Cells may be classified as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
As you saw in Key Concept 1.1, biologists classify all living things into three domains: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. The organisms in Archaea and Bacteria are collectively called prokaryotes, and they have in common a prokaryotic cell organization. A prokaryotic cell does not typically have membrane-
85
Eukaryotic cell organization is found in members of the domain Eukarya (eukaryotes), which includes the protists, plants, fungi, and animals. In contrast to prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells contain membrane-
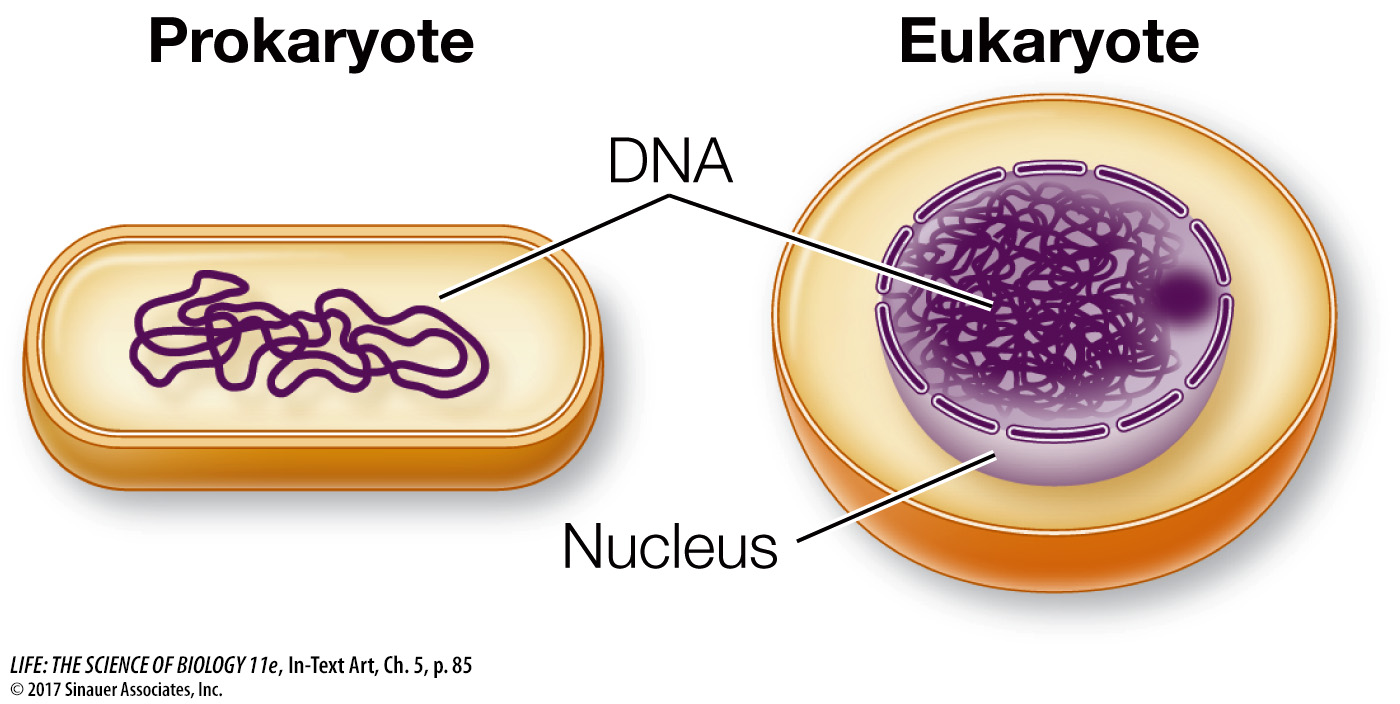
Just as a cell is an enclosed compartment, separating its contents from the surrounding environment, so each organelle provides a compartment that separates molecules and biochemical reactions from the rest of the cell. This “division of labor” provides possibilities for regulation and efficiency that were important in the evolution of complex organisms and helps explain the complexity of eukaryotic cells relative to prokaryotic cells.