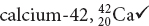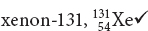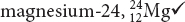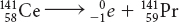Unit 1: Alchemy
C-1
Lesson 1
Possible answer: We use glass because substances in a glass container are visible and glass containers are relatively easy to clean and reuse. Tempered glass containers can be heated over flames without shattering.
Possible answers: Know the location of safety equipment. Read lab instructions carefully. Check to be sure that you are using the right chemicals and equipment.
Possible answers: Put all equipment in its proper place. Clean your work area. Make sure all bottles and containers holding chemicals are closed and stored properly.
Lesson 2
Alchemists developed some of the first laboratory tools and chemistry techniques. They classified substances into categories and experimented with mixing and heating different substances to create something new.
Observable changes that involve chemistry often involve an alteration in the appearance of matter. Examples include metal rusting, cookies baking, and ice cubes forming. Changes that do not involve chemistry only involve matter moving to a different location. Examples include the Sun going down, objects falling, and hands moving on a clock.
Lesson 3
Mass is the amount of material in an object. Volume is the amount of space the object takes up.
Possible answer: Examples of things that are matter: a car, a tree, a person, water. Each of these objects has mass and volume. Examples of things that are not matter: sound, movement, feelings, energy. These objects do not have mass or volume.
Lesson 4
Measure the dimensions of the object and calculate its volume using a geometric formula, or if it does not float or dissolve, measure the amount of liquid that it displaces when it is submerged.
Yes, the volume of an object is the amount of space it fills. You can usually see how much space an object fills and estimate its volume based on its dimensions. However, for objects that have an irregular shape, are very thin, or have a surface with lots of holes or pits, determining the volume of the object by sight may be difficult.
Yes, the mass of the rubber band is the same because only the shape of the rubber band changes, not the amount of matter in it.
Possible answer: The balance or scale that was used to measure the two different cubes may not be able to measure accurately to a hundredth of a gram. The two cubes could have exactly the same mass because the measurement error is greater than 0.03 g.
Lesson 5
Possible answer: Density is the mass of an object divided by its volume.
The density of aluminum is less than the density of gold. More matter is present in a given volume of gold than in the same volume of aluminum.
Possible answer: The object that has a density of 2.7 g/cm3 has the larger volume. The two objects have the same mass, but the mass is packed into a smaller space in the denser object.
2.87 g/cm3
111 g, 38.7 cm3, 2.87 g/cm3
The density is the same.
Chapter 1 Review Exercises
Possible answer: Determine the volume of a powdered solid or of a liquid by pouring the substance into a graduated cylinder or beaker and reading the markings on the side. Determine the volume of a rock by submerging the rock in a graduated cylinder partially filled with water and then reading how much the water level changes.
Density is no help in determining which object will displace more water. A large object will displace more water than a small object no matter how dense the two objects are.
Lesson 6
C-2
Elements are the building materials of all matter. A compound is matter that is made up of two or more elements combined in a specific ratio. An element cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means, but a compound can be broken down into elements.
Sodium nitrate contains three elements: sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen.
The chemical formula for cubic zirconia is ZiO2. The chemical formula for a diamond is C. The stone cannot be a diamond because it has a different chemical formula than a diamond.
Lesson 7
Possible answer: A chemical reaction is a change leading to the final substance or substances being different from the original substance or substances. Some of the signs that a new substance has formed include color changes, formation of a new solid or gas, and the release of energy as heat or light.
Possible answer: A chemical reaction combined the zinc with part of the dissolved copper compound. The resulting zinc compound was also dissolved in water. The zinc was still present, but not as a pure element.
The baking soda is a solid, the vinegar is a liquid, the clear colorless liquid is a liquid, and the CO2 is a gas.
Yes, the production of carbon dioxide gas is evidence that a chemical change has occurred after the original liquid and solid substances were mixed.
Before the change, the sodium is in the solid baking soda. After the change, the sodium must be in the clear colorless liquid.
Lesson 8
Possible answer: The chemical names and symbols indicate what compounds were combined in each step. Because matter is conserved, the products must contain the same elements as the original compounds, which enables you to make a reasonable guess about the products. For example, when sulfuric acid combines with copper oxide, it is likely that copper sulfate and water are the products.
The solution would be yellow because the combination of nickel, Ni, and hydrochloric acid, HCl, can only produce a solution containing compounds with nickel, hydrogen, and chlorine. Nickel chloride, NiCl2, is a possible product. Nickel sulfate, NiSO4 is not.
Lesson 9
Three useful properties for sorting elements are reactivity, formulas of their compounds, and atomic mass.
CaS
The compound with sulfur will have more mass for a given amount of calcium. The two compounds have the same number of atoms, but the atomic mass of sulfur is 32, and the atomic mass of oxygen is only 16.
Lesson 10
Within Group 1A, the elements tend to get more reactive as you move from the top of the column to the bottom.
(B) titanium
(C) lead
(E) potassium
(F) silicon
Elements copper and mercury are the least reactive. On the periodic table the least reactive elements (aside from the noble gases) are the transition metals that are located in the center of the table. The other elements listed are from more reactive groups near the edge of the table: alkali metals (potassium and rubidium), alkaline earth metals (barium), and halogens (chlorine).
Chapter 2 Review Exercises
Gold, represented by the symbol Au, is a transition metal that is a solid at room temperature. It has an atomic number equal to 79 and an average atomic mass of 196.97. Gold is nonreactive, a good conductor of heat, and a good conductor of electricity. It has properties similar to those of copper and silver.
Possible answer: A chemical formula is a symbol that represents a compound. The chemical formula shows what elements are in the compound and the ratio in which the elements combined. It can also show what physical form the compound is in.
Lesson 11
When Thomson zapped atoms with electricity, he found that a negatively charged particle was removed. Because the solid sphere model does not allow for particles splitting off atoms, he created the plum pudding model.
Bohr revised the nuclear model of the atom when he noticed different atoms giving off different colors of light when exposed to flame or electric fields. Because the nuclear model fails to account for this process, he created the solar system model.
Possible answer: The two types of atoms could have different amounts of positive fluid and different numbers of electrons. Each atom would still have a net charge of zero.
C-3
No, the Greeks were not correct. It is now known that atoms are made up of smaller particles such as electrons, protons, and neutrons. Each of these particles has a mass and a volume, so they are matter.
Lesson 12
The atomic number indicates the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
magnesium
The atomic mass is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Although boron and carbon each have six neutrons, carbon has six protons while boron has only five protons.
Lesson 13
Atomic number refers to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Atomic mass, when expressed in amu, is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons.
Possible answer: The isotopes differ from one another in the number of neutrons in their nuclei. The isotopes are 3919K, 4019K, 4119K.
58 amu
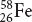
35.48 amu
(B) Because nitrogen has an atomic number of 7 on the periodic table, any possible isotopes must have an atomic number of 7.
Lesson 14
Possible answer: An element is a fundamental building block of matter. An atom is the smallest possible unit of an element. An atom is the smallest unit of an element that still has the same characteristics as the element.
Oxygen has three stable isotopes. Neodymium has five stable isotopes. Copper has two stable isotopes. Tin has ten stable isotopes.
The diagonal line on the graph represents isotopes that have equal numbers of protons and neutrons, because the line passes through points that have the same x- and y-coordinates.
No, because no isotope is indicated on the graph of isotopes of the first 95 elements that has 31 protons and 31 neutrons.
no
Lesson 15
A nuclear reaction is a change in the nucleus of an atom.
Possible answer: Gamma radiation is the most harmful because it has the most power to penetrate living tissues and cause damage.
The mass number of the atom does not change during beta decay because the nucleus loses one electron, which has a mass that is only a tiny fraction of the total mass of the nucleus.
Lesson 16
Possible answers: In alpha decay, a nucleus emits a particle consisting of two protons and two neutrons. The atomic number decreases by 2 and the atomic mass decreases by 4. In beta decay, a nucleus emits an electron. The atomic number increases by 1 as one of the neutrons becomes a proton. The atomic mass does not change. In nuclear fission, a nucleus splits apart to form the nuclei of two or more lighter elements. In nuclear fusion, two nuclei combine to form the nucleus of a heavier element.
Possible answer:
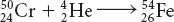
Chapter 3 Review Exercises
Possible answer: An atom changes identity when the number of protons in its nucleus changes. Processes in which this can occur are radioactive decay, fission, and fusion. In radioactive decay, emission of an alpha particle decreases the atomic number by 2, while emission of a beta particle increases the atomic number by 1. Nuclear fission is the process in which a nucleus breaks apart, forming two or more smaller nuclei. In nuclear fusion, two nuclei join to form one larger nucleus.
Lesson 17
The color of the flame produced during a flame test is a characteristic of particular metallic elements. When a compound containing one of the metallic elements is heated, its atoms emit light of a specific color.
Possible answer: Red fireworks could contain lithium chloride, and purple fireworks could contain a mixture of lithium chloride and copper chloride. Red fireworks could contain lithium sulfate, and purple fireworks could contain a mixture of lithium sulfate and copper sulfate.
No, the flame color of each nitrate compound is different and matches the flame color of the metal in the compound. This indicates that the nitrate is not responsible for the color of the flame.
yellow-orange
green
pink-lilac
pink-lilac
green
Lesson 18
C-4
For main group elements, the number of shells containing electrons is equal to the period number. All of the shells, except the highest, are completely filled. The group number indicates the number of electrons in the outermost shell.
Possible answer: Beryllium, magnesium, and calcium are all alkaline earth metals. They are located in Group 2A, so their atoms all have two valence electrons.
The number of core electrons does not change across a period.
Element number 17 is chlorine. It has the chemical symbol Cl and is located in Group 7A. This information comes directly from square 17 on the periodic table.
The nucleus contains 17 protons. The number of protons is equal to the atomic number.
Possible answer: The nucleus can contain either 18 or 20 neutrons. This information is given in the graph of isotopes of the first 95 elements.
The number of electrons in a neutral atom of chlorine is 17. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons.
Chlorine has 7 valence electrons. The number of valence electrons is equal to the group number.
Chlorine has 10 core electrons. The number of core electrons equals the difference between the total number of electrons and the number of valence electrons, or 17 – 7.
Possible answer (any three elements): Fluorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine all have the same number of valence electrons. All of these elements are in the same Group, 7A, as chlorine.
Lesson 19
A cation is an ion that has a positive charge. An anion is an ion that has a negative charge.
2 electrons, 3 protons, and either 3 or 4 neutrons
The noble gas closest to sulfur is argon. A sulfur atom gains two electrons to have an electron arrangement similar to that of argon.
Possible answers: S2–, Cl–, K+, Ca2+
Ti4+
Elements on the right side of the table gain electrons to have a noble gas arrangement. They do not tend to lose electrons because the charge would be too large.
Lesson 20
The number of valence electrons can predict whether an atom will form a cation or an anion, as well as the size of the charge on the ion. Ionic compounds form between cations and anions in a ratio so that the charges are balanced.
+1
–3
Lithium nitride has three lithium ions with charge +1 and one nitride ion with charge –3.
3(+1) + (–3) =3 + (–3) = 0
8 valence electrons
KBr has one potassium ion with charge +1 and one bromide ion with charge –1.
+1 + (=1) = 0
CaO has one calcium ion with charge +2 and one oxide ion with charge –2.
+2 + (–2) = 0
Li2O has two lithium ions with charge +1 and one oxide ion with charge –2.
2(+1) + (–2) = 2 + (–2) = 0
CaCl2 has one calcium ion with charge +2 and two chloride ions with charge –1.
+2 + 2(–1) = 2 + (–2) = 0
AlCl3 has one aluminum ion with charge +3 and three chloride ions with charge –1.
+3 + 3(–1) = 3 + (–3) = 0
NaCl2 does not form because it has a net charge of –1. The sodium ion has a charge of +1 and each chloride ion has a charge of –1.
CaCl does not form because it has a net charge of +1. The calcium ion has a charge of +2 and the chloride ion has a charge of –1.
AlO does not form because it has a net charge of +1. The aluminum ion has a charge of +3 and the oxide ion has a charge of –2.
Lesson 21
For main group elements, the group number shows the number of valence electrons. Metal atoms lose all of their valence electrons when they form an ion, adding a positive charge for each electron lost. Nonmetal atoms gain enough electrons to have eight valence electrons, adding one negative charge for each electron gained.
LiCl is possible because the total of the charges on the ions equals zero. The lithium ion has a charge of –1 and the chloride ion has a charge of +1.
LiCl2 is not possible because the total of the charges on the ions equals –1.
MgCl is not possible because the total of the charges on the ions equals +1. Magnesium ions have a charge of +2.
MgCl2 is possible because the total of the charges on the ions equals zero.
AlCl3 is possible because the total of the charges on the ions equals zero. Aluminum ions have a charge of +3.
C-5
AlBr3, aluminum bromide
Al2S3, aluminum sulfide
AlAs, aluminum arsenide
Na2S, sodium sulfide
CaS, calcium sulfide
Ga2S3, gallium sulfide
Lesson 22
A polyatomic ion is an ion that consists of two or more elements.
ammonium chloride
potassium sulfate
aluminum hydroxide
magnesium carbonate
–1
Lesson 23
The Roman numeral indicates the charge on the transition metal cation in the compound.
+2, mercury (II) sulfide
+2, copper (II) carbonate
+2, nickel (II) chloride
+3, cobalt (III) nitrate
+2, copper (II) hydroxide
+2 iron (II) sulfate
Co3(PO4)2
Lesson 24
Electron subshells are divisions within a specific electron shell of an atom.
As the number of electrons in an element increases, they are added in a specific sequence that is illustrated by the position of the element on the periodic table. Each section of the table corresponds to a particular subshell of electrons.
15 subshells
4p
1s22s22p63s23p1
Element 13 has 3 valence electrons because it has three electrons in the outer shell, n = 3.
Element 13 has 10 core electrons because it has two shells filled completely: n = 1 with 2 electrons and n = 2 with 8 electrons.
1s22s22p4, [He] 2s22p4
1s22s22p63s23p5, [Ne] 3s23p5
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6, [Ar] 4s23d6
1s22s22p63s23p64s2, [Ar] 4s2
1s22s22p63s2, [Ne] 3s2
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d9, [Kr] 5s24d9
1s22s22p63s23p2, [Ne] 3s23p2
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d105p66s24f145d10, [Xe] 6s24f145d10
Chromium
Silicon
Nitrogen
Cesium
Lead
silver
Chapter 4 Review Exercises
Valence electrons are important because they are in the outermost electron shell of an atom and will interact with other atoms. This interaction is what determines the properties of an element.
As the number of electrons in an element increases, they are added in a specific sequence that is illustrated by the position of the element on the periodic table. Each section of the table corresponds to a particular subshell of electrons.
The anion is Mg2+ and has a charge of +2.
The cation is Cl– and has a charge of –1.
The anion is Ca2+ and has a charge of +2.
The cation is NO2– and has a charge of –1.
Lesson 25
A substance is insoluble if it fails to dissolve in a particular solvent.
Possible answer: The substance is most likely an ionic compound. Many compounds dissolve in water, but electrical conductivity is a characteristic of compounds that separate into ions, such as ionic compounds.
No, though ionic compounds generally do not conduct electricity as solids, they do conduct electricity as aqueous solutions.
Lesson 26
The atoms that make up substances are held together by chemical bonds. The bond is an attraction between the positively charged nuclei of atoms and the valence electrons of other atoms.
Metallic
molecular covalent
ionic
NO2 is a gas that is made up of nonmetal atoms, so it has molecular covalent bonds.
Possible answer: Drop the mixture into a beaker of water. The sodium chloride will dissolve in the water, but the carbon will not.
Carbon is a solid because many carbon atoms are held together in a large array by network covalent bonds.
Lesson 27
C-6
Possible answers: finding pure metals in nature, heating ionic compounds to separate the metal, extracting metals with electricity.
Attach the coated object to the positive terminal of a battery in an electroplating circuit.
The copper sulfate solution is composed of cations (Cu2+) and anions (SO4–) dissolved in water. The only thing that is added to the solution during the experiment is a stream of electrons. When the electrons are added to the copper ions, copper atoms (Cu) are formed on the metal strip. This indicates that the Cu2+ ions are simply copper ions that are missing electrons.
Possible answer: Nickel cannot change into copper unless the number of protons in the nucleus changes. The plating apparatus only adds electrons to the nickel strip, causing the plating to occur. Adding electrons does not change the nucleus, so it cannot change the identity of the atoms.
Chapter 5 Review Exercises
Possible answer: While it is not practical to try to make gold, many substances that are quite valuable can be made through chemistry.
Unit 1 Review Exercises
General Review
Possible answer: An element is the basic building block of compounds. An element has only one type of atom, while a compound has at least two types of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
Lithium, Li, has atomic number 2 and is in Group 2A. It has 2 protons and 2 electrons.
Bromine, Br, has atomic number 35 and is in Group 7A. It has 35 rotons and 35 electrons.
Zinc, Zn, has atomic number 30 and is in Group 2B. It has 30 protons and 30 electrons.
Sulfur, S, has atomic number 16 and is in Group 6A. It has 16 protons and 16 electrons.
Barium, Ba, has atomic number 56 and is in Group 2A. It has 56 protons and 56 electrons.
Carbon, C, has atomic number 6 and is in Group 4A. It has 6 protons and 6 electrons.
An isotope is an atom of an element with a specific number of neutrons in its nucleus. Predict the most common isotope by rounding the average atomic mass of the element to the nearest whole number.
Cations are ions that have lost electrons, causing them to have a positive charge. Anions are ions that have gained electrons, causing them to have a negative charge.
Magnesium chloride has ionic bonding and conducts electricity in solution only.
Oxygen has molecular covalent bonding and does not conduct electricity.
Silver (I) hydroxide has ionic bonding and conducts electricity in solution only.
Platinum has metallic bonding and conducts electricity.
A material that does not dissolve in water and does not conduct electricity is held together by network covalent bonds or molecular covalent bonds.
Standardized Test Preparation
1. C
3. C
5. B
7. A
9. D
11. C
13. D
15. A
17. B
19. B, C
21. B