Apply What You’ve Learned
Review
15.1
Use a definded DNA sequence to illustrate how the following occur and describe their effect upon phenotype: transitions, transversions, missense mutations, nonsense mutations, frame-
15.2
Genetic diseases often result from mutations that render proteins nonfunctional.
15.2
Mutations that cause disease include the full range of affected DNA from point mutations to entire chromosomes.
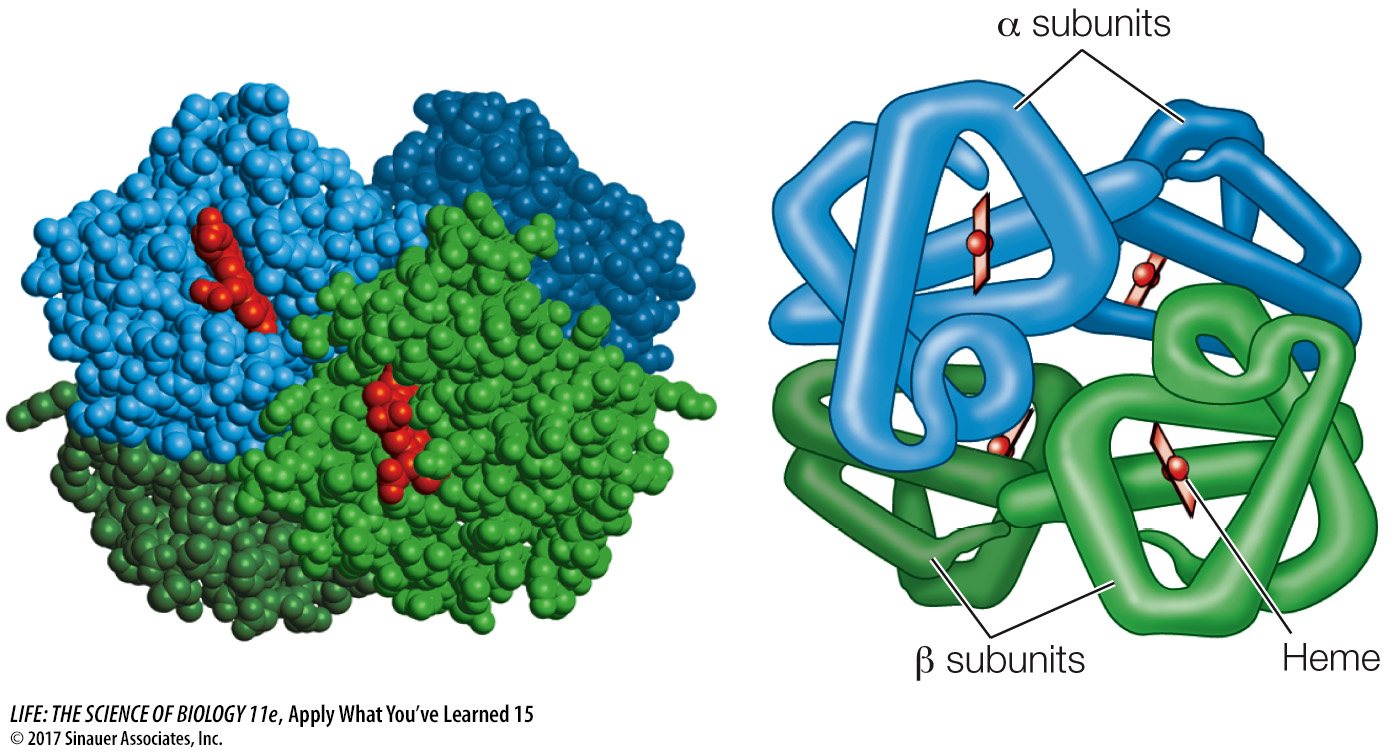
Hemoglobin, composed of four polypeptide subunits and an oxygen-
People with thalassemia typically make little to no α- or β-globin and so have anemia—
Consider the following scenario: Two people have a mild, persistent anemia. Because each has relatives who suffered from thalassemia, they are concerned that they may be carriers for a thalassemia mutation. Tissue samples of both people are taken and DNA for globin genes sequenced. Here is a region for the normal β-globin gene in the coding strand of DNA:
Codon # 36 37 38 39 40 41
Normal: CCT TGG ACC CAG AGG TTC
Below are the DNA sequences of the coding strands for the same region of the β-globin gene in the two people with mild anemia. Person 1 has two different sequences in this region:
Sequence 1: CCT TGG ACC CAG AGG TTC
Sequence 2: CCT TGG ACC TAG AGG TTC
Person 2 also has two different sequences in this region:
Sequence 1: CCT TGG ACC CAG AGG TTC
Sequence 2: CCT GGA CCC AGA GGT TCT
Questions
1.
Analyze the DNA sequences to identify the type of mutation (silent, nonsense, missense, or frame-
Person 1 is heterozygous, with one normal allele and one mutant allele. The normal allele translates to the amino acids: pro-
Person 2 is heterozygous, with one normal and one mutant allele. In this case, the mutant allele is a deletion of the first T in the second codon. This causes a frame shift: Pro-
2.
Describe a mutation that would have an effect similar to that of the two mutations described but that would involve a change outside the coding region for the β-globin gene.
One example is a mutation that affects the promoter such that RNA polymerase cannot bind to initiate transcription. Another example is a mutation that affects mRNA splicing sites in the DNA that leads to abnormal deletions or insertions in the mature mRNA transcript.
3.
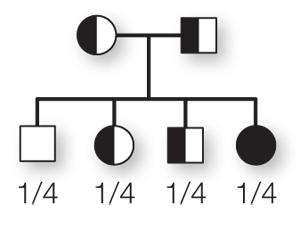
If person 1 were to have a child with person 2, what are the risks involved for this couple’s children? Draw a pedigree chart to illustrate the possible outcomes.
The couple has a 1 in 4 chance of producing a child who is homozygous with two normal alleles, a 1 in 2 chance of producing a child who is heterozygous with one normal allele and one mutant allele, and a 1 in 4 chance of producing a child who is homozygous with two mutant alleles. A child with two mutant alleles would suffer severe anemia and would have to receive regular blood transfusions throughout life.