Chapter 10
RECAP 10.1
The light reactions convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. In the light-
independent reactions, ATP and NADPH power the fixation of CO2 to form carbohydrate. NADP and ADP are regenerated. Researchers used the isotope 18O to show that the O2 produced during photosynthesis came from water labeled with 18O and not from carbon dioxide labeled with 18O.
RECAP 10.2
A pigment molecule tends to lose the absorbed energy of a photon by returning to ground state and emitting the energy as light or heat. Alternatively, the energy can be transferred as an excited electron from the pigment to another molecule, reducing that molecule.
An absorption spectrum plots the extent of absorption by pigments (y axis) versus the wavelength of light to which the pigments are exposed (x axis). An action spectrum also plots wavelengths of light, but in this case the y axis is a biological activity (e.g., photosynthesis).
See Figure 10.8. In cyclic electron transport, ATP is produced chemiosmotically by electron transport in the thylakoid membrane.
RECAP 10.3
Researchers exposed algae to CO2 labeled with 14C for varying times and looked to see where the 14C label ended up. After a very short exposure time of 3 seconds, all of the label was found in 3-
phosphoglycerate (3PG). After a longer exposure time of 30 seconds, the label could be found in more compounds, suggesting that 3PG is the initial product that is then used for synthesis of additional molecules. See Figure 10.10. The light reactions produce ATP and NADPH, which are used in CO2 fixation reactions (Calvin cycle).
Light-
induced pH changes in the stroma activate some Calvin cycle enzymes. Light-
induced electron transport reduces disulfide bridges in four of the Calvin cycle enzymes, thereby activating them.
In the dark, photosynthetic electron transport stops at photosystem II → reduced PQ (plastoquinone). Initially the chlorophylls in light-
harvesting complexes remain reduced, so reaction center chlorophylls remain reduced and thus photosystem II remains reduced. In the dark, the Calvin cycle stops at the reduction phase, which requires NADH. No RuBP is regenerated, so there is no rubisco activity. The initial reactions are no oxidation of photosystem I and no reduction of NADP to NADPH.
RECAP 10.4
In C4 plants, CO2 is initially fixed in the leaf mesophyll cells but is then transferred (as a four-
carbon molecule) to the bundle sheath cells, where decarboxylation reactions release CO2 for use in the Calvin cycle. The bundle sheath cells are located in the interior of the leaf where less atmospheric O2 can reach them than reaches cells near the surface of the leaf. In CAM plants, CO2 is initially fixed into a four-
carbon compound (malate) at night when it is cooler and water loss is minimized, and the stomata open. During the day, when the stomata close to reduce water loss, the accumulated malate is transferred from the vacuole to the chloroplasts, where its decarboxylation supplies the CO2 for the Calvin cycle and the light reactions supply the necessary ATP and NADPH.
RECAP 10.5
See Figure 10.17. 3PG and G3P link the Calvin cycle and glycolysis. Acetyl CoA links glycolysis to the citric acid cycle.
Most of sunlight is not absorbed by plants. This is because it has wavelengths that are not part of the absorption spectrum of plant pigments; because it is reflected back to space; and because it is not intercepted by plant organs (e.g., it reaches the ground).
WORK WITH THE DATA, P. 195
In Experiment 1, the 18O/16O ratio of O2 (0.84–
0.86) was similar to that of the H2O (0.85) and not to that of the CO2 sources (0.2– 0.61). In Experiment 2, the ratio in O2 (0.20) was again more similar to that of the H2O (0.20) than to that of the CO2 sources (0.40– 0.50). The source of the oxygen atoms in O2 is H2O.
WORK WITH THE DATA, P. 203
The data show an initial rise of 3PG (in first 30 sec) because rubisco is initially still active and can catalyze the reaction of CO2 with RuBP to produce 3PG. Between 30 sec and 2 min, the amount of 3PG levels off as rubisco becomes inactive in the dark. After 2 min, the amount of 3PG falls as it enters other pathways (see Figure 10.18).
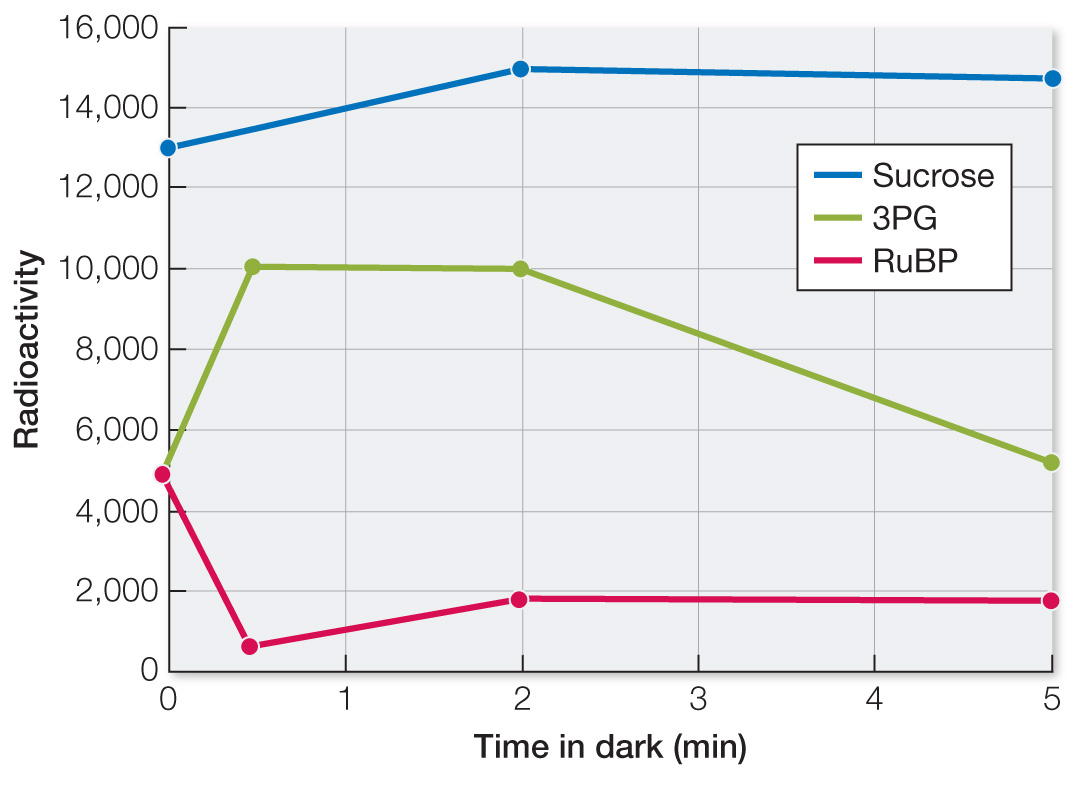
The level of RuBP went down in the dark initially because it was consumed in the reaction catalyzed by rubisco.
FIGURE QUESTIONS
Figure 10.2 Reduction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast and the reducing agent is NADPH.
Figure 10.4 In phycobilins, yellow light absorbs at a shorter wavelength (540 nm) that is more energetic than the longer wavelength (660 nm) at which chlorophyll absorbs. This means that the energy transfer from phycobilins to chlorophyll is thermodynamically favored (higher to lower energy).
Figure 10.7 The herbicide rather than NADP reductase would accept electrons from noncyclic photosystem I. NADPH would not be formed. This would severely reduce the transfer of solar energy to chemical energy in the light-
APPLY WHAT YOU’VE LEARNED
Light stimulates the light reactions to occur, which then stimulates the Calvin cycle. Also, light-
induced changes activate Calvin cycle enzymes. Shade-
tolerant plants have much lower maximum rates of photosynthesis even when raised in the same light conditions as shade- intolerant plants and exposed to the same light intensities. This suggests that either there are fewer light- harvesting centers and fewer Calvin cycle enzymes in shade- tolerant plants, and/or that the Calvin cycle enzymes of shade- tolerant plants are adapted to function at lower rates than those of shade- intolerant plants. Both shade-
tolerant and shade- intolerant plants develop more chlorophyll when raised under greater degrees of shade. This helps compensate for the low light levels to allow the plants to collect greater amounts of light. Specific leaf surface areas are larger in shade-
tolerant plants. This allows the light- harvesting centers to be spread out as much as possible so that they can capture maximum light under shade conditions. This helps compensate for the low light levels to allow the plants to collect enough light to carry out photosynthesis. The shade-
intolerant plants will have a much greater fluctuation in photosynthesis rate than the shade- tolerant plants. This prediction is made based on the much larger range of photosynthesis rate data in the graph of the shade- intolerant species compared with that of the shade- tolerant species.