Flowering plants have microscopic gametophytes
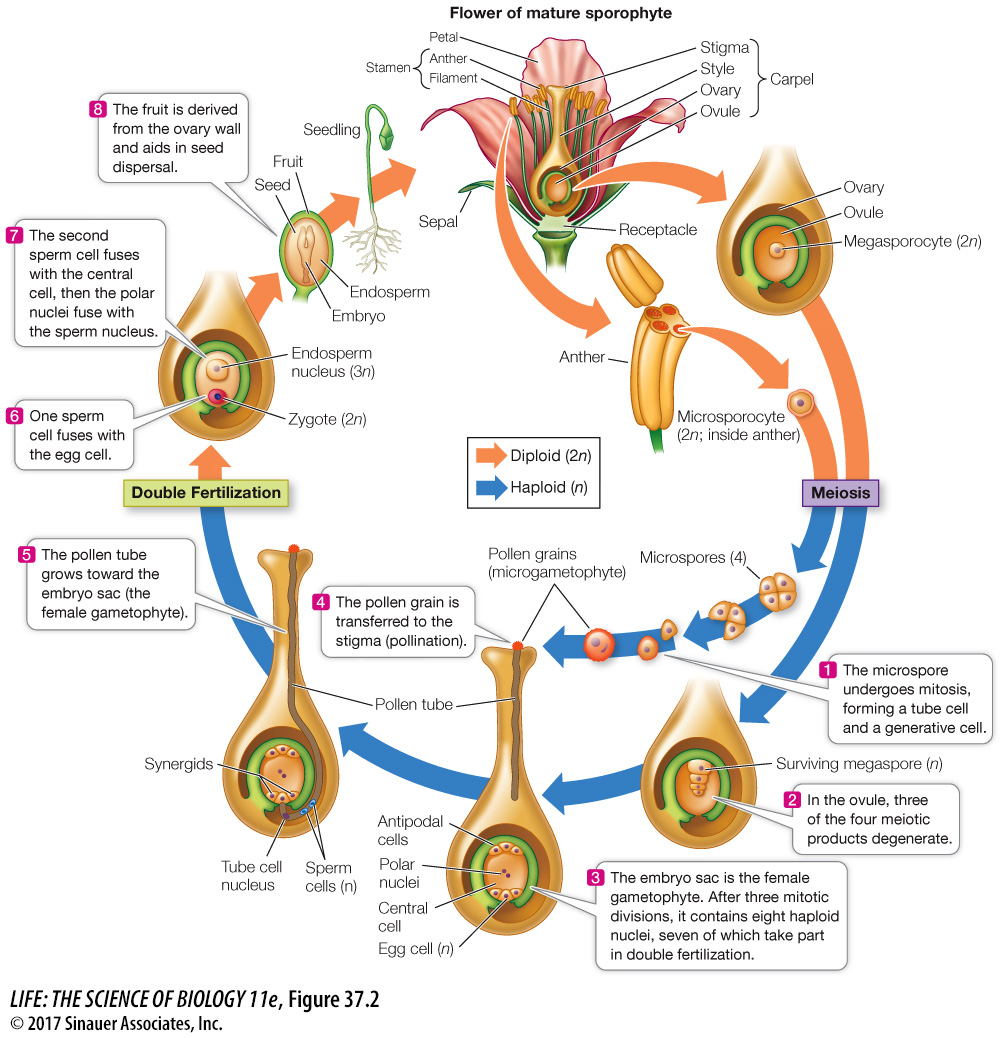
You can follow the roles of male and female gametophytes in angiosperm reproduction in Figure 37.2. The gametophytes develop from haploid spores in the flower:
Activity 37.1 Sexual Reproduction in Angiosperms
www.life11e.com/
Each female gametophyte (megagametophyte) is called an embryo sac, and it develops inside an ovule. One or more ovules are contained within the ovary, which is the lower part of the carpel.
Male gametophytes (microgametophytes), which are called pollen grains, develop inside the anther, which is part of the stamen.
FEMALE GAMETOPHYTE Of the four haploid megaspores resulting from meiosis, three undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death). The remaining megaspore undergoes three mitotic divisions without cytokinesis, producing eight haploid nuclei, all initially contained within a single cell—
At one end of the megagametophyte are three small cells: the egg cell and two cells called synergids. The egg cell is the female gamete, and the synergids participate in fertilization by attracting the pollen tube. The pollen tube enters one of the synergids before the sperm cells are released for fertilization.
788
At the opposite end of the megagametophyte are three antipodal cells, which eventually degenerate.
In the large central cell are two polar nuclei.
The megagametophyte, or embryo sac, is the entire seven-
MALE GAMETOPHYTE The four haploid products of meiosis (the microspores) each develop a cell wall and undergo a single mitotic division, usually producing four two-
After pollination (see below) the generative cell divides by mitosis to form two sperm cells that participate in fertilization.
The tube cell forms the elongating pollen tube that delivers the sperm to the embryo sac.
These events occur after the pollen grain is transferred to a stigma (part of the female reproductive organ)—a process called *pollination.
*connect the concepts Flower structure evolved over time. Natural selection has favored floral features that have increased the likelihood of successful pollination. Key Concepts 28.3 and 56.4 describe how angiosperms coevolved with animal pollinators and how ecological communities are formed through interactions among plant and animal species.