Pyruvate oxidation links glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
In eukaryotes, pyruvate is transported into the mitochondrial matrix (see Figure 5.11), where the next step in the aerobic catabolism of glucose occurs. This step involves the oxidation of pyruvate to a two-
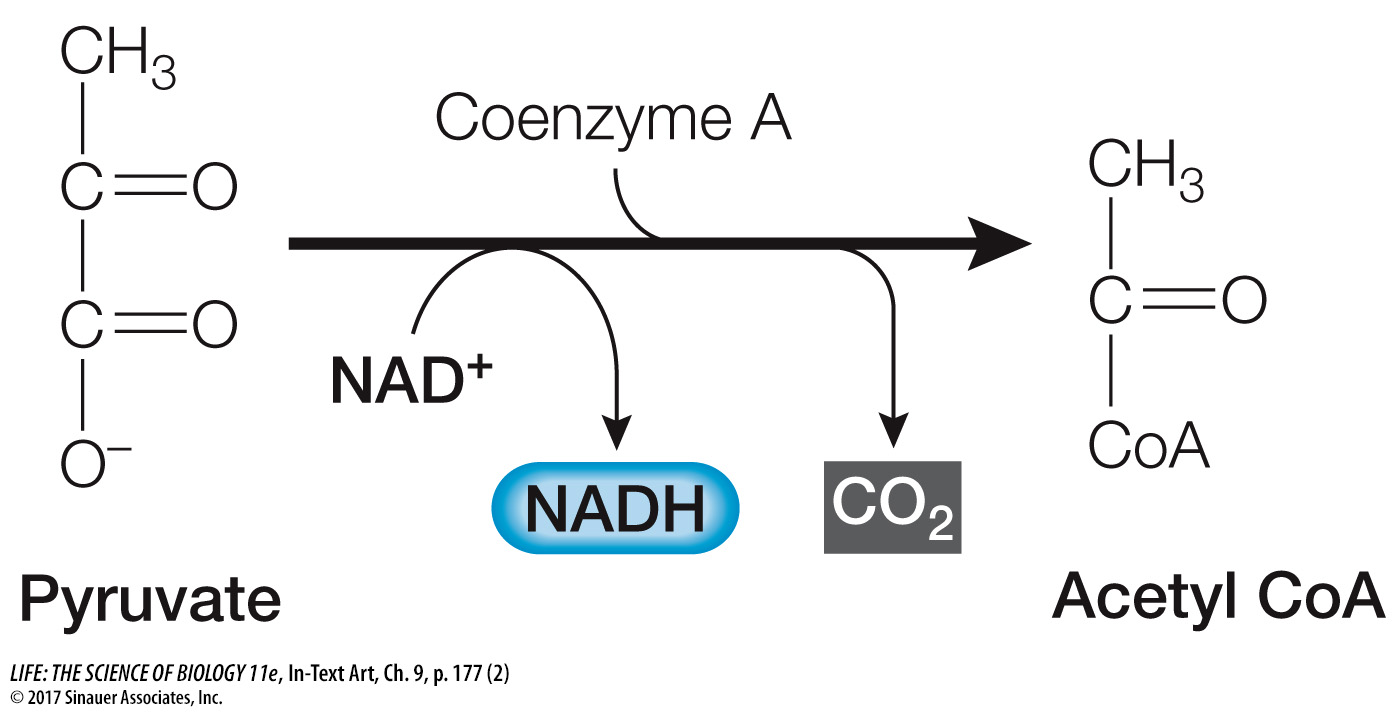
Pyruvate is the link between glycolysis and further oxidative reactions (see Figure 9.4).
The formation of acetyl CoA is a multistep reaction catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which contains 60 individual proteins and 5 different coenzymes. The overall reaction is exergonic, in which one molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH. However, the main role of acetyl CoA is to donate its acetyl group to the four-