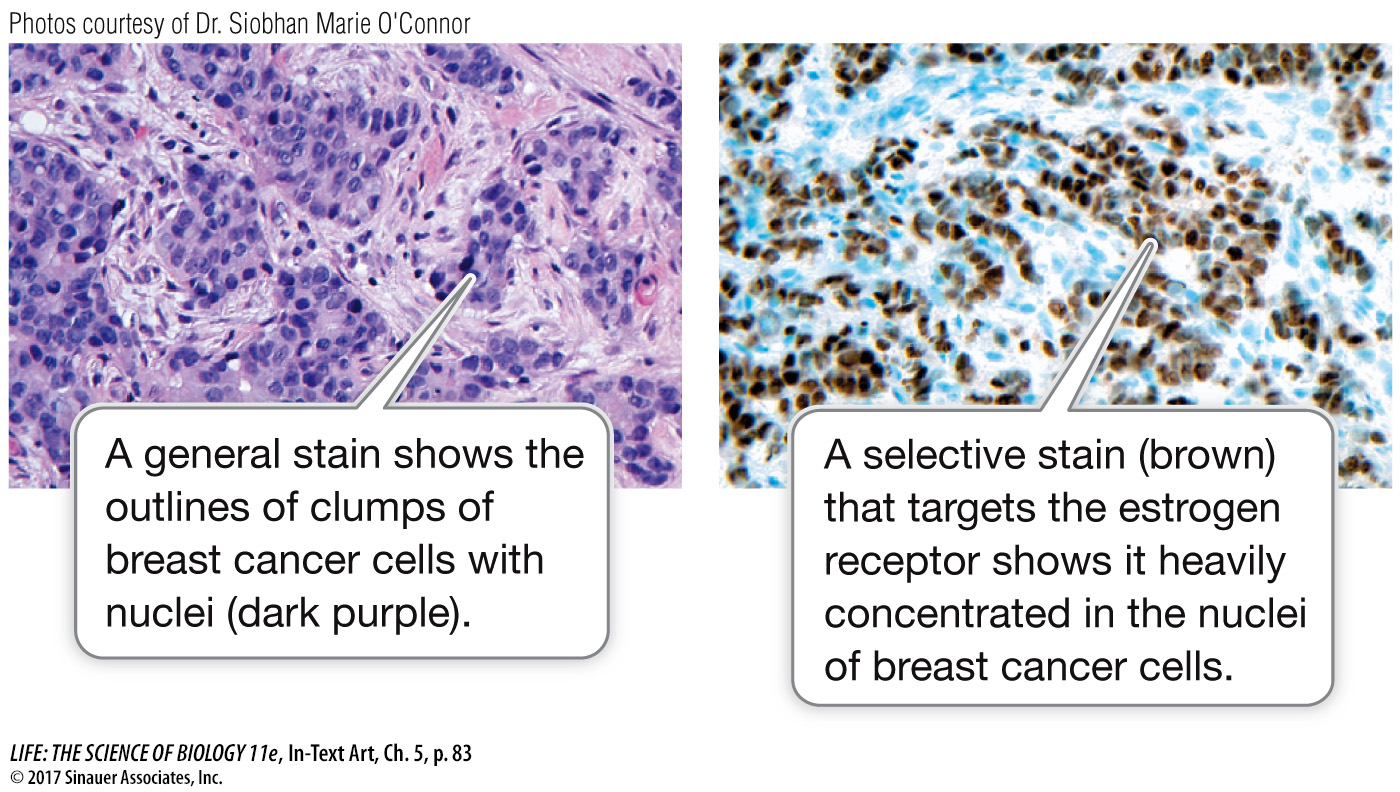
Before we look at cell structure, it is useful to consider the many uses of microscopy. Here is an example: an entire branch of medicine, pathology, makes use of many different methods of microscopy to aid in the analysis of cells and the diagnosis of diseases. For instance, a surgeon might remove from a body some tissue suspected of being cancerous. The pathologist might:
examine the tissue quickly by phase-
contrast microscopy to determine the size, shape, and spread of the cells; stain the tissue with a general dye and examine it by bright-
field microscopy to bring out features such as the shapes of the nuclei, or cell division characteristics; examine the tissue under the transmission electron microscope to observe internal structures such as the mitochondria or the chromatin (these are described in Key Concept 5.3);
stain the tissue with a specific dye and examine it by microscopy for the presence of proteins that are diagnostic of particular cancers. The results can influence the choice of therapy.