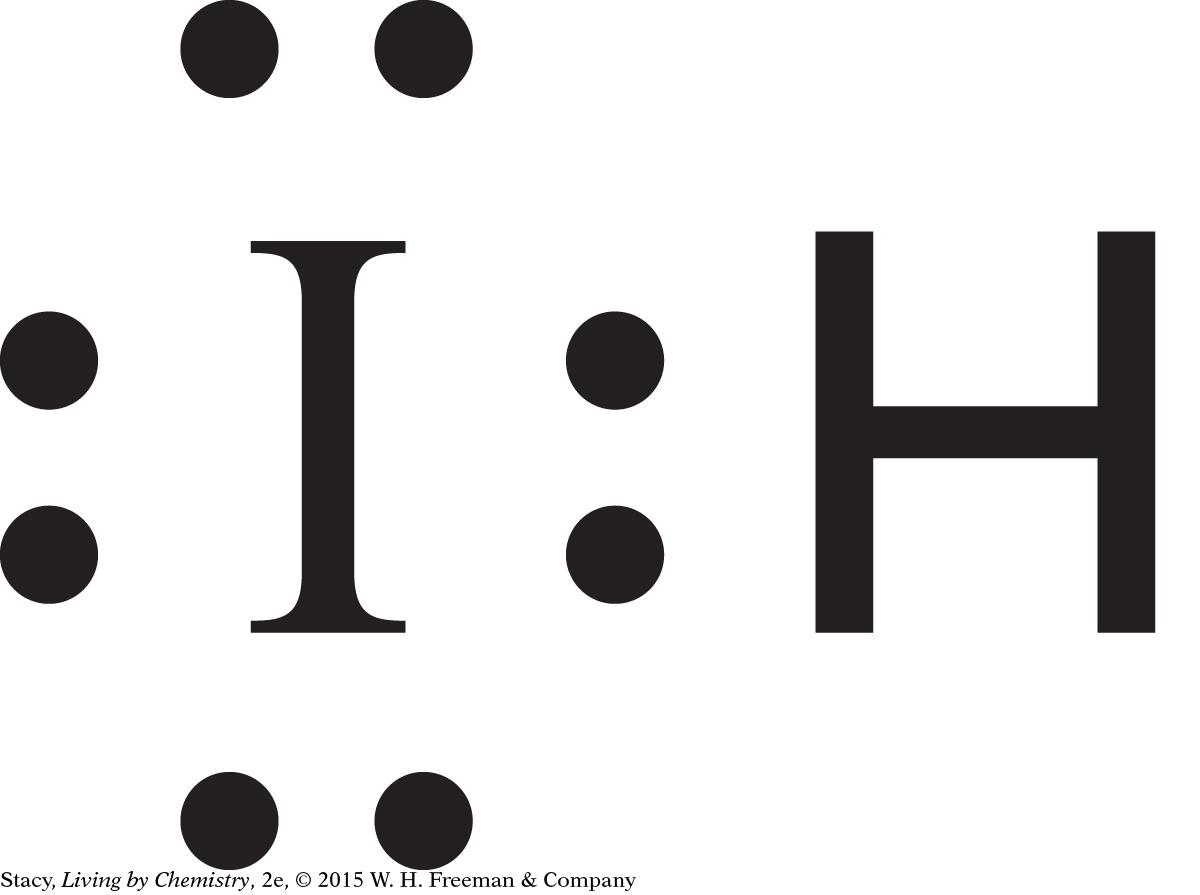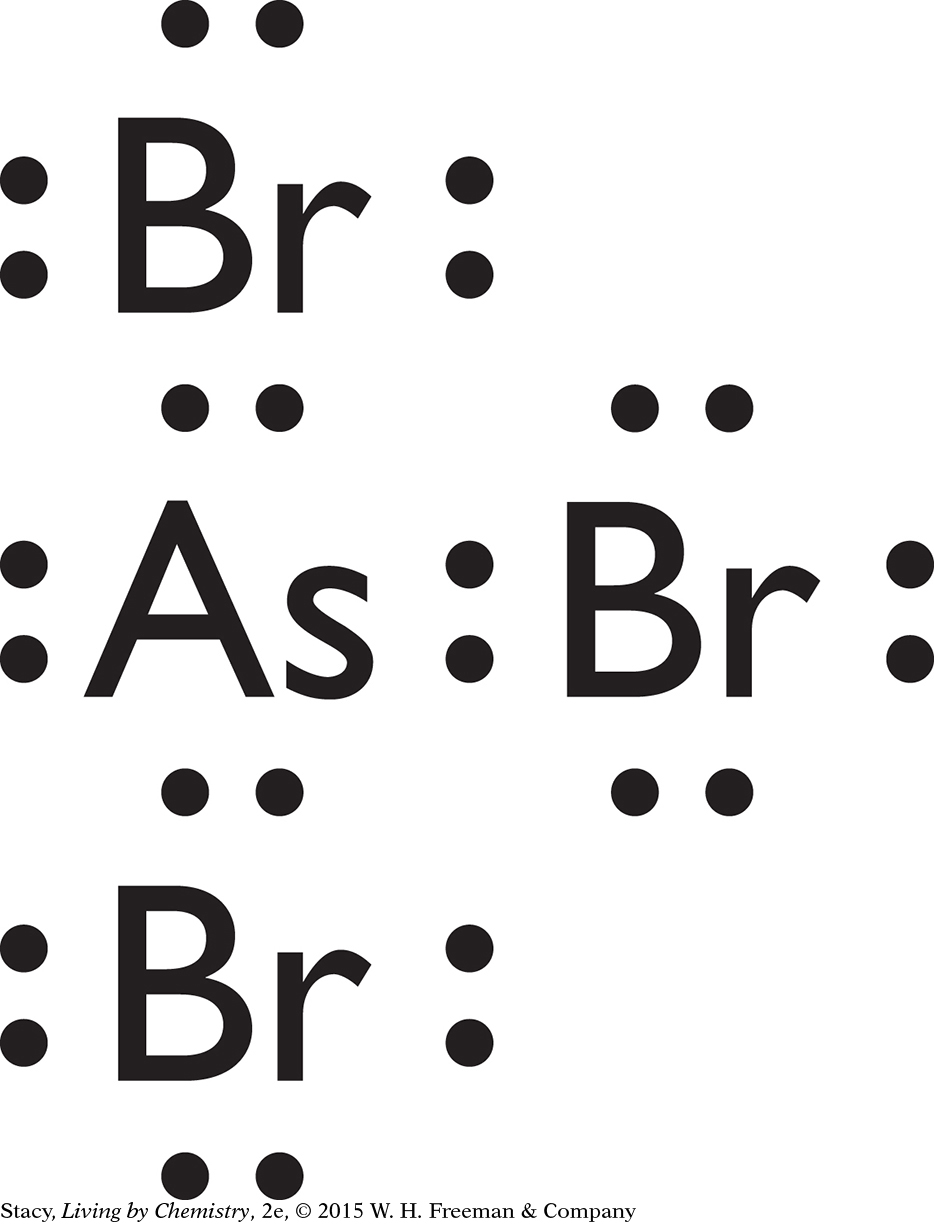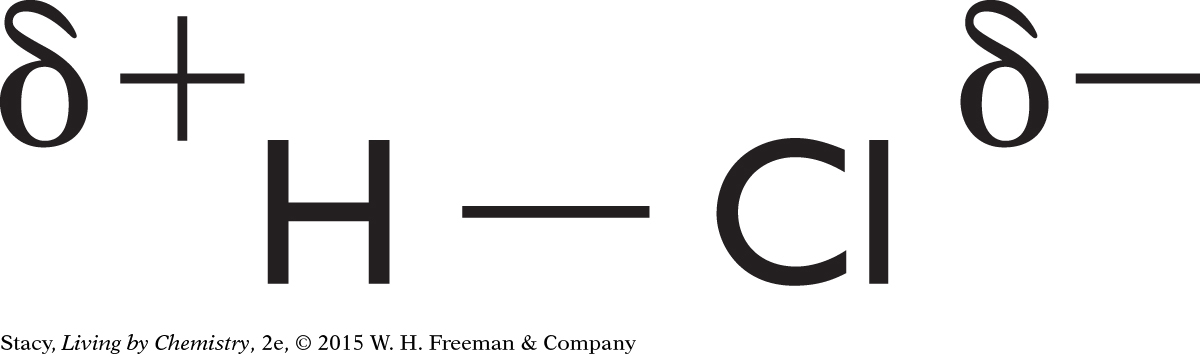Unit 2: Smells
Lesson 28
Possible answer: Scientists classify smells by placing similar types of smells in a category. This allows scientists to talk about smells in a consistent way.
Methyl octenoate probably smells sweet because it has two oxygen atoms and twice as many hydrogen atoms as carbon atoms in each molecule. The chemical name also ends in “-ate.”
Monoethylamine probably smells fishy because it has one nitrogen atom and no oxygen atoms in each molecule.
Ethyl acetate probably smells sweet because it has two oxygen atoms and twice as many hydrogen atoms as carbon atoms in each molecule. The chemical name also ends in “-ate.”
Lesson 29
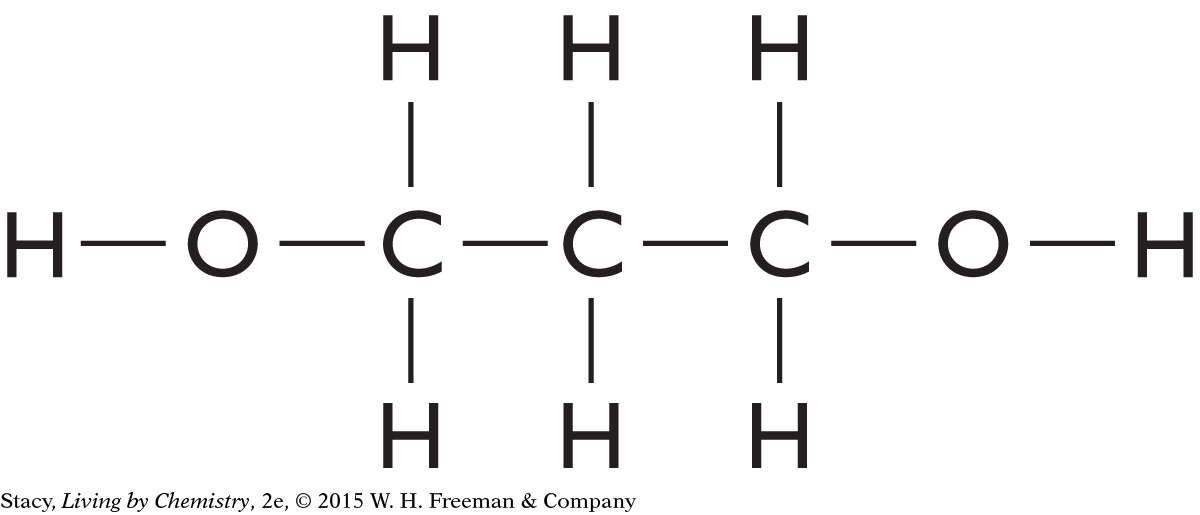
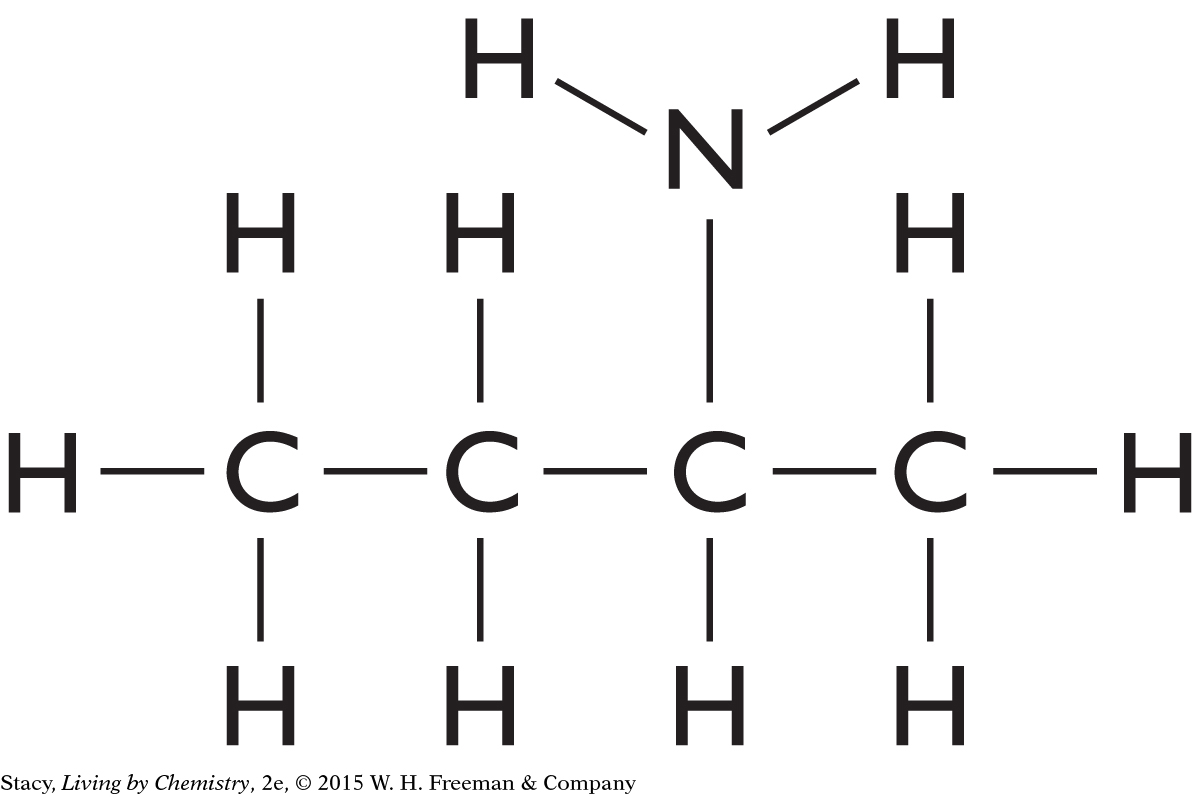
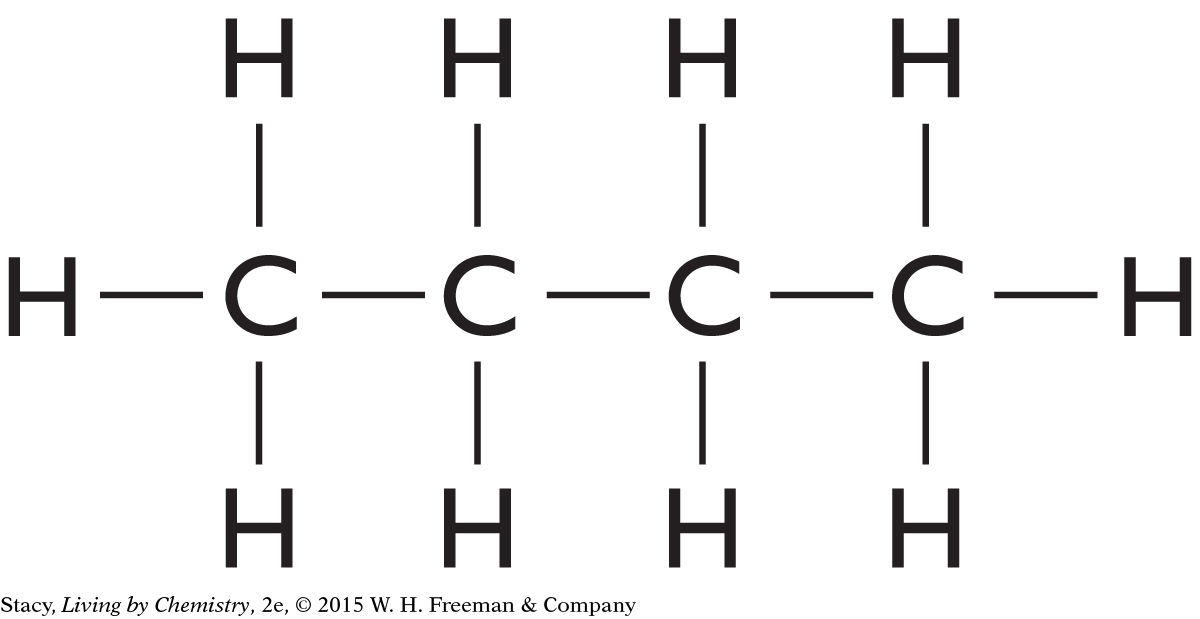
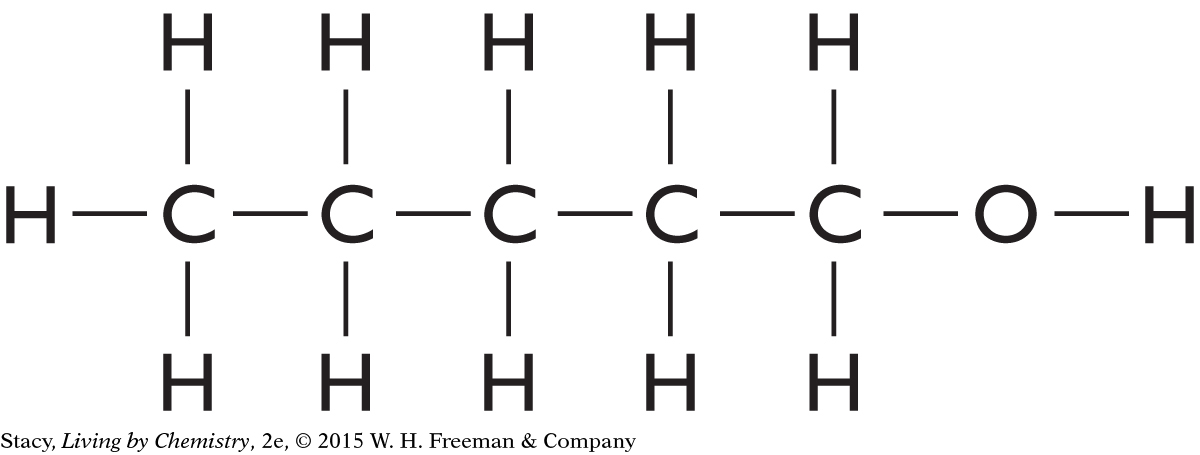
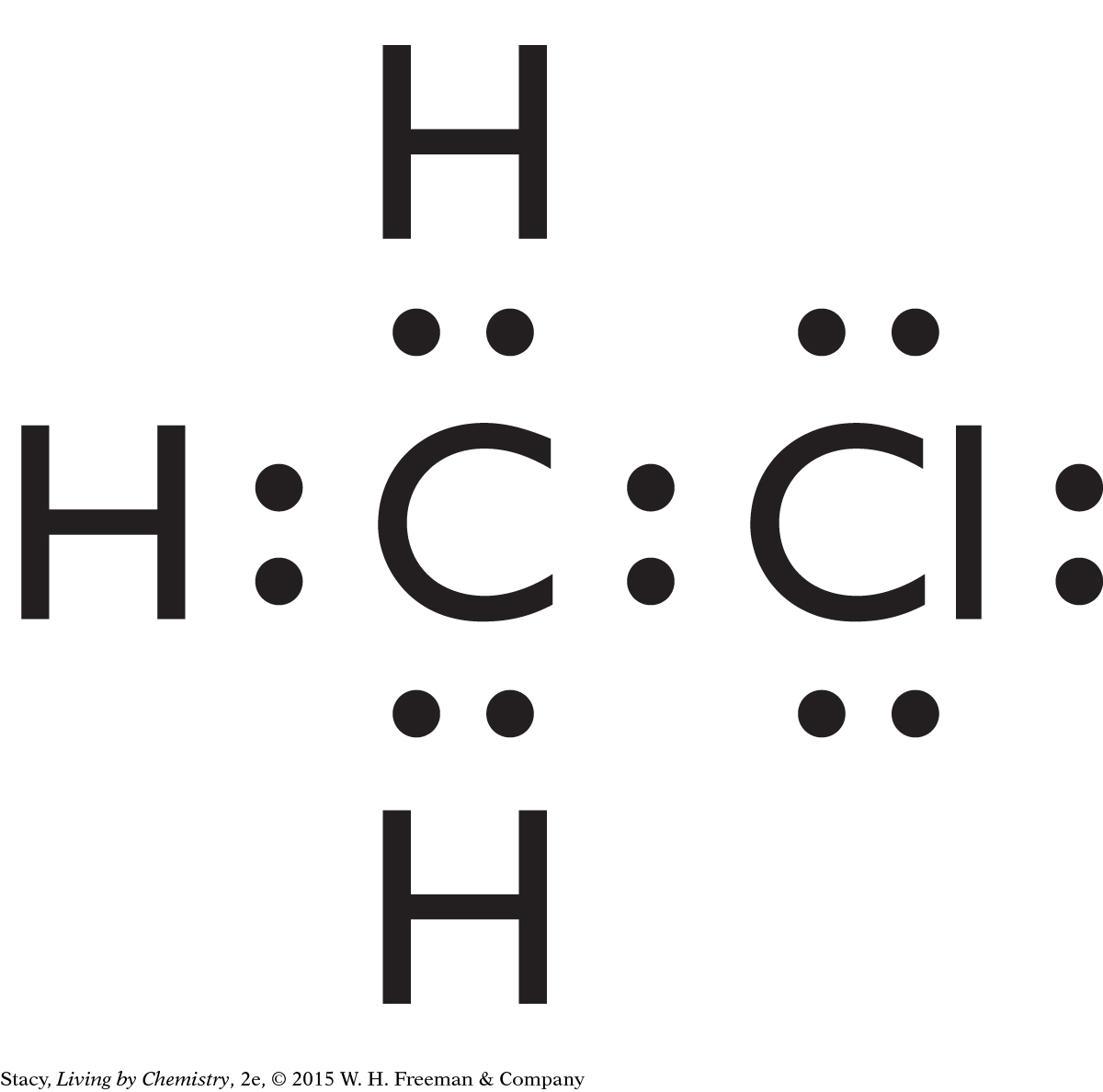
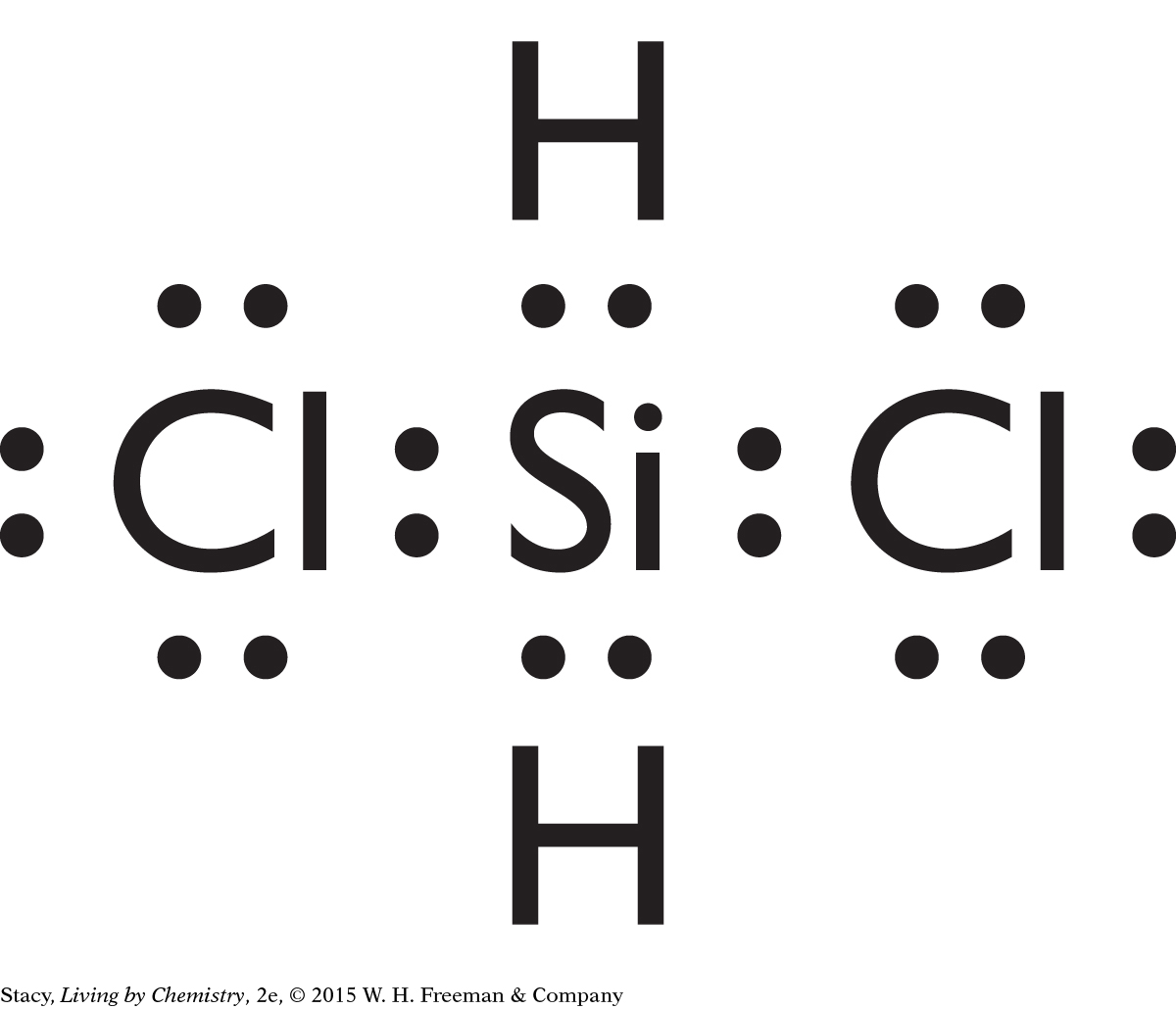
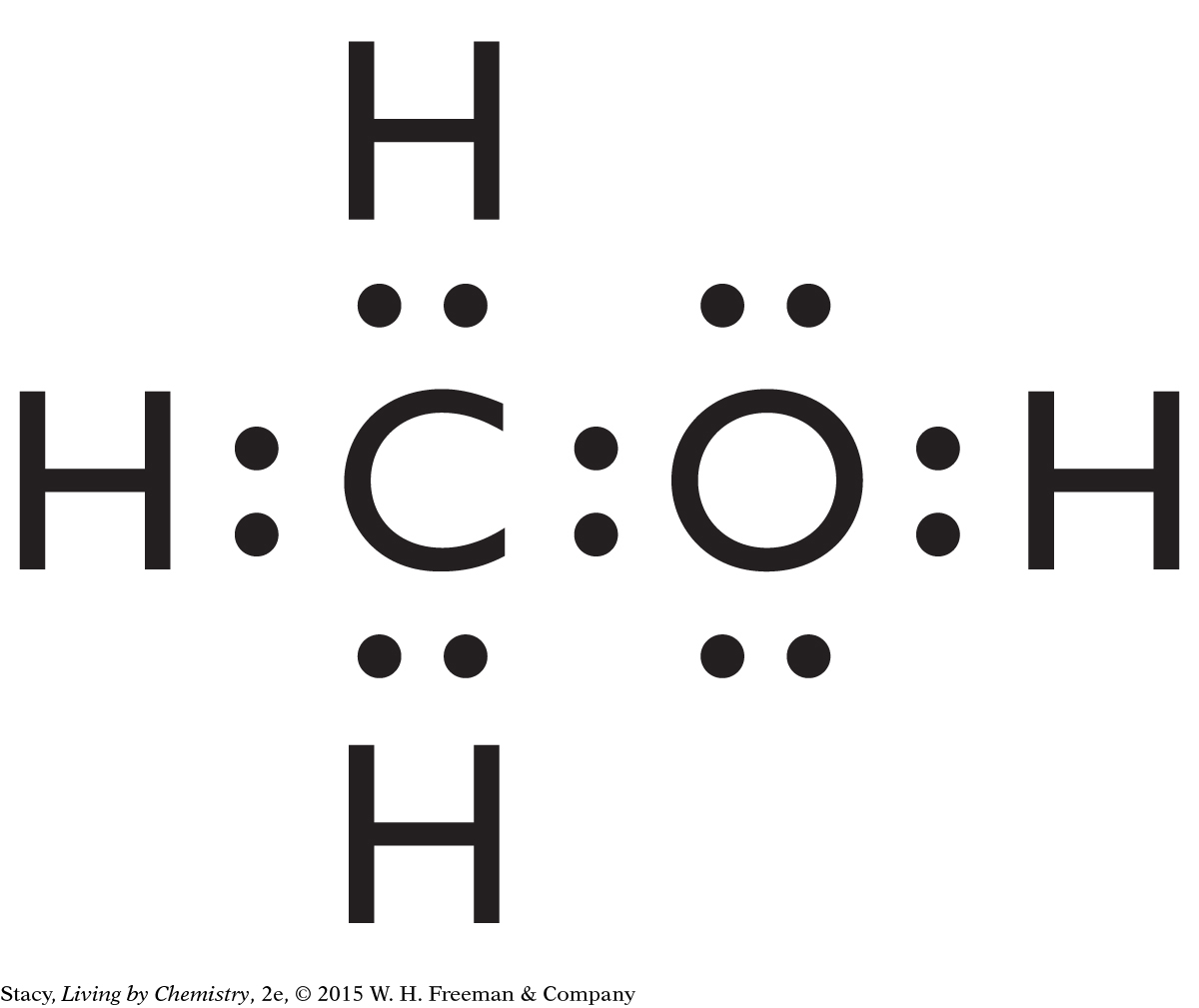
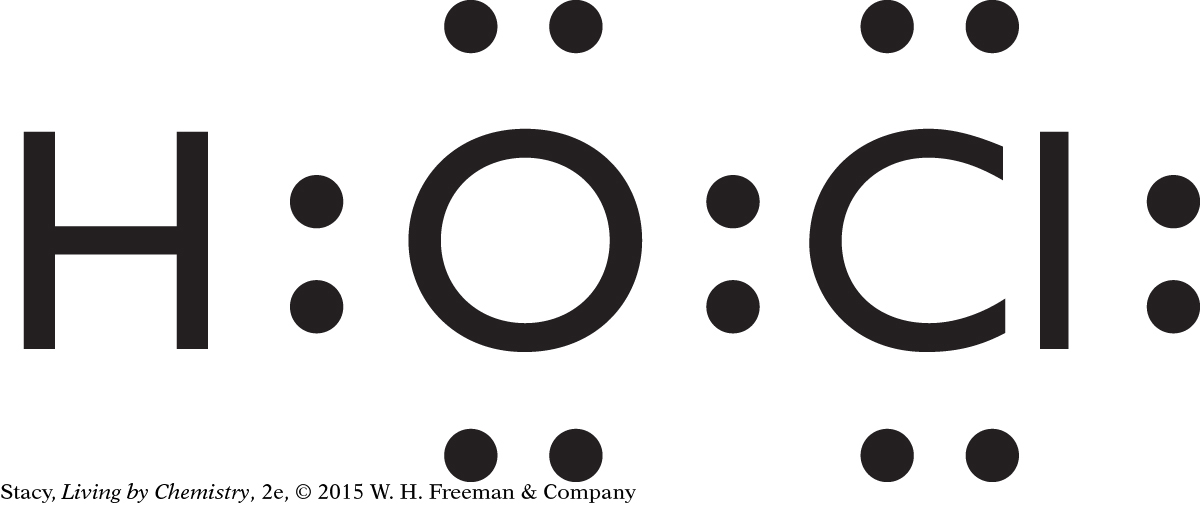
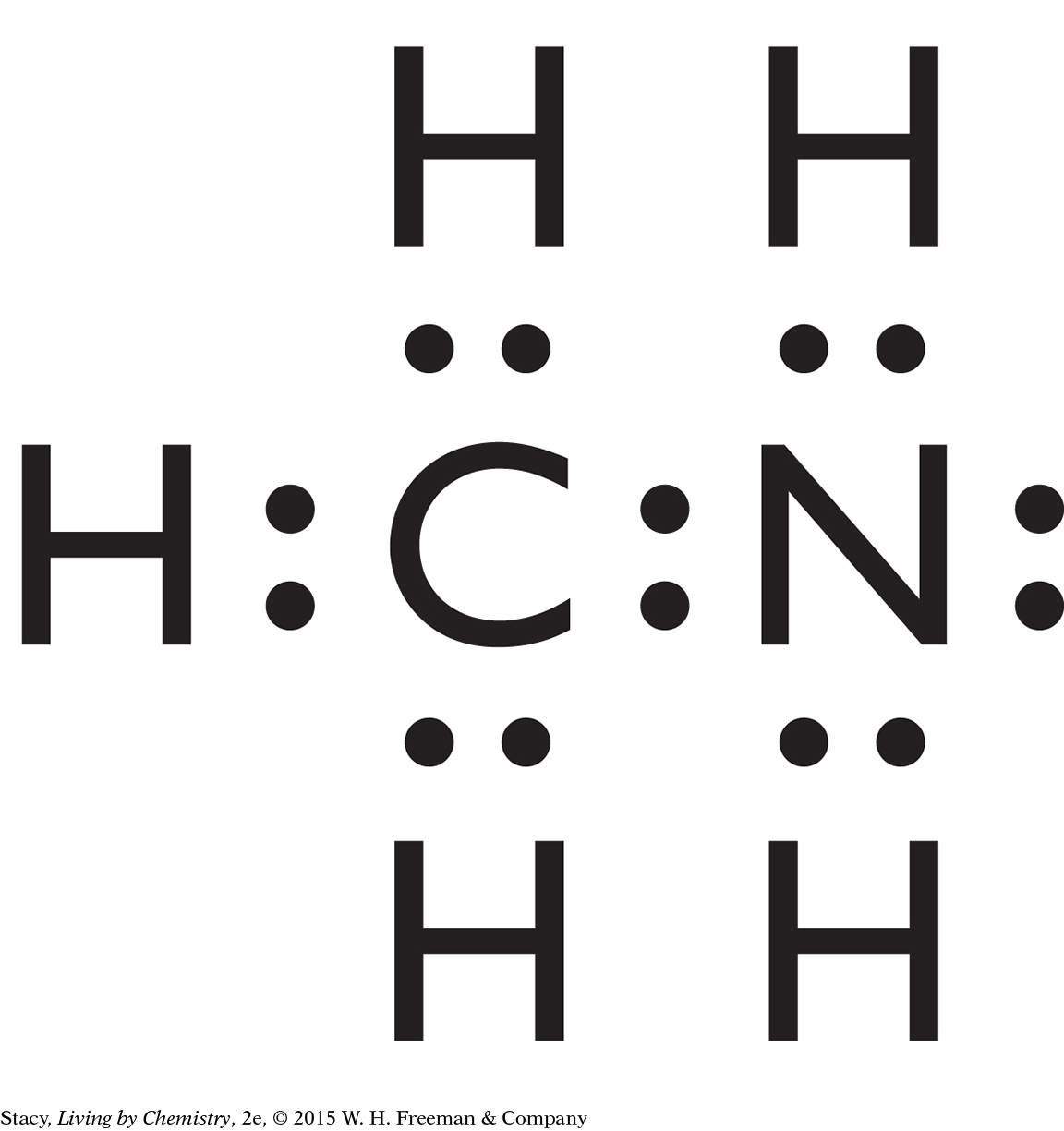
Structural formulas show what atoms are present in a molecule and how the atoms are bonded to one another.
Yes, the structural formula shows all of the atoms in a molecule, enabling use of the structural formula to determine the molecular formula.
C3H6O2
C5H10O
C4H10O
C4H8O2
C4H11N
C2H4O2
Lesson 30
The HONC 1234 rule describes the bonding patterns in molecules. Hydrogen forms one bond with other atoms. Oxygen forms two bonds with other atoms. Nitrogen forms three bonds with other atoms. Carbon forms four bonds with other atoms.
Possible answers:
Possible answer: Atoms on the molecules might react with smell receptors inside the nose. Different receptors may detect different types of molecular structures, leading to different sensations of smell.
Lesson 31
C-7
Possible answer: In an ionic bond, a valence electron is transferred from one metal atom to a nonmetal atom. In a covalent bond, two nonmetal atoms share a pair of electrons. Ionic and covalent bonds are similar because both involve the valence electrons of the atoms that are bonded together. The result of the bond is that the two atoms have an outer shell that is filled. In both types of bonds, electrical forces hold the atoms together.
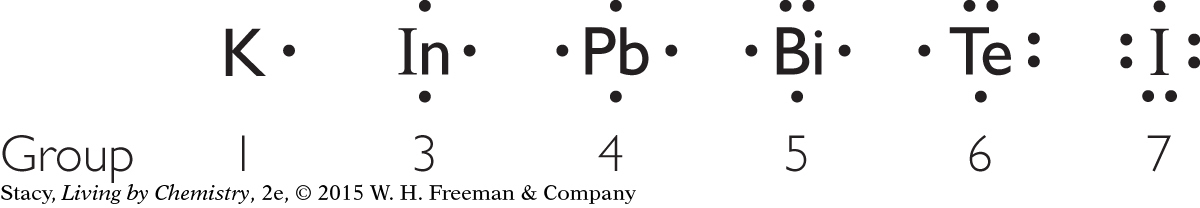
two covalent bonds: Te, one covalent bond: I, does not form covalent bonds: K, In, Pb, Bi
Lesson 32 Exercises
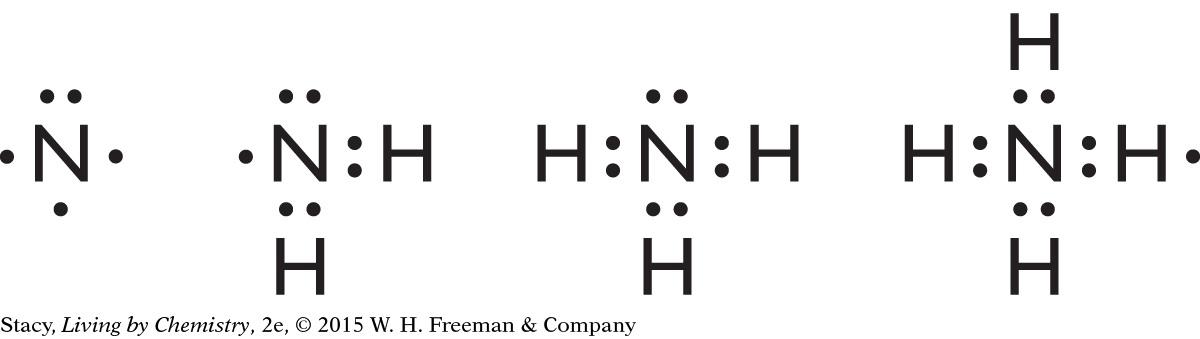
Possible answer: Nitrogen has three unpaired electrons, as shown in the Lewis dot structure. Hydrogen atoms have one unpaired electron, so three hydrogen atoms can form bonds with one nitrogen, giving the nitrogen an octet of electrons and each hydrogen two electrons. In NH2, nitrogen would have only seven electrons, and in NH4, an extra hydrogen atom is left over after all the unpaired electrons in the nitrogen atom have formed bonds.
Possible answer: hydrogen, chlorine, or another fluorine
CH4 would form a stable compound because all of the atoms in the molecule are surrounded by the most stable number of valence electrons—eight for carbon, two for hydrogen. In CH3, the carbon atom would have only seven electrons in its outer shell.
Lesson 33
A functional group is a portion of a molecular structure that is the same in all molecules of a certain type.
C2H4 has fewer hydrogen atoms than C2H6 because the two carbon atoms are held together by a double bond. That means there are only two unpaired electrons in each carbon atom available to form bonds with hydrogen.
C6H14O
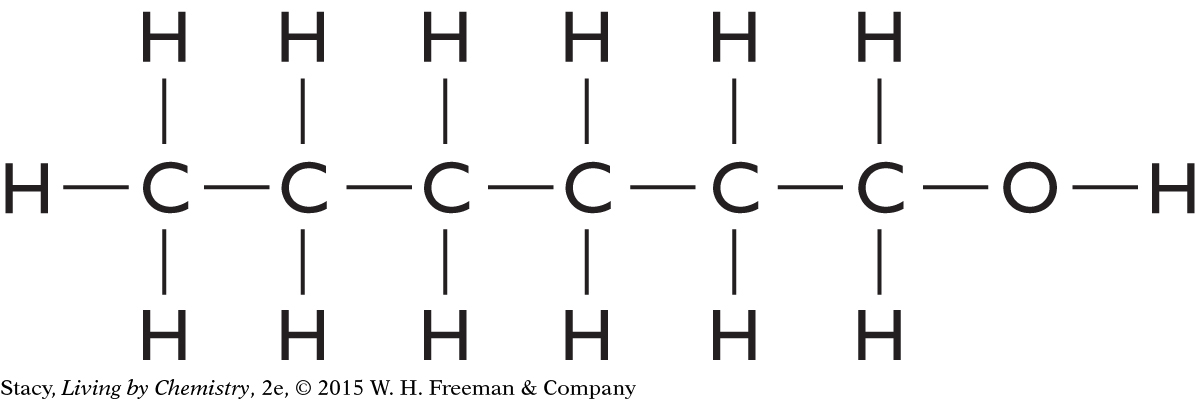
The structural formula is more useful because it shows the –OH functional group that is characteristic of alcohols, and alcohols have a characteristic smell.
C3H6O2
C5H10O
C5H10O
C4H8O2
C4H11N
C2H4O2
Lesson 34
C-8
Combine the alcohol and acid with a strong acid and heat the mixture.
Possible answer: When butyric acid is heated with methanol, the two compounds react to form a new compound, which is a sweet-smelling ester. The butyric acid, which has a foul smell, is no longer present.
Possible answer: Combine the acetic acid with an alcohol and sulfuric acid and then heat the mixture. The hydrogen atom of the acid is replaced by the part of the alcohol molecule that is attached to the –OH functional group.
Lesson 35
Possible answer: Converting a carboxylic acid into an ester is a way to make a new compound with more desirable properties. For example, eliminating a putrid odor is one possible goal of converting a carboxylic acid into an ester.
A catalyst is a chemical that is added to a reaction mixture to help get the reaction started, but is not consumed by the reaction.
C8H16O2
C7H14O2
C9H18O2
C6H12O2
Chapter 6 Review Exercises
Ester
Ketone
Carboxyl
amine
4 lone pairs
12 lone pairs
no lone pairs
Possible answer: The smell of a compound is strongly related to the functional group of the molecule.
Lesson 36
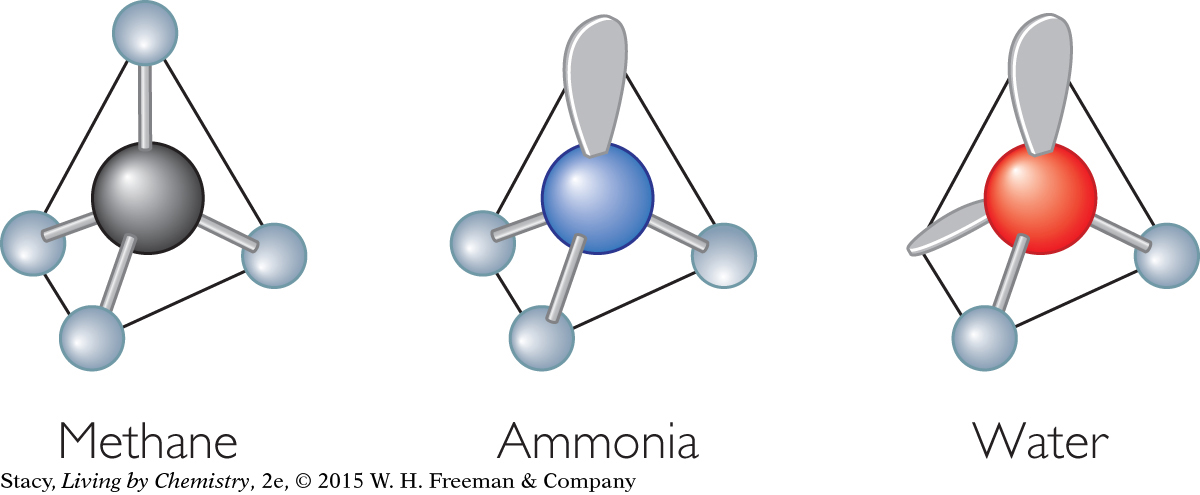
Possible answer: A structural formula shows the arrangement of atoms and the types of bonds within a molecule in a two-dimensional form. A ball-and-stick model adds information about the arrangement of the atoms in three dimensions.
10 black balls (carbon), 18 white balls (hydrogen), 1 red ball (oxygen), 30 connectors (chemical bonds)
Possible answer: The three molecules geraniol, menthol, and fenchol each have ester functional groups in their structural formulas. However, each of the three molecules has a distinctive smell.
Lesson 37
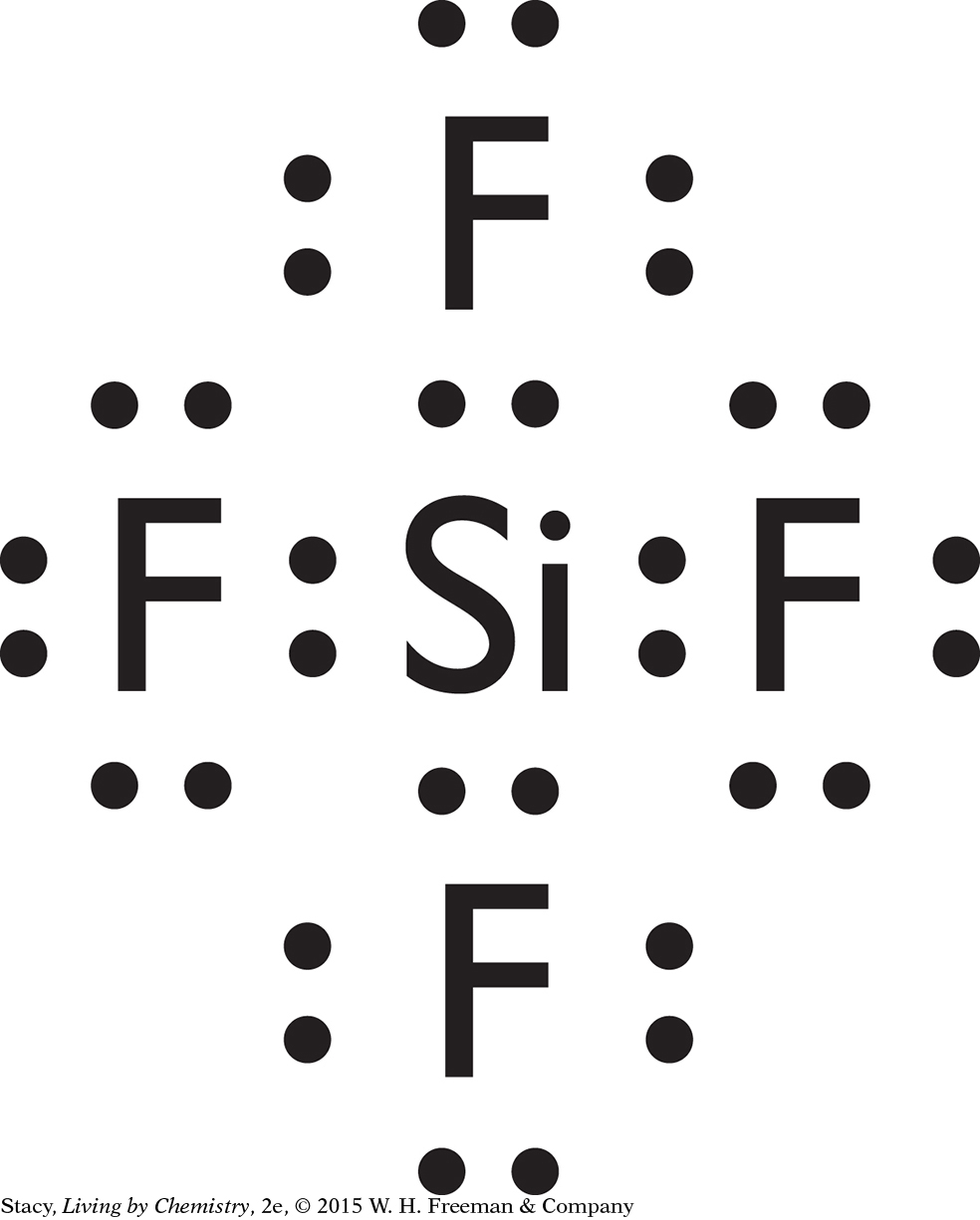
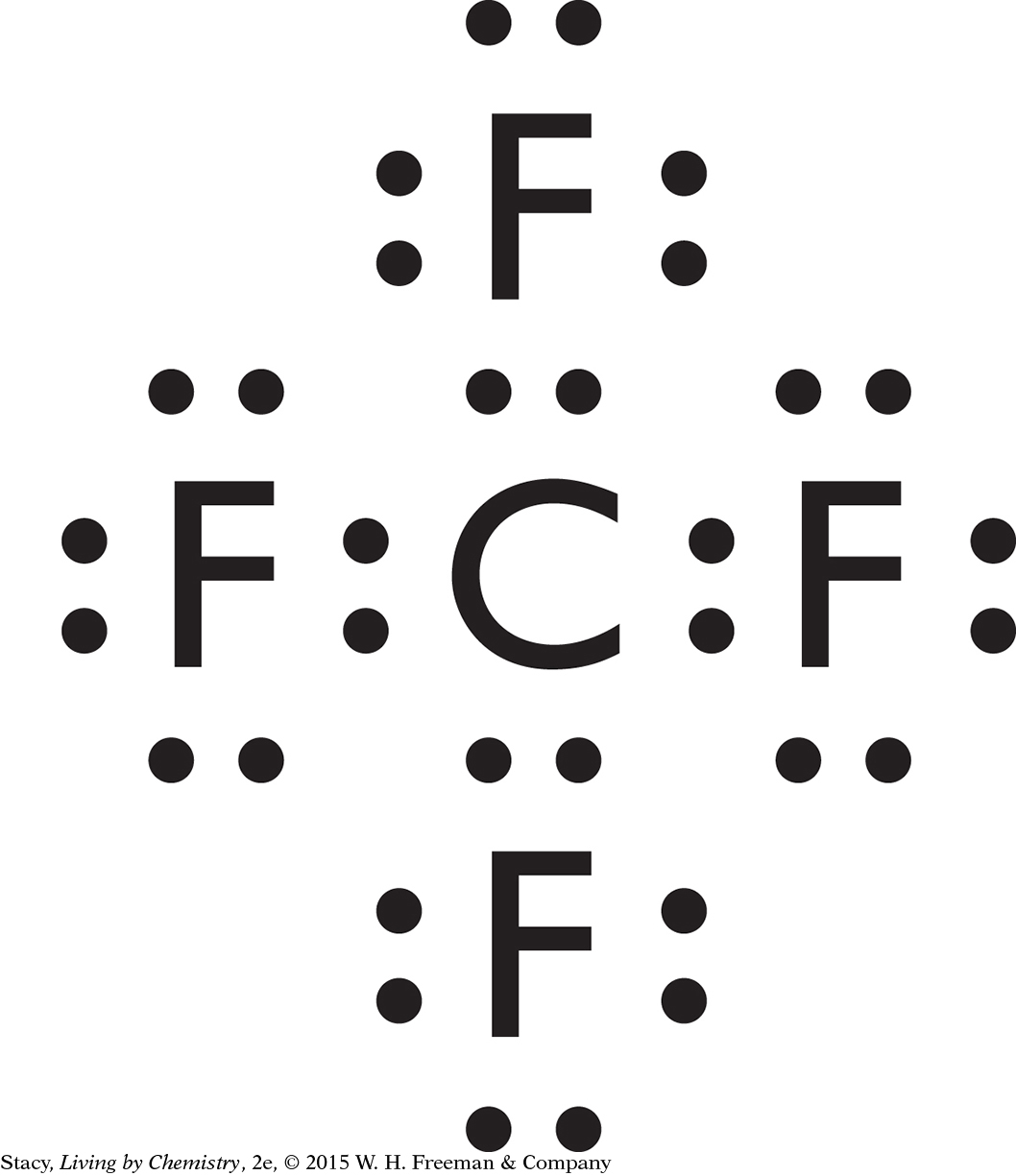
A tetrahedral shape has four single bonds spaced equally around one central atom.
Possible answer: CH4, SiCl4, CF4
AsH3 will have a pyramidal shape because the three bonded pairs and the one lone pair on the arsenic atom form a tetrahedron. Therefore, the three single bonds form a pyramid shape with the arsenic atom at its top.
Lesson 38
If a molecule has three electron domains, its shape will be trigonal planar.
Cl2 and CO2 are linear and H2O is bent.
A molecule with two atoms will be linear. A molecule with three atoms can be either linear or bent. A molecule with four atoms can be linear, bent, trigonal planar, or pyramid-shaped. A molecule with five atoms can be linear, bent, tetrahedral, or trigonal planar or pyramidal with the fifth molecule attached to one of the triangle’s or pyramid’s vertices.
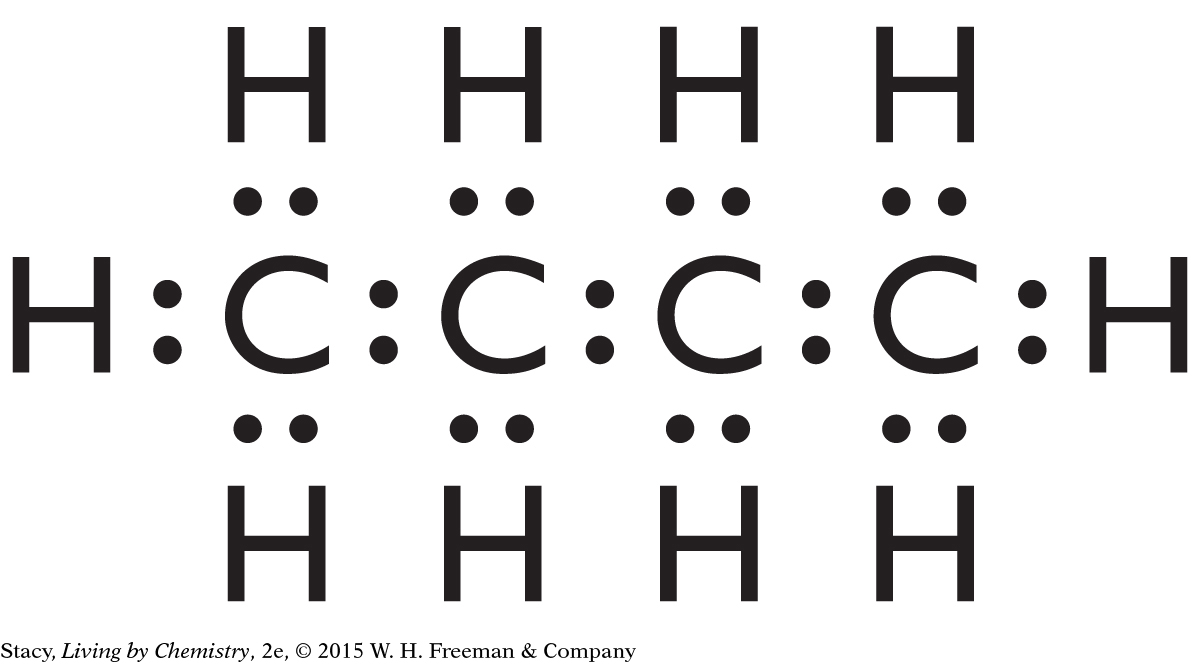
13
Possible answer: a crooked, zigzag shape
Each carbon atom is surrounded by four electron domains. Therefore, the shape of the molecule is a series of linked tetrahedra.
Lesson 39
A space-filling model is a more accurate model of how the atoms of the molecule are arranged in space. Space-filling models give a better picture of the shape of the molecule than ball-and-stick models.
Possible answer:
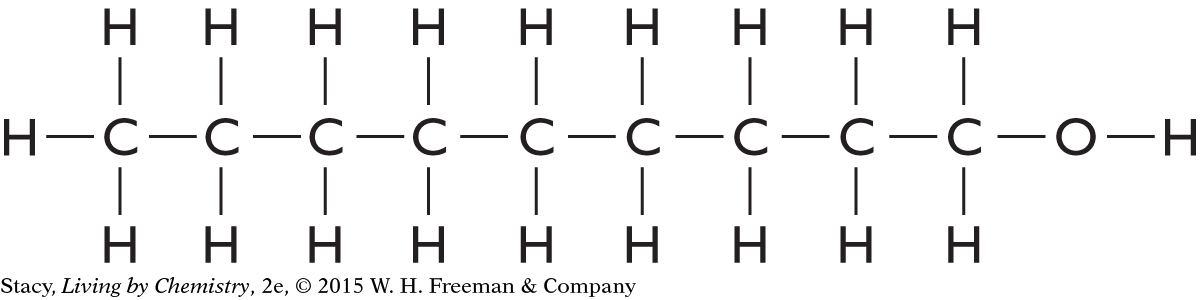
C9H20O is long and stringy, with a zigzag shape.
Possible answer:
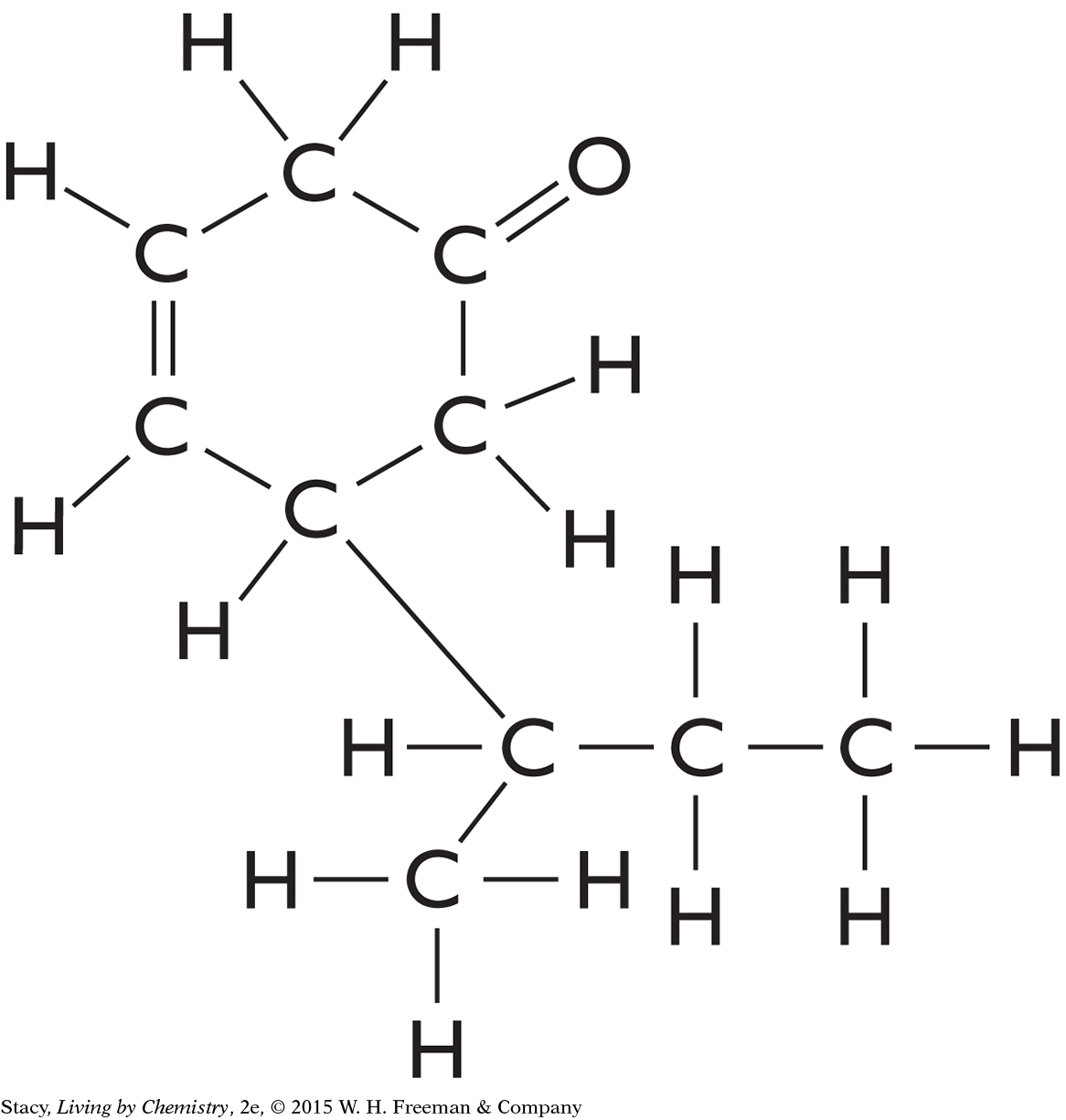
C10H16O has a ring-shaped structure of carbon atoms with a “handle.” The overall shape of the molecule resembles a frying pan.
Lesson 40
C-9
The molecular formula of a compound can provide some information about its smell but is not useful in most cases because it fails to give information about functional groups. For alkanes and amines, the chemical formula is a good indicator of smell.
Possible answer: The minimum information required to determine that a molecule smells sweet is the shape and the functional group or, if it is an ester, just the functional group.
Lesson 41
According to the receptor site theory, the nose is lined with sites that match the shapes of molecules that have smells. When a molecule fits into this site, it stimulates nerves to send a message to the brain. The brain interprets the message as a smell.
Possible answer: The compound would most likely have a minty smell. The nose detects the minty smell when the molecule shown fits into a receptor site in the nose that detects minty smells. In order for this to happen, some of the rub must change phase and become a gas.
Chapter 7 Review Exercises
C5H10O2
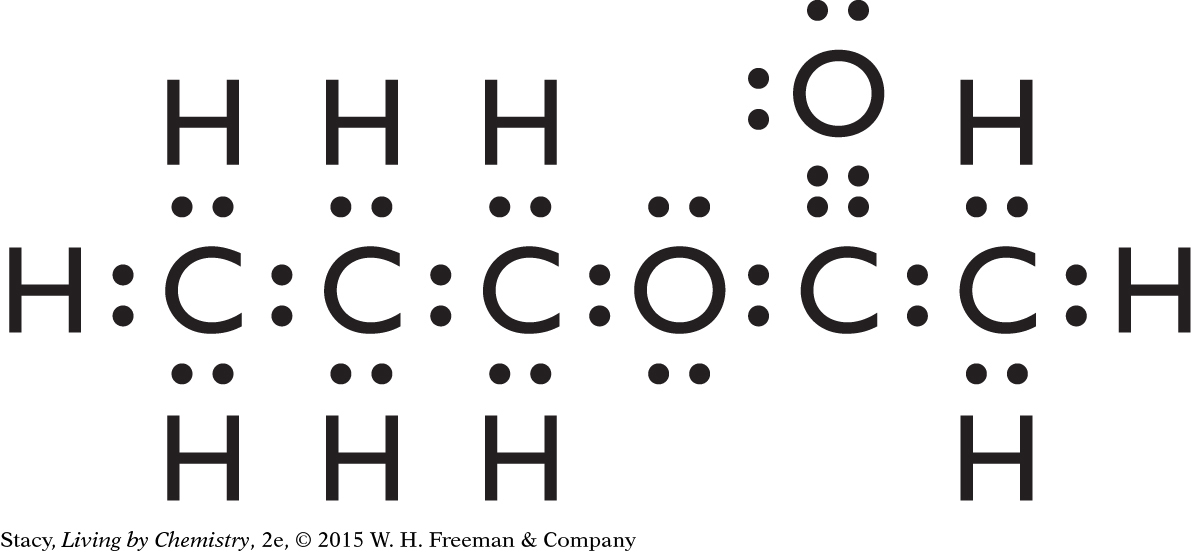
ester
The molecule probably has a sweet smell.
The shape of a molecule is determined by the number of electron domains around its atoms. The electron domains are all negatively charged, so they are positioned as far apart as possible.
Possible answer: Although the functional group appears to be a main factor that determines the smell of a molecule, its shape also affects the smell because it helps determine which receptors will be stimulated to send a signal to the brain.
Lesson 42
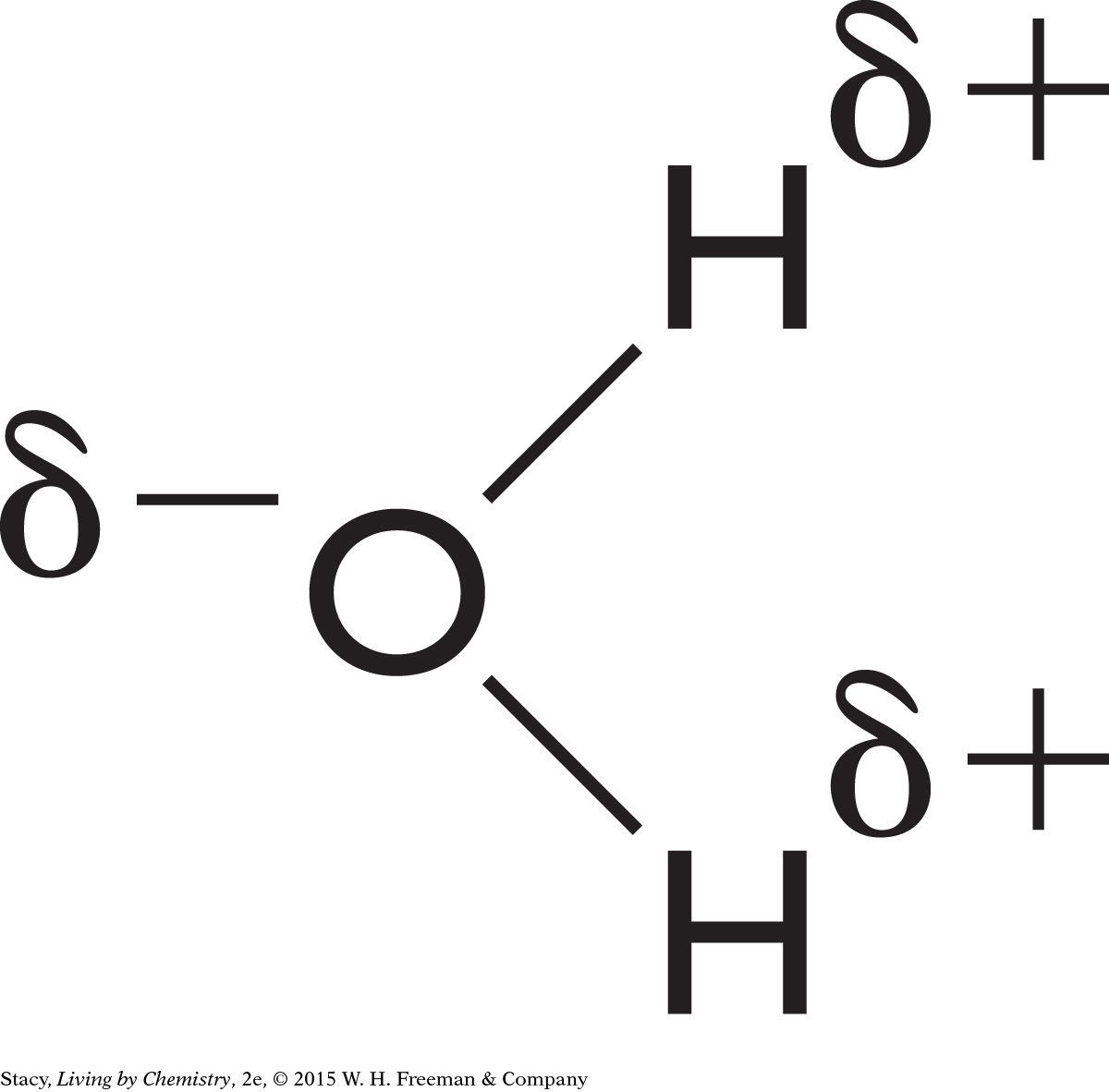
Possible answer: A polar molecule is a molecule in which the charge is not evenly distributed around the molecule. This means that different portions of the molecule will have partial electric charges.
Hexane would not be expected to dissolve in water because the information given indicates that it is a nonpolar compound. Compounds with nonpolar molecules do not tend to dissolve in water.
Lesson 43
Possible answer: In a polar covalent bond, the electron is attracted more by one atom than by the other, so one of the atoms has a partial negative charge and the other has a partial positive charge. In a nonpolar covalent bond, in which the two atoms share the electrons equally, there are no partial charges.
Although the two carbon-oxygen bonds of carbon dioxide are polar, the molecule itself has a linear shape, so the partial negative charges are on opposite sides of the molecule. These charges balance one another, so there is no dipole.
Lesson 44
Electronegativity values help determine the polarity of the bond between two atoms because they can be used to determine the tendency of an electron to be attracted to one atom rather than to another atom. The greater the difference in the electronegativities of the two atoms, the more polar the bond that forms between the atoms.
Li—F, Na—F, K—F, and Rb—F (same polarity), Cs—F; For an alkali metal bonding with fluorine, the polarity increases from the top of the group to the bottom.
P—S, N—F, Al—N, Mg—O, K—Cl; The polarity of the molecules increases as the distance between the atoms on the periodic table increases.
No, hydrogen will have a partial positive charge only when it is bonded to an atom that has a greater electronegativity. If the hydrogen atom is bonded to an atom with a smaller electronegativity, such as boron, then the hydrogen atom will have a partial negative charge. If a hydrogen atom is bonded with another hydrogen atom, the bond will be nonpolar.
Possible answer: O—F, 0.54; C—H, 0.45; S—F, 1.40
To say that bonding is on a continuum means that the type of bonding changes gradually as the difference in electronegativity between atoms increases. There is no sharp distinction between polar covalent and ionic bonds.
Lesson 45
To determine whether a molecule is polar, use a Lewis dot structure or structural diagram to figure out the shape of the molecule. Then look at whether the individual bonds are polar. If the molecule is asymmetrical and has polar bonds, then it will be a polar molecule.
C-10
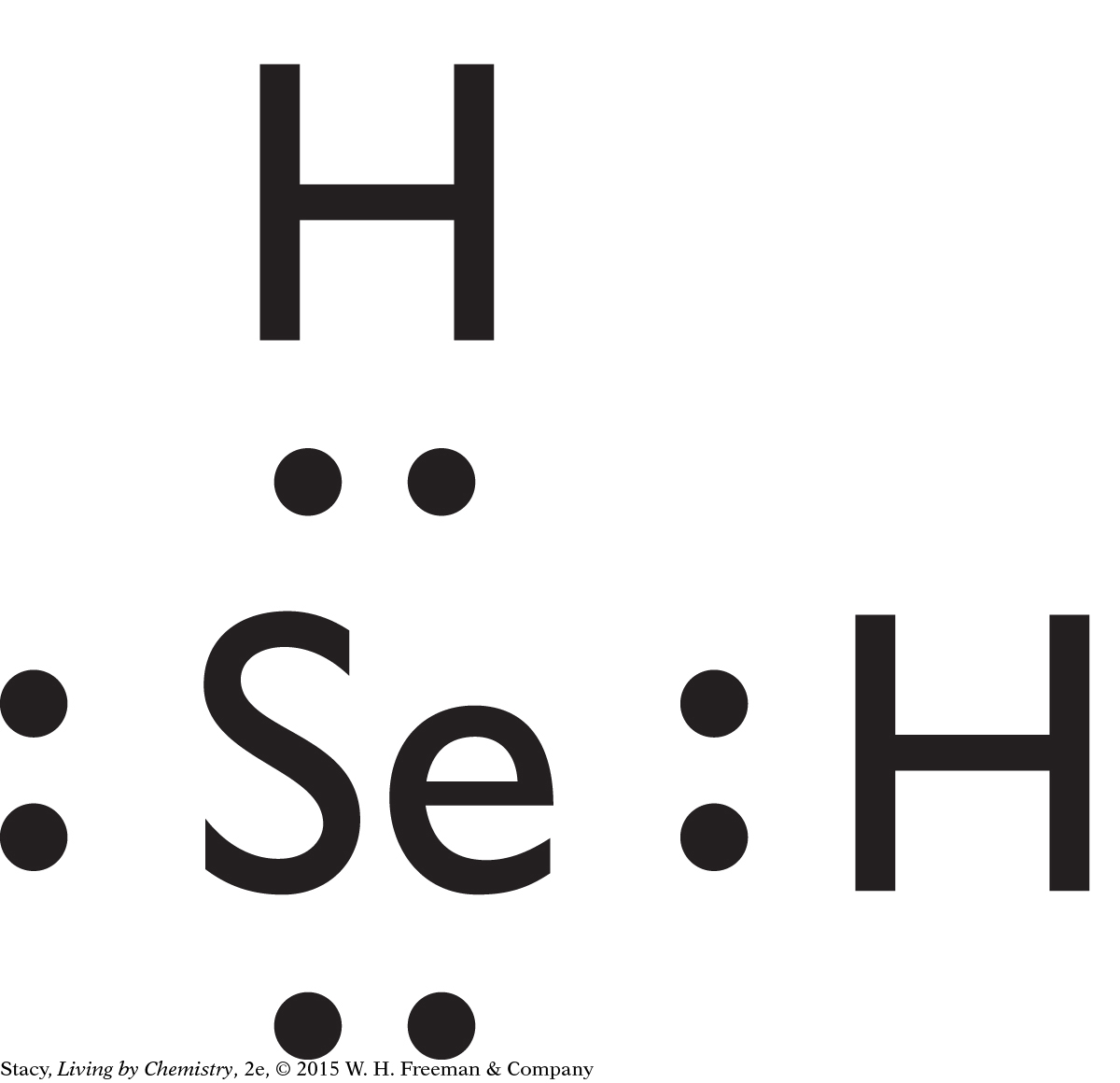
H2Se is a bent molecule. Because its bonds are polar and it is asymmetrical, it is likely to have a smell.

H2 is a linear molecule. Its bond is nonpolar. Because it is symmetrical and has a nonpolar bond, it is not likely to have a smell.

Because Ar consists of a single atom, it is not polar and is not likely to have a smell.
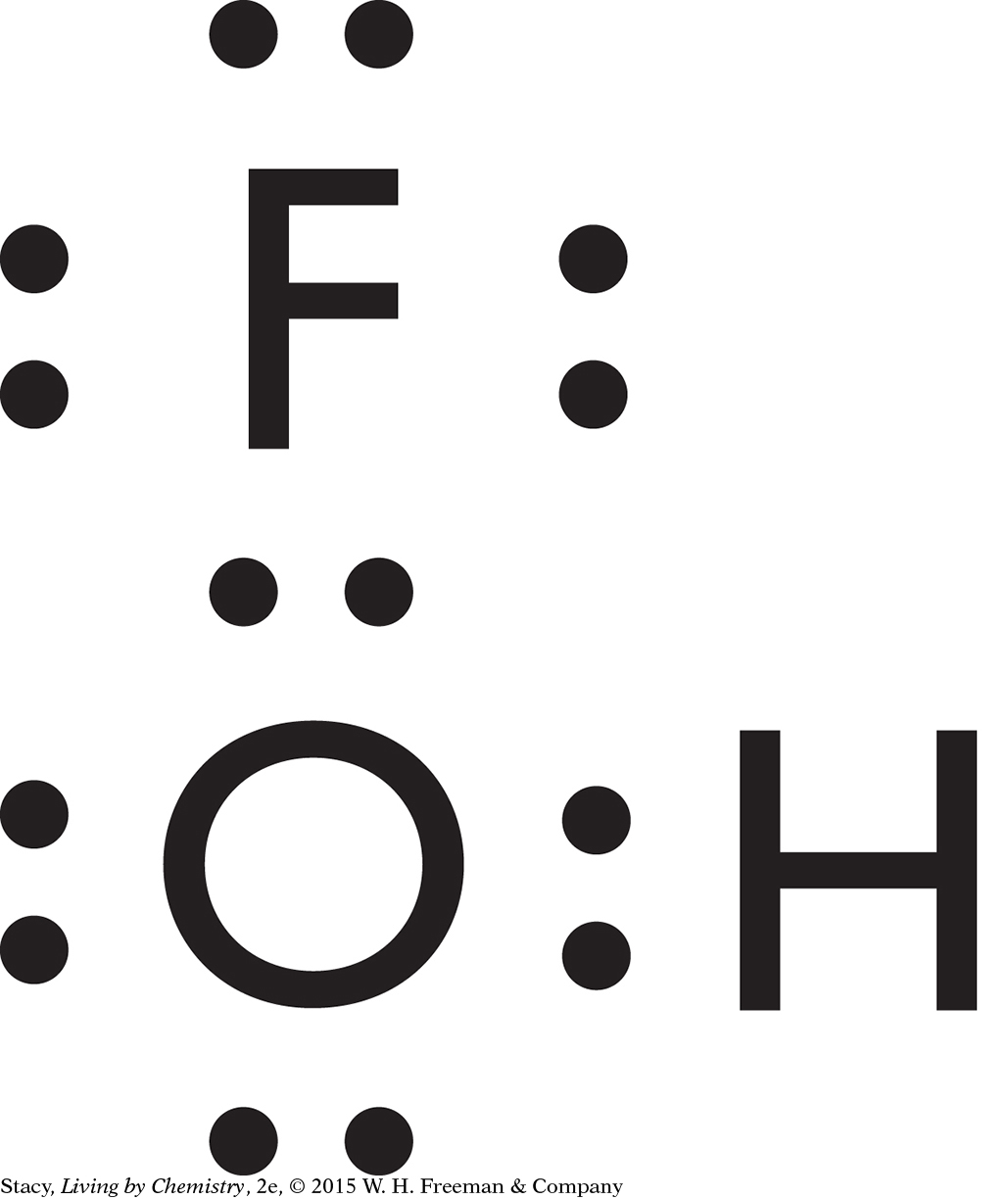
HOF is a bent molecule. Its bonds are polar and it is asymmetrical, so it is likely to have a smell.
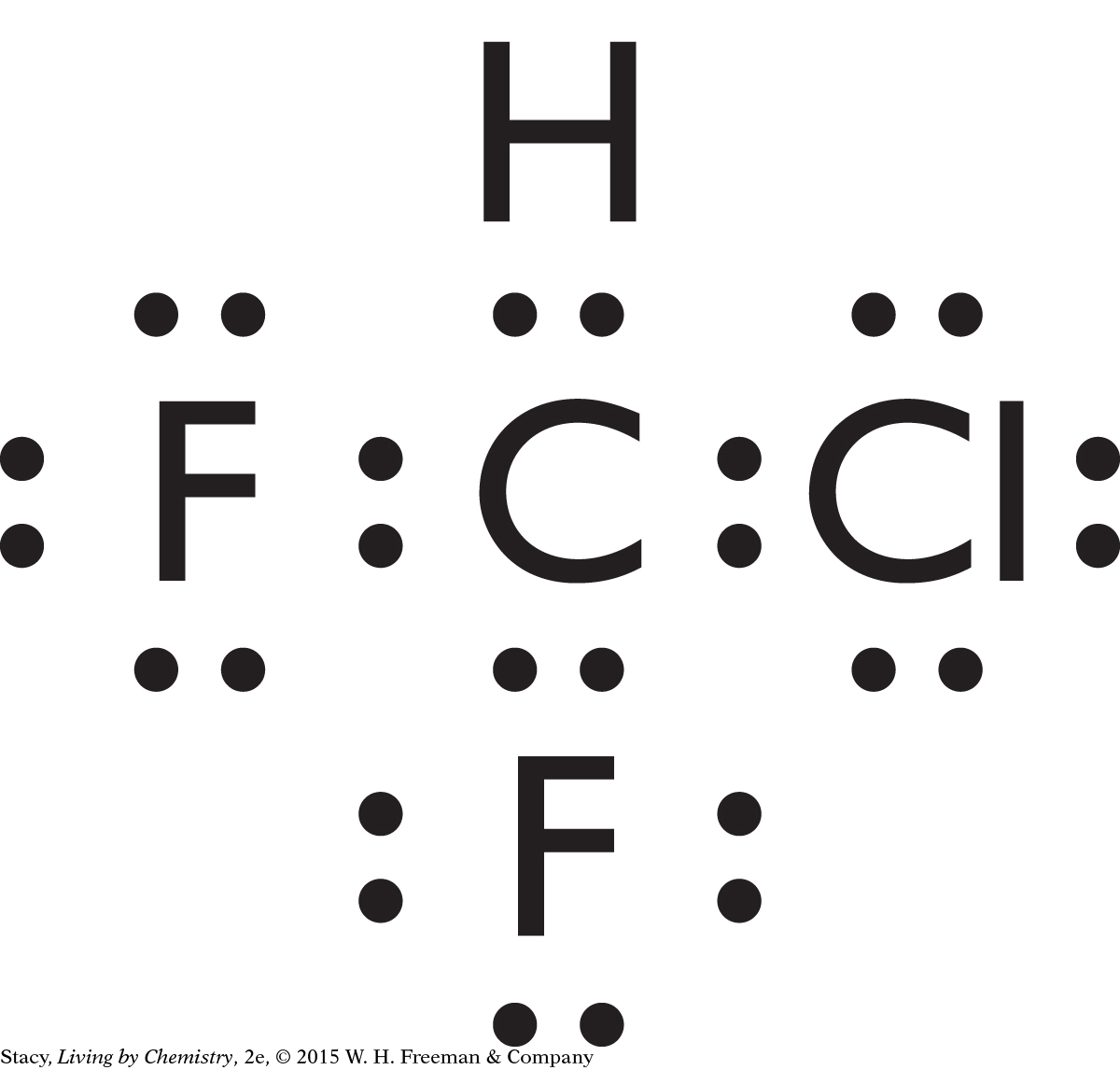
CHClF2 is a tetrahedral molecule and it has polar bonds. Its shape is symmetrical, but because the atoms at each point in the tetrahedron are different, the bonds are not symmetrical. It is likely to have a smell.
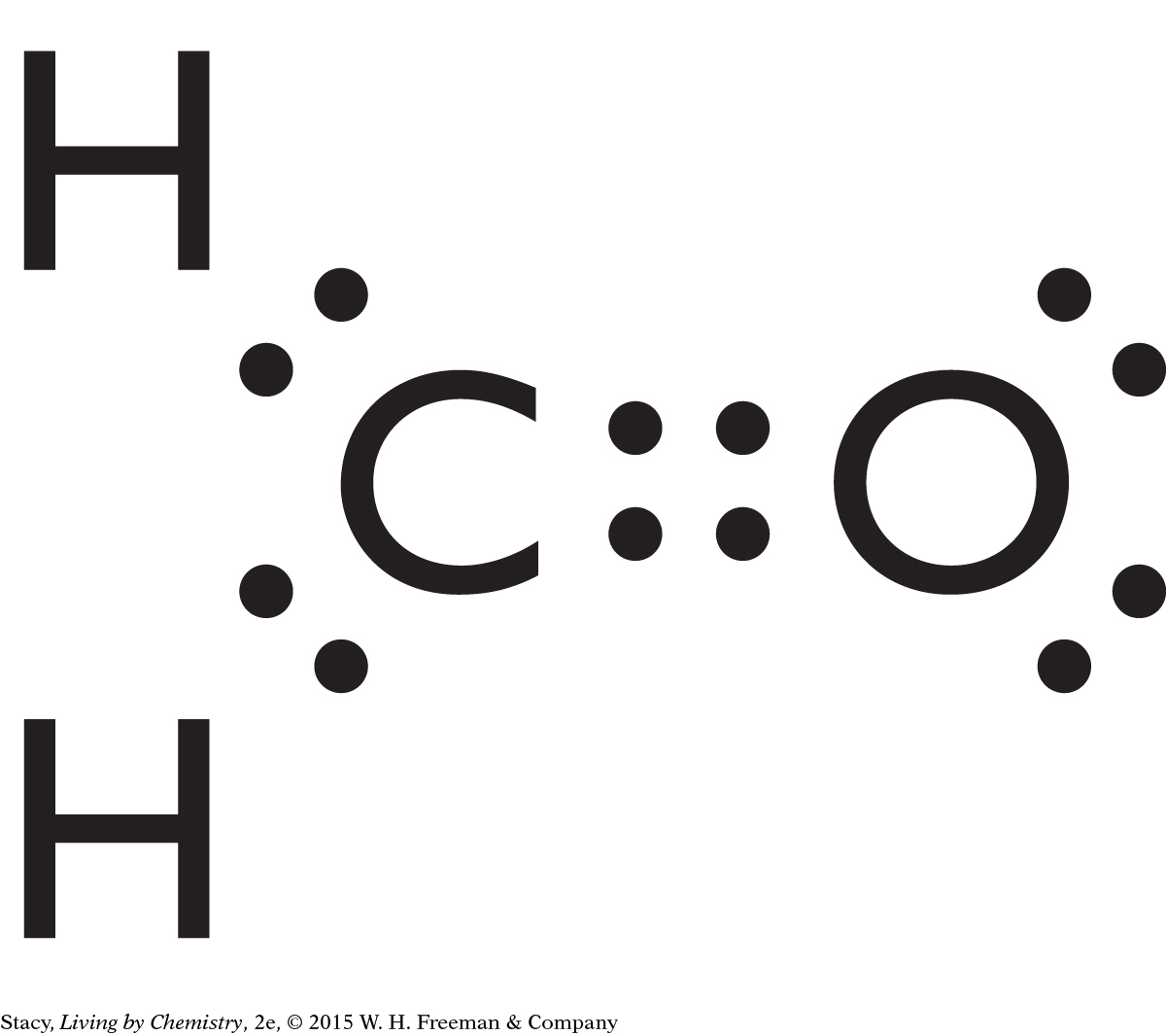
CH2O is a trigonal planar molecule. Its bonds are polar and it is asymmetrical, so it is likely to have a smell.
Possible answer: Water does not have a smell because there are no receptors in the nose that are sensitive to water molecules. If the nose had receptor sites that were sensitive to water, they would always be filled by the water in the mucous membrane.
Lesson 46
Decanol has a smell because it is a medium-sized molecular compound and because it is polar. Lead does not have a smell because it is a metal. Iron oxide does not have a smell because it is an ionic compound. Potassium chloride does not have a smell because it is an ionic compound.
Possible answer: If a substance can become a gas under normal conditions, you should be able to smell it as long as receptor sites in the nose can detect it. In general, small nonpolar molecules are odorless.
Possible answer: When the T-shirt comes out of the clothes dryer, it is so warm that molecules from the detergent and fabric softener are likely to have changed phase and become gases. When they reach your nose, you are able to smell them.
Chapter 8 Review Exercises
Br
Li
Au
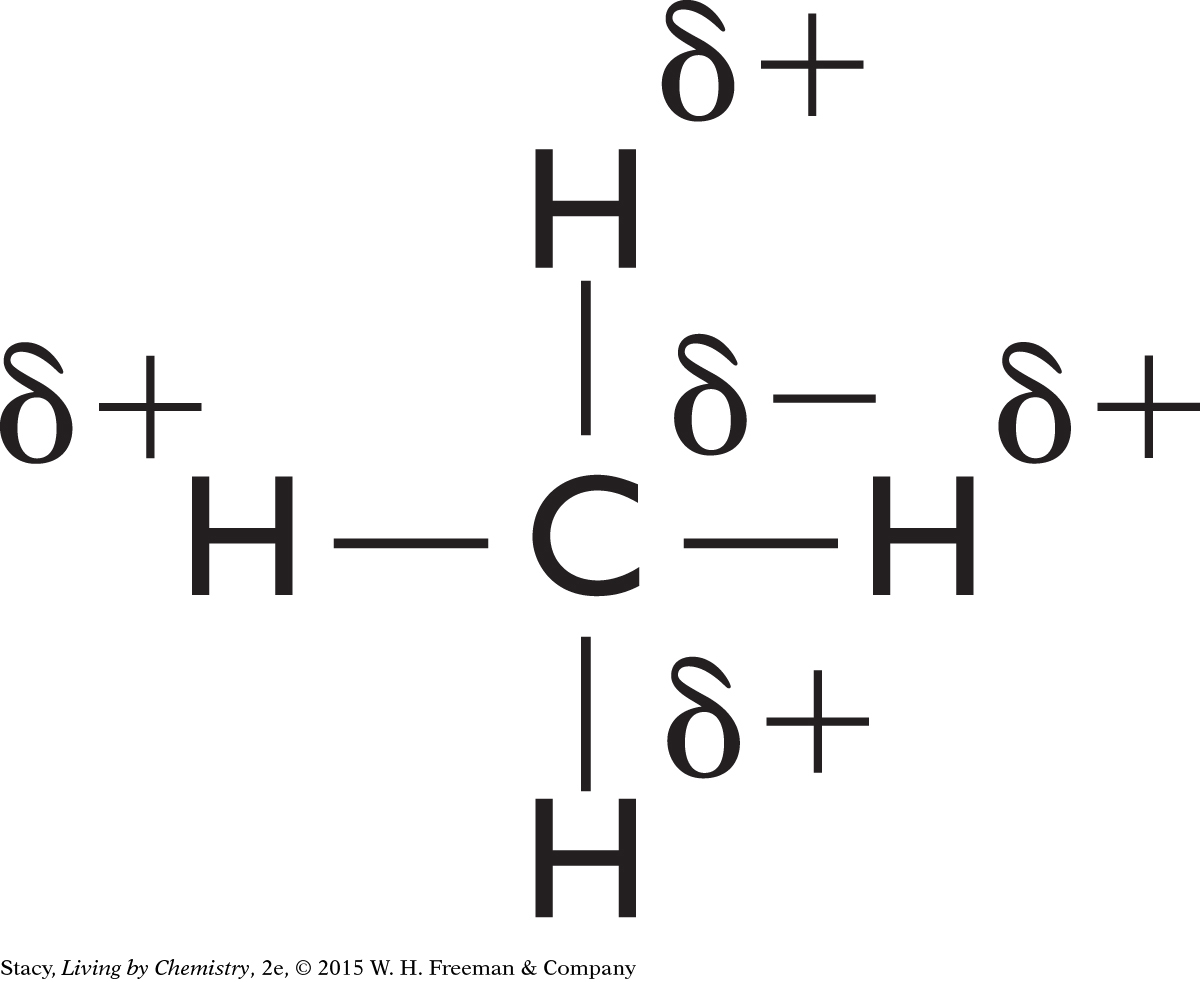
HCl and H2O are polar molecules because they are asymmetrical and have polar bonds. CH4 is not a polar molecule because its polar bonds are symmetrically arranged around the carbon atom.
Lesson 47
The mirror image of the letter “D” can be superimposed on the original as long as the mirror is placed horizontally with respect to the letter. Then the mirror image and the original image are identical.
Examples of objects that look different in a mirror include a glove, a written sentence, a pair of scissors. Examples of objects that look the same in a mirror include a spoon, an empty glass, and a pencil with no writing on it.
citronellol: C10H20O; geraniol: C10H18O
Citronellol has two distinct smells because the structural formulas have mirror-image isomers that interact with different receptors in the nose. Citronellol has mirror-image isomers because the third carbon atom from the right in the structural formula is bonded to four different groups.
The geraniol molecule has only one smell because the molecule and its mirror image are identical. None of the carbon atoms in the structure are bonded to four different groups.
Lesson 48
Amino acids are the building materials for many of the structures in the body, especially those related to the functioning of cells. An amino acid has a carbon backbone and two functional groups, an amine group and a carboxylic acid group.
Chapter 9 Review Exercises
C-11
Possible answer: Two molecular models represent mirror-image isomers if they are mirror images of each other and one cannot be rotated in space to be superimposed on top of the other. When the models have a carbon atom that is attached to four different groups, then they will be mirror-image isomers.
Possible answer: A molecule fits into its receptor site only when the receptor has the same “handedness” as the molecule. This is similar to the way that each of your feet will fit into only one shoe of a pair of shoes, even though the shoes are mirror images of one another.
Unit 2 Review Exercises
General Review
Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
A molecular formula provides the elements and number of atoms per element in a compound. A structural formula shows the way in which these atoms are bound to each other. A ball-and-stick model provides a three-dimensional image of the bonds. A space-filling model shows the actual amount of space each atom takes up, with atoms that are sharing electrons overlapped in space.
Yes
C8H8O3
The molecule has a flat section with the ester functional group attached to its side, similar to the shape of a frying pan.
The bond is bent because there are four electron domains. The oxygen atom has two bonded pairs and two lone pairs. The shape that separates the four domains as much as possible is tetrahedral, which causes the two bonds to be bent.
Standardized Test Preparation
D
B
D
C
C
C
C
D
B
B