recap
128
6.5 recap
Endocytosis and exocytosis are the processes by which large particles and molecules are transported into and out of the cell. Endocytosis may be mediated by a receptor protein in the cell membrane.
learning outcomes
You should be able to:
Compare and contrast the three types of endocytosis.
Describe the process of receptor-
mediated endocytosis. Provide examples of processes that involve endocytosis and/or exocytosis.
Question 1
What are the differences between phagocytosis and pinocytosis?
Phagocytosis involves a large cell membrane–
Question 2
Describe receptor-
In receptor-
Question 3
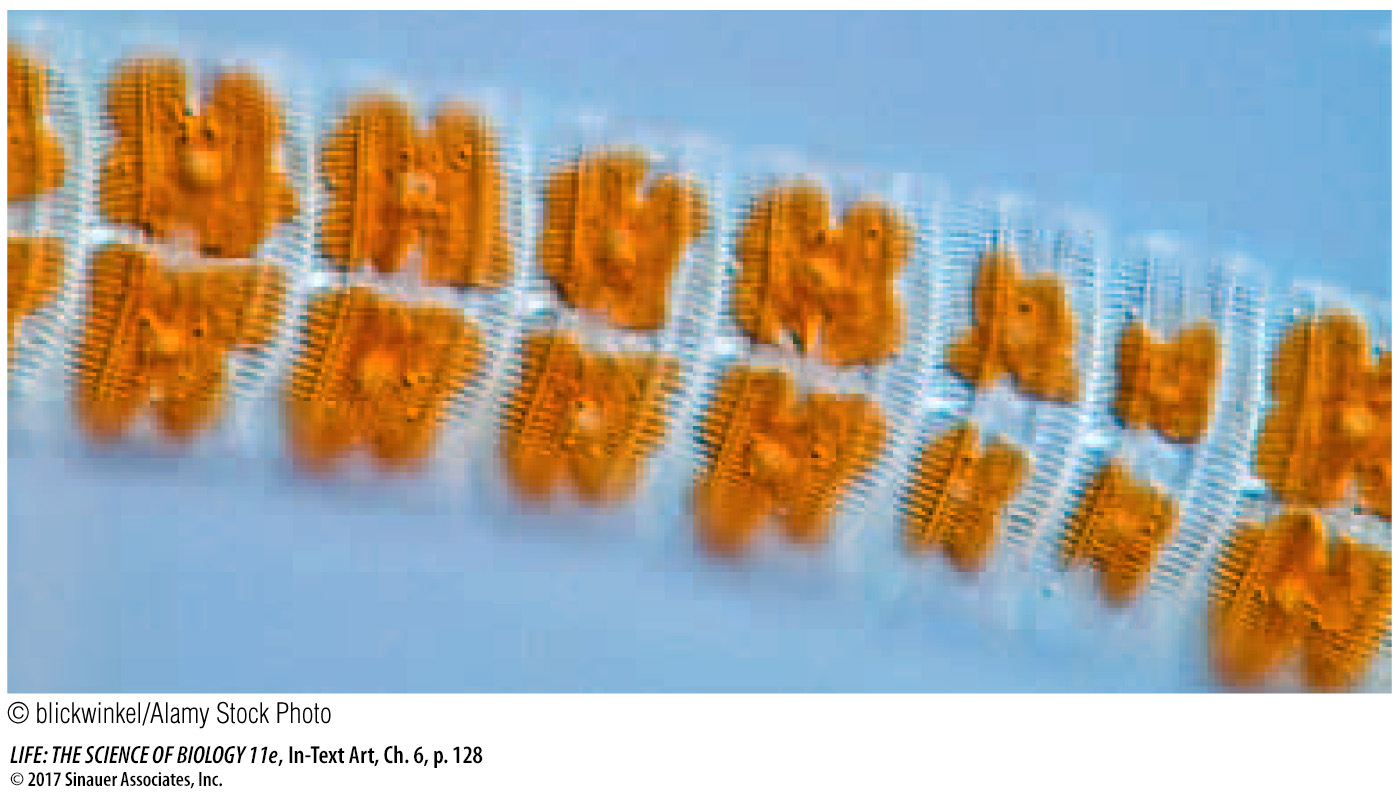
Key Concept 27.2 describes the diatoms, which are protists that have complex glassy structures in their cell walls (see Figure 27.8 and the photo below of eight diatom cells inside their ornate cell walls). These structures form within the Golgi apparatus. How do they reach the cell wall without having to pass through a membrane?
Diatom wall components move from the Golgi apparatus to the cell wall by exocytosis.