The first law of thermodynamics: Energy is neither created nor destroyed
The first law of thermodynamics states that in any energy conversion, energy is neither created nor destroyed. In other words, during any conversion of energy, the total energy in the system under consideration before and after the conversion is the same (Figure 8.2A). As you will see in the next two chapters, the potential energy present in the chemical bonds of carbohydrates and lipids can be converted to potential energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This can then be converted into kinetic energy to do mechanical work (such as in muscle contractions) or biochemical work (such as protein synthesis).
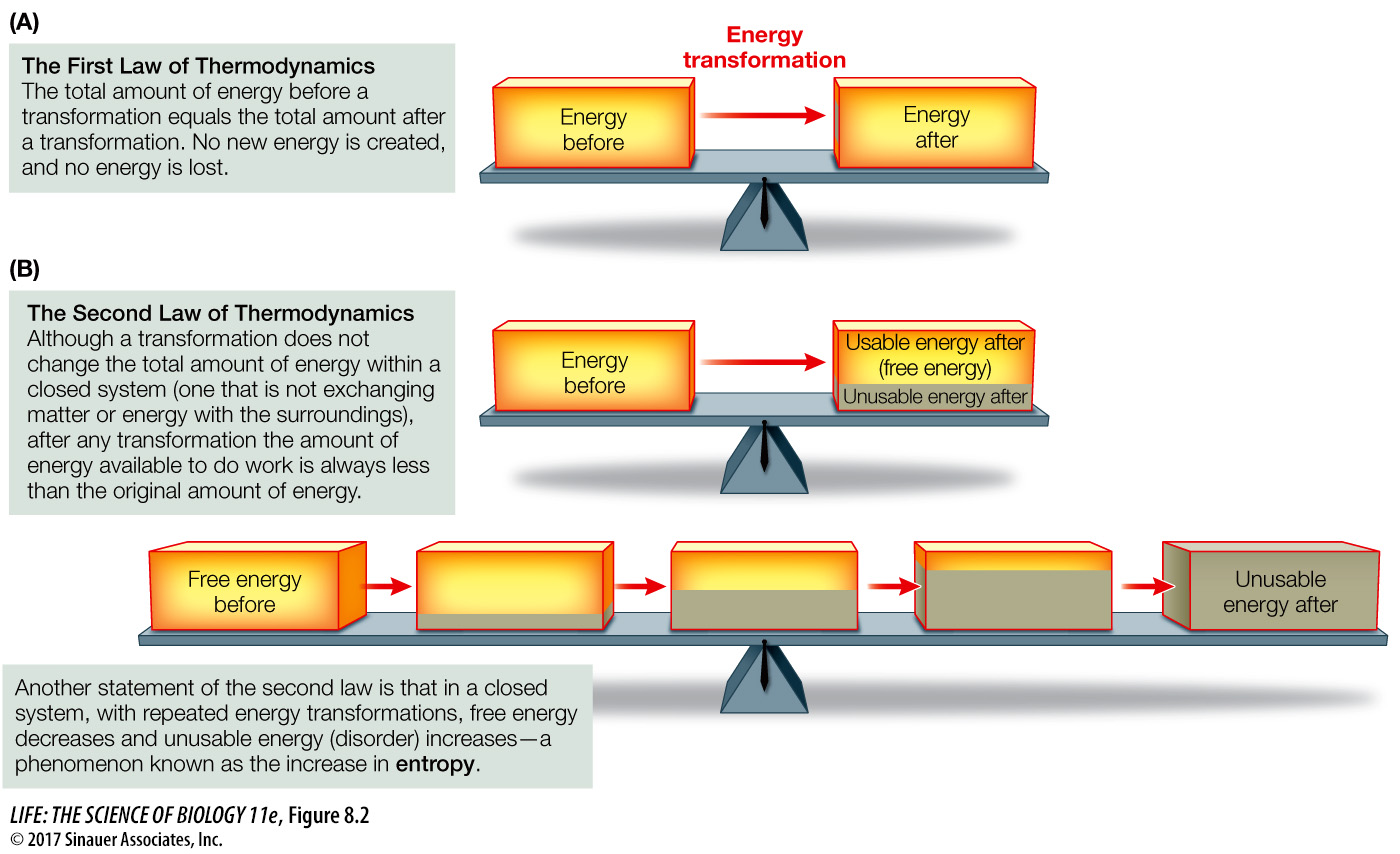
Figure 8.2 The Laws of Thermodynamics (A) The first law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. (B) The second law states that after energy transformations, some energy becomes unavailable to do work.