key concept8.5Enzyme Activities Can Be Regulated
The biochemical reactions in cells operate within metabolic pathways in which the product of one reaction is a reactant for the next. These pathways do not exist in isolation, but interact extensively, and each reaction in each pathway is catalyzed by a specific enzyme.
focus your learning
The cell carries out large numbers of metabolic reactions that are interconnected and regulated by the enzymes that catalyze them.
Small molecules can regulate enzyme activity by binding to and activating or inhibiting an enzyme.
Allosteric regulation results from the binding of regulator molecules to sites on an enzyme other than the active site.
Environmental factors such as pH and temperature affect enzyme activity.
Within a cell or organism, the presence and activity of enzymes determine the “flow” of chemicals through different metabolic pathways. The amount of enzyme activity, in turn, can be controlled in two ways:
Regulation of gene expression. The gene for an enzyme protein may be expressed more or less, resulting in more or fewer enzyme molecules in the cell. You learned in Chapter 7 that some signal transduction pathways result in changes in gene expression, and that often the genes that are switched on or off encode enzymes.
Regulation of enzyme activity. The enzyme may change its shape to hide its active site from the substrate, or a regulator molecule may prevent the substrate from reaching the active site. Blocking the activity of a single enzyme can affect an entire metabolic pathway.
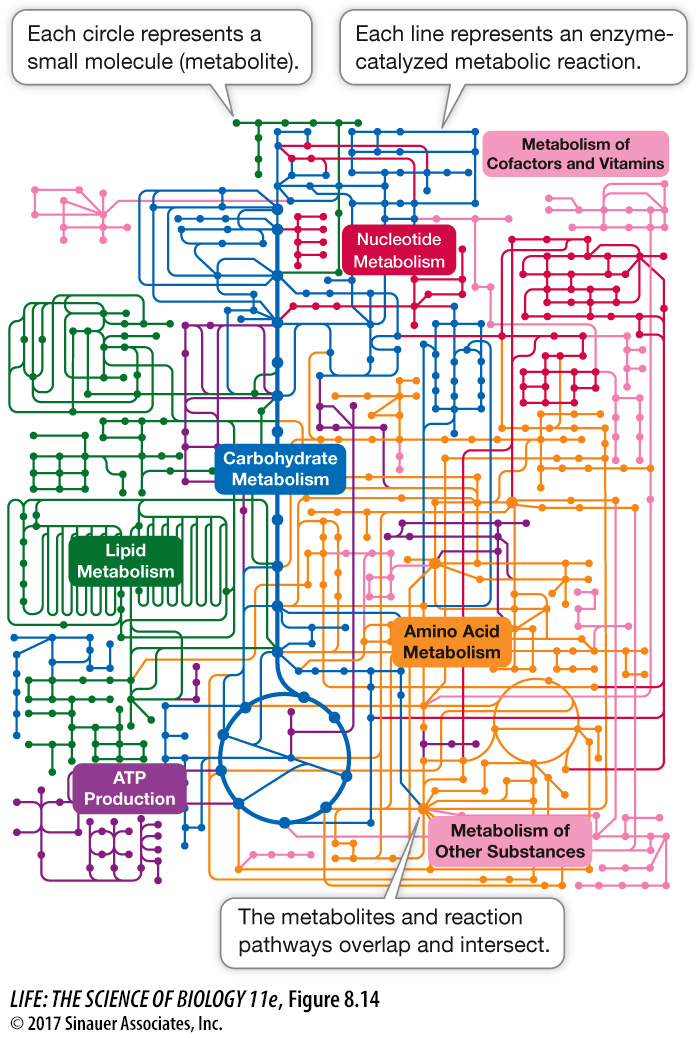
The flow of molecules through interacting metabolic pathways can be studied, but this process quickly becomes complicated, because each pathway influences the others. Computer algorithms are used to model these pathways and show how they mesh in an interdependent system (Figure 8.14). Such models can help predict what will happen if the concentration of one molecule or another is altered. This new field of biology is called systems biology, and it has numerous applications.
In this section we will investigate the roles of enzymes in organizing and regulating metabolic pathways. We will also examine how the environment—
Activity 8.3 System Simulation
www.life11e.com/