Photosynthesis involves two pathways
196
Equation 10.2 above summarizes the overall process of photosynthesis, but not the steps by which it happens. Water serves as the electron donor, but there is an intermediary carrier of the H+ and electrons between the oxidation and reduction reactions. The carrier is the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+).
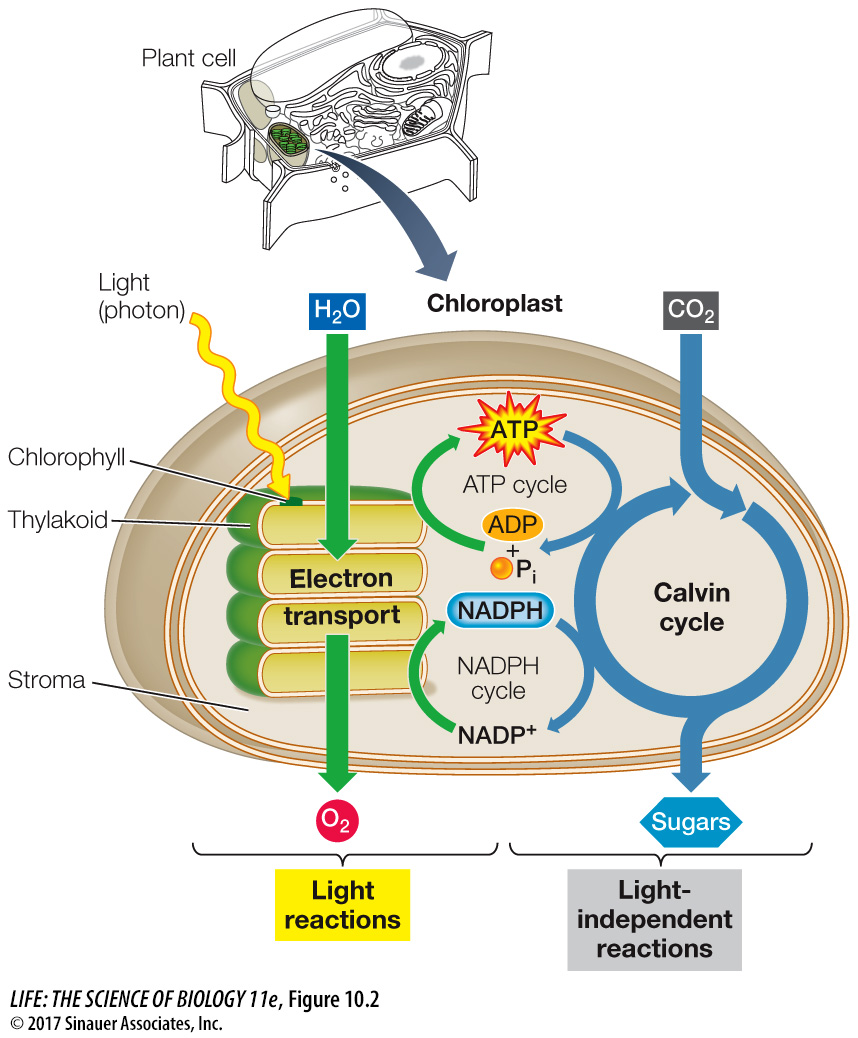
Like glycolysis and the other metabolic pathways that harvest energy in cells, photosynthesis has many steps. These reactions are commonly divided into two main pathways:
The light reactions convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and the reduced electron carrier NADPH. This molecule is similar to the coenzyme NADH (see Key Concept 9.1) but with an additional phosphate group attached to the sugar of its adenosine. In general, NADPH acts as a reducing agent in photosynthesis and other anabolic reactions.
The light-
independent reactions (carbon- fixation reactions) do not use light directly, but instead use ATP, NADPH (made by the light reactions), and CO2 to produce carbohydrate.
The light-
focus: key figure
Question
Q: In the cell, where does the reduction of CO2 occur and what is the reducing agent?
Reduction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast and the reducing agent is NADPH.
As we describe these two series of reactions in more detail, you will see that they conform to the principles of biochemistry that we discussed in Chapters 8 and 9: energy transformations, oxidation–