Chapter Introduction
213
The Cell Cycle
and Cell Division
PART FOUR Genes and Heredity
11
key concepts
11.1
All Cells Derive from Other Cells
11.2
The Eukaryotic Cell Division Cycle Is Regulated
11.3
Eukaryotic Cells Divide by Mitosis
11.4
Cell Division Plays Important Roles in the Sexual Life Cycle
11.5
Meiosis Leads to the Formation of Gametes
11.6
Cell Death Is Important in Living Organisms
11.7
Unregulated Cell Division Can Lead to Cancer
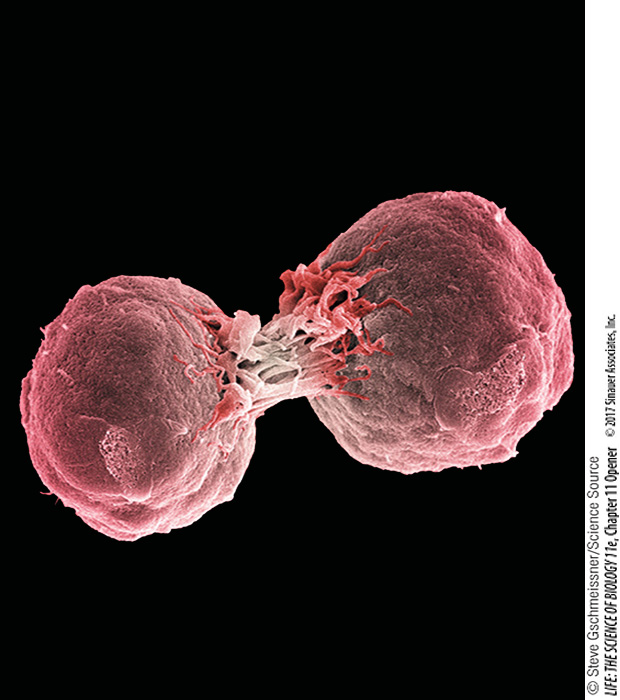
investigating life
Immortal Cells
On January 29, 1951, 30-
A week later Ms. Lacks returned to the hospital, where physicians treated her tumor with radiation to try to kill it. But before the treatment began, they took a small sample of cells and sent them without her permission—
Because of their robust ability to reproduce, HeLa cells quickly became a staple of cell biology research. In controlled settings they could be infected with viruses, and they were instrumental in developing the supply of polioviruses that led to the first vaccine against that dread disease. HeLa cells have been used for important basic and applied research ever since, especially on the ways that human cells reproduce by cell division. Although Lacks had never been outside Virginia and Maryland, her cells have traveled all over the world and even into space on the space shuttle. Over the past 60 years, tens of thousands of research articles have been published using information obtained from Lacks’s cells. You’ll study one of them in this chapter.
Understanding the cell division cycle and its control is clearly an important subject for understanding cancer. But cell division is not just important in medicine. It underlies the growth, development, and reproduction of all organisms.
What controls the reproduction of cancer cells?