key concept 19.1 The Four Major Processes of Development Are Determination, Differentiation, Morphogenesis, and Growth
400
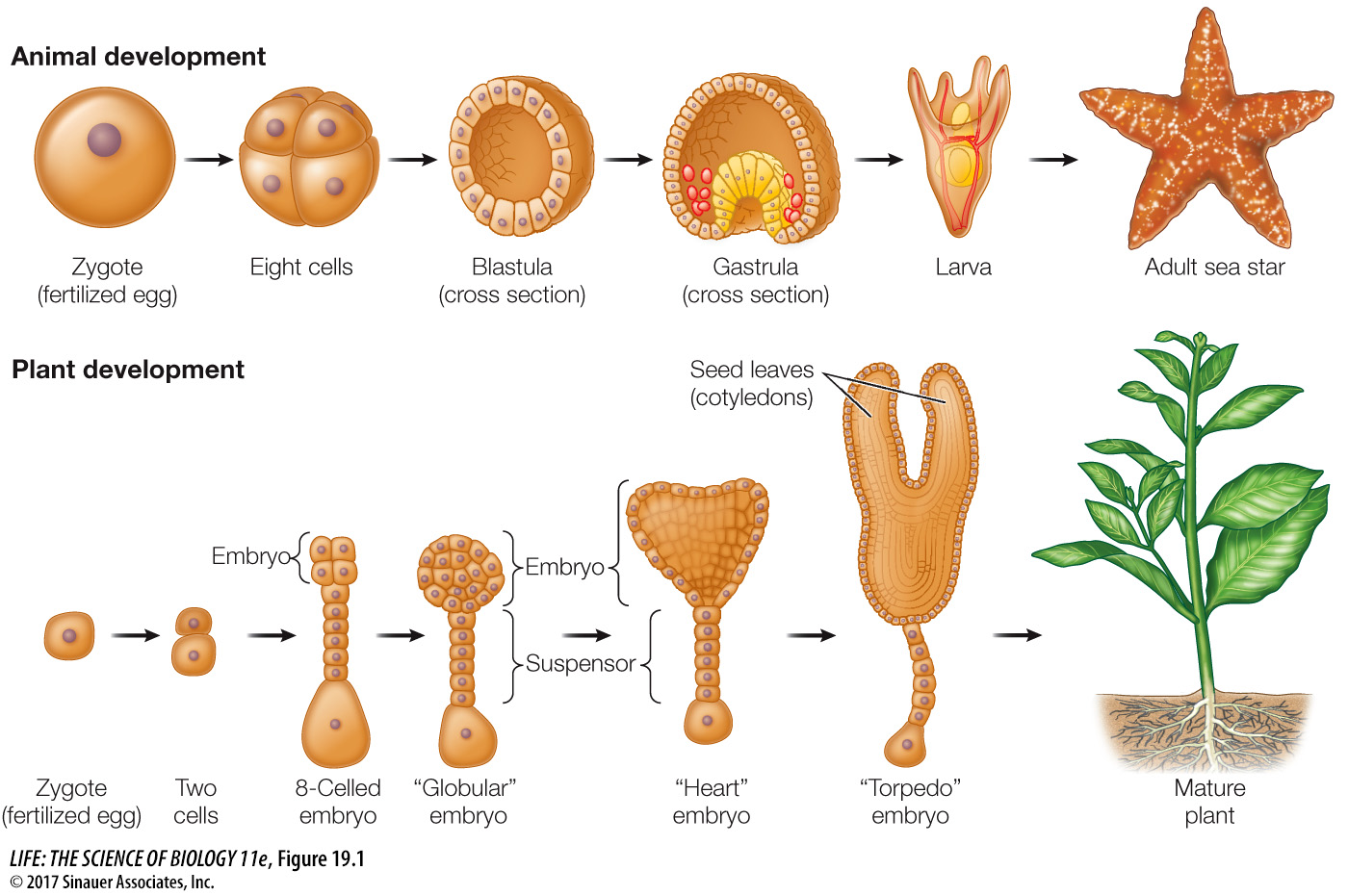
Development is the process by which a multicellular organism, beginning with a single cell, goes through a series of changes, taking on the successive forms that characterize its life cycle (Figure 19.1). After the egg is fertilized it is called a zygote, and in the earliest stages of development a plant or animal is called an embryo. Sometimes the embryo is contained within a protective structure such as a seed coat, an eggshell, or a uterus. Embryogenesis results in a new organism with a body plan characteristic of its species. Many organisms continue to develop throughout their life cycles, with development ceasing only at death.
Activity 19.1 Stages of Development
www.life11e.com/
focus your learning
In the embryo, determination of the fate of a cell occurs before actual cell differentiation.
Experimental manipulations indicate that a differentiated cell in a plant or animal has the whole genome of the organism and the potential to form all other cells of that organism.
Cloning of plants and animals using differentiated cells or cell nuclei has several potential uses.
Pluripotent stem cells can be obtained from animal embryos or formed from differentiated cells in the laboratory.