Allele-
Nucleic acid hybridization (see Figure 14.6) can be used to detect the presence of a specific DNA sequence, such as a sequence containing a particular mutation. Samples of DNA are collected from people who may or may not carry the mutation, and PCR is used to amplify the region of DNA where the mutation may occur. Short synthetic DNA strands called oligonucleotide probes are hybridized with the denatured PCR products. The probe is labeled in some way (e.g., with radioactivity or a fluorescent dye) so that hybridization can be readily detected (Figure 15.16).
research tools
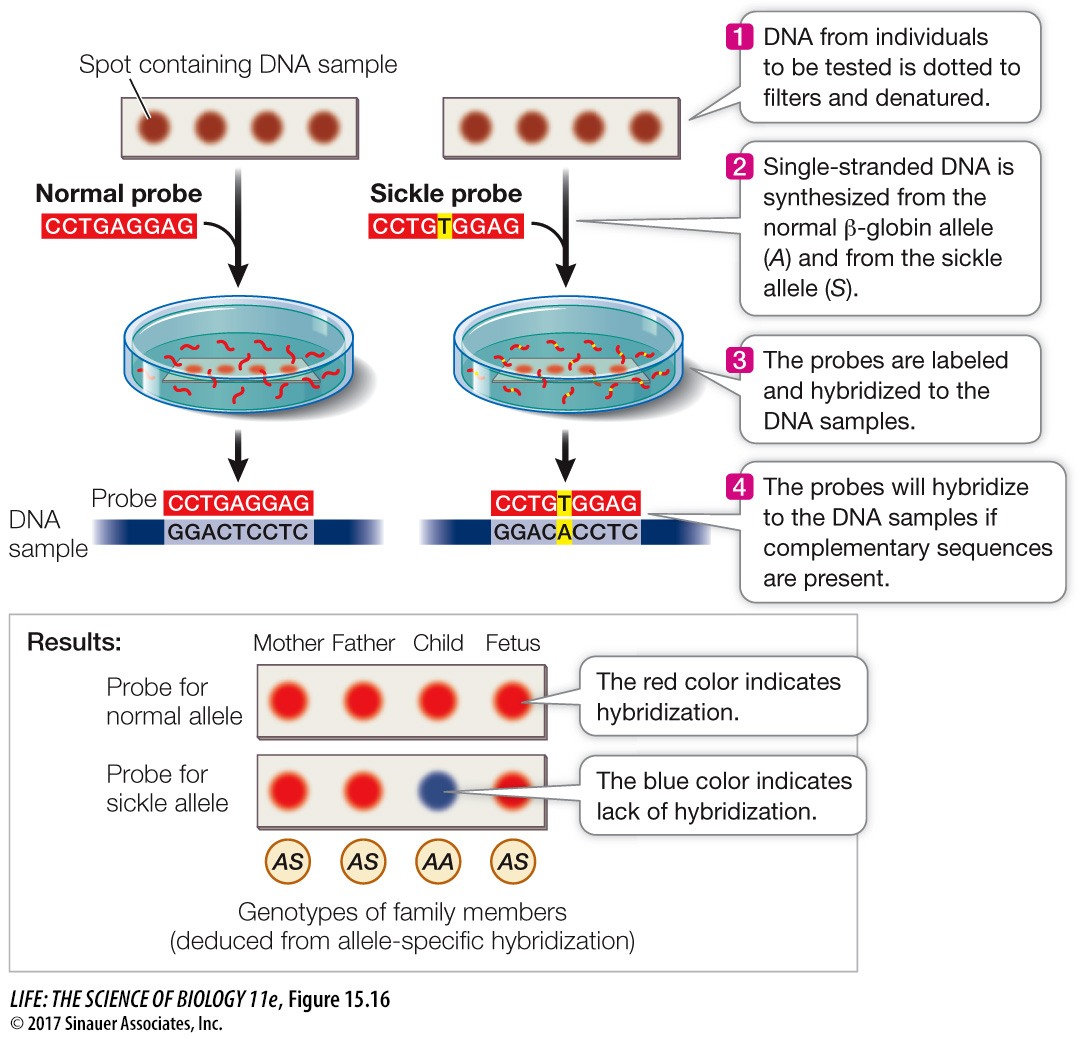
Figure 15.16 DNA Testing by Allele-
Animation 15.2 DNA Testing
www.life11e.com/
Detection of a mutation by DNA screening can be used for diagnosis of a genetic disease, so that appropriate treatment can begin. In addition, DNA screening provides a person with important information about his or her genome.