Chapter Introduction
193
10
key concepts
10.1
Photosynthesis Uses Light to Make Carbohydrates
10.2
Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy into Chemical Energy
10.3
Chemical Energy Trapped in Photosynthesis Is Used to Synthesize Carbohydrates
10.4
Plants Have Adapted Photosynthesis to Environmental Conditions
10.5
Photosynthesis Is an Integral Part of Plant Metabolism
Photosynthesis:
Energy from Sunlight

investigating life
Saving FACE
In July 2014, a satellite was launched into space to measure photosynthesis over all of Earth. The Orbiting Carbon Observatory has instruments aboard that map not only the concentration of carbon dioxide, but also the presence of the green plant pigment chlorophyll. Why these measurements, and why now?
As you may know, green plants use the pigment chlorophyll in photosynthesis, which has the general equation
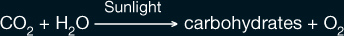
The orbiting satellite is measuring chlorophyll, a reflection of the presence of green plants, and CO2 over time because the global atmosphere and biological communities are changing. Over the past 200 years, the concentration of atmospheric CO2 has increased—
To answer these questions, scientists developed a way to expose plants to high levels of CO2 in the field. Free-
Will this increase in photosynthesis result in an increase in plant growth? Keep in mind that plants, like all organisms, use carbohydrates as an energy source. They perform cellular respiration with the general equation
Carbohydrates + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy
The challenge facing plant biologists is to determine the balance between photosynthesis and respiration and how this affects the rate of plant growth. The FACE experiments indicate that plant growth and crop yields increase under higher CO2 concentrations, suggesting that the overall increase in photosynthesis is greater than the increase in respiration.
What is the chemistry of photosynthesis, and how will it be affected by rising atmospheric CO2?