key concept9.2In the Presence of Oxygen, Glucose Is Fully Oxidized
The aerobic pathways of glucose catabolism oxidize glucose completely to CO2 and H2O. Initially, the glycolysis reactions convert the six-
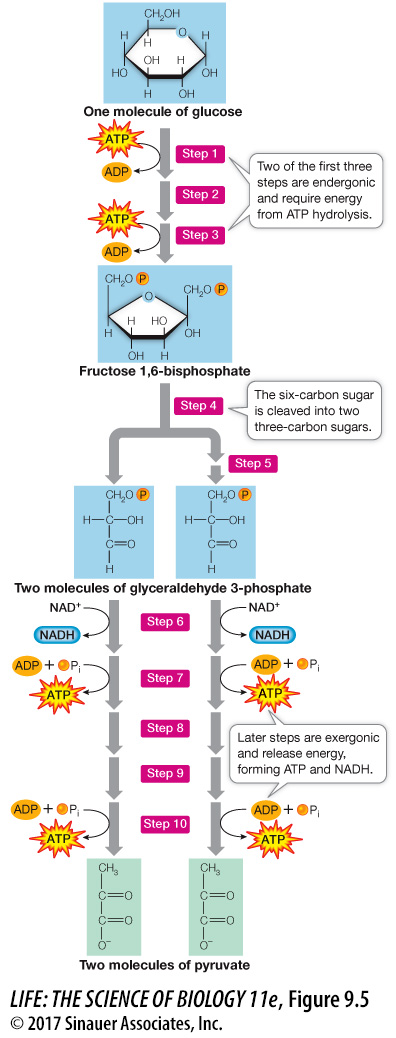
177
focus your learning
Glucose is partially oxidized to pyruvate during glycolysis.
The generation of acetyl coenzyme A by pyruvate oxidation enables the entry of carbon from glucose into the citric acid cycle for further oxidation.
A large amount of energy is captured in electron carriers and in GTP as acetyl CoA is fully oxidized during the citric acid cycle.
We will begin our consideration of the catabolism of glucose with a closer look at glycolysis.