Unit 5: Fire
Lesson 94
Possible answer: Energy is a measure of the ability to cause a change in matter.
Possible answer: Most of a fire is hot gases that become part of the atmosphere. Ashes are leftover material that was not converted to light and heat by a fire. The heat from the ashes transfers into the air and other materials around the site of the fire as it cools.
Lesson 95
Possible answer: Exothermic chemical changes are changes that transfer heat into the environment, and endothermic chemical changes are changes that absorb heat from the environment.
The average kinetic energy of the products is greater than the average kinetic energy of the reactants because the reaction is exothermic.
In a molecular view, the gas particles in the reactant would be moving more slowly than the particles in the products.
barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2 · 8H2O; ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3; ammonia, NH3; water, H2O; barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2
Possible answer: the beaker, the pool of water outside the beaker, air, my hand
The Ba(NO3) 2 is at a lower temperature than the NH4NO3 because the water freezing outside the beaker shows the temperature decreased after the reactants were mixed.
The beaker will feel cold.
The process is endothermic because the temperature decreases during the reaction. Energy was transferred from the surrounding environment into the reaction.
A chemical reaction must have occurred for a change in energy to occur. The reaction must have been the cause of the water outside the beaker turning into ice.
Lesson 96
The ice cube feels cold to your hand because heat is being transferred from your hand to the ice cube, which is at a lower temperature.
When a liquid evaporates energy is transferred to it, and when it solidifies it transfers energy to the surroundings.
Evaporation is the process of a liquid changing into a gas. It is a cooling process because the substance absorbs energy during the phase change, so that energy must be transferred from the surrounding environment. Objects and substances in the surroundings of the evaporating liquid are cooled.
Possible answer: When an object is warmer than its environment, the heat spreads into the environment. For example, a fire will eventually cause air in all parts of a room to feel warmer.
Yes, if the ice cube is warmer than the air around it or an object that is touching it, heat will transfer from the ice cube to its surroundings or into the other object.
Lesson 97
Because the larger sample has more particles, it takes more energy to increase the average kinetic energy of that sample by the same amount as the smaller sample.
5 cal
10 cal
315 cal
Lesson 98
Possible answer: The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of thermal energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 g of the substance by 1 ºC. For example, the specific heat capacity of aluminum is 0.21 cal/g ºC, which means that 0.21 cal of thermal energy is needed to increase the temperature of 1 g of aluminum by 1 ºC.
Possible answer: Because metals have a lower specific heat capacity than plastic, they experience a greater change in temperature when they absorb a specific amount of energy from sunlight. Plastics are composed of large molecules that require more energy to cause a rise in temperature than a metal does.
The copper will cool faster because it has a lower specific heat capacity. Copper does not need to transfer as much thermal energy as aluminum does to cool to the temperature of the water.
Lesson 99
C-19
Water temperature doesn’t change during boiling because the energy added to the water doesn’t increase the kinetic energy of molecules.
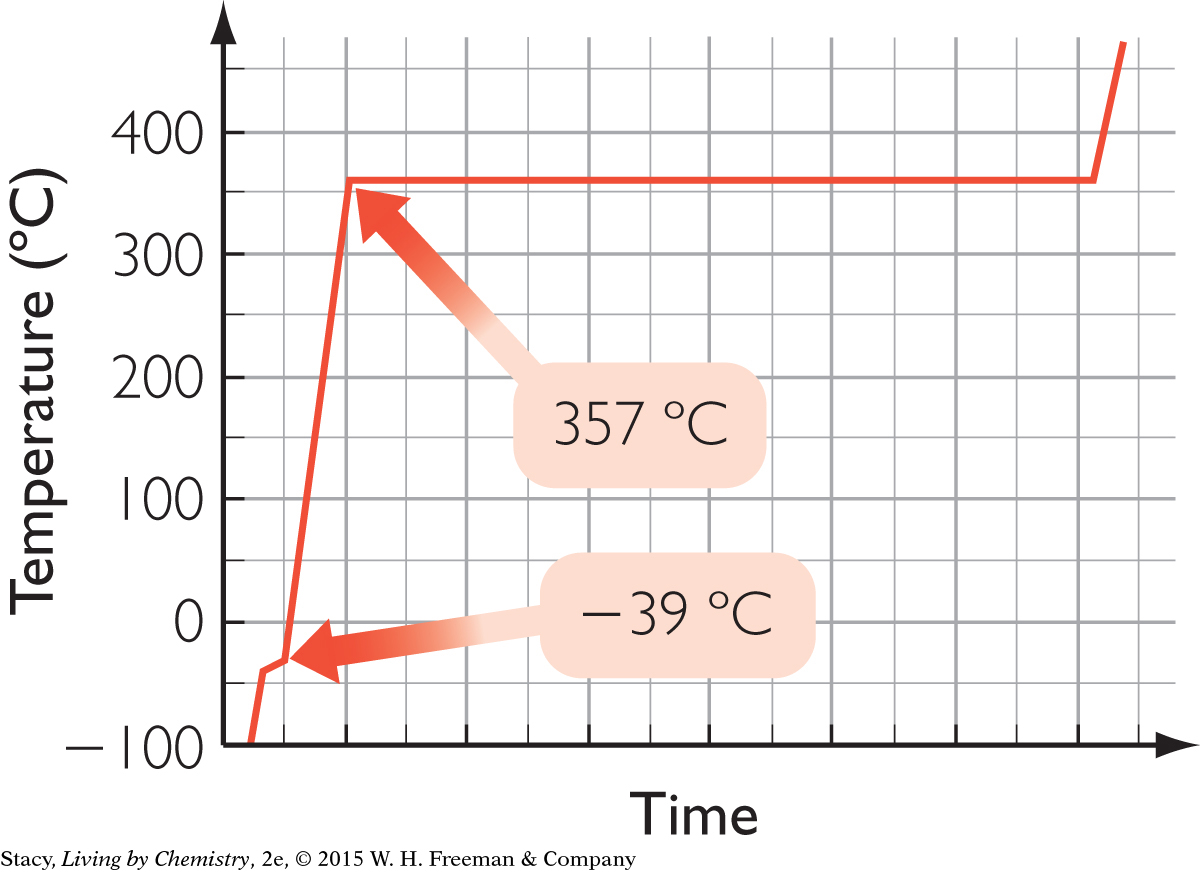
B.
24.4 g
Chapter 18 Review Exercises
methanol (460 cal), water (500 cal), copper (900 cal)
57 ºC
Lesson 100
If a compound is ionic, or a substance contains water or carbon dioxide, it is unlikely to combust.
Na2SO4 will not combust because it is an ionic compound.
Cu will combust because it is a metallic element.
MgO will not combust because it is an ionic compound.
Na will combust because it is a metallic element.
C2H6O will combust because it is a molecular substance containing carbon and hydrogen.
Ar will not combust because it is a noble gas.
Lesson 101
Possible answer: Calories are a measure of heat. The heat that is produced by the reaction of the substance with oxygen during combustion can be measured in calories.
No, placing a thermometer in the flames measures the temperature of the combustion reaction, but it cannot measure the total heat energy given off by the reaction.
Lesson 102
150 cal
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of water in the beakers. It takes more energy to increase the temperature of the third beaker because there are many more particles of water, making the amount of thermal energy needed to increase the temperature greater even though there is less temperature change.
Lesson 103
Heat of combustion is expressed as a negative number because energy transfers out of the system and into the environment.
Chapter 19 Review Exercises
Possible answer: The reaction does not appear to release light and heat because it occurs slowly, so the energy is lost to the environment without being noticed.
Lesson 104
O–O, C–C, H–H, O=O, C=C
3237 kJ
methanol: –660 kJ/mol; butanol: –2509 kJ/mol
The calculated values are slightly higher (slightly less negative) than the values given in the table.
Lesson 105
During an exothermic reaction, the potential energy of the system decreases and the kinetic energy of the system increases. Some of the potential energy in the system is converted into kinetic energy.
2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g)
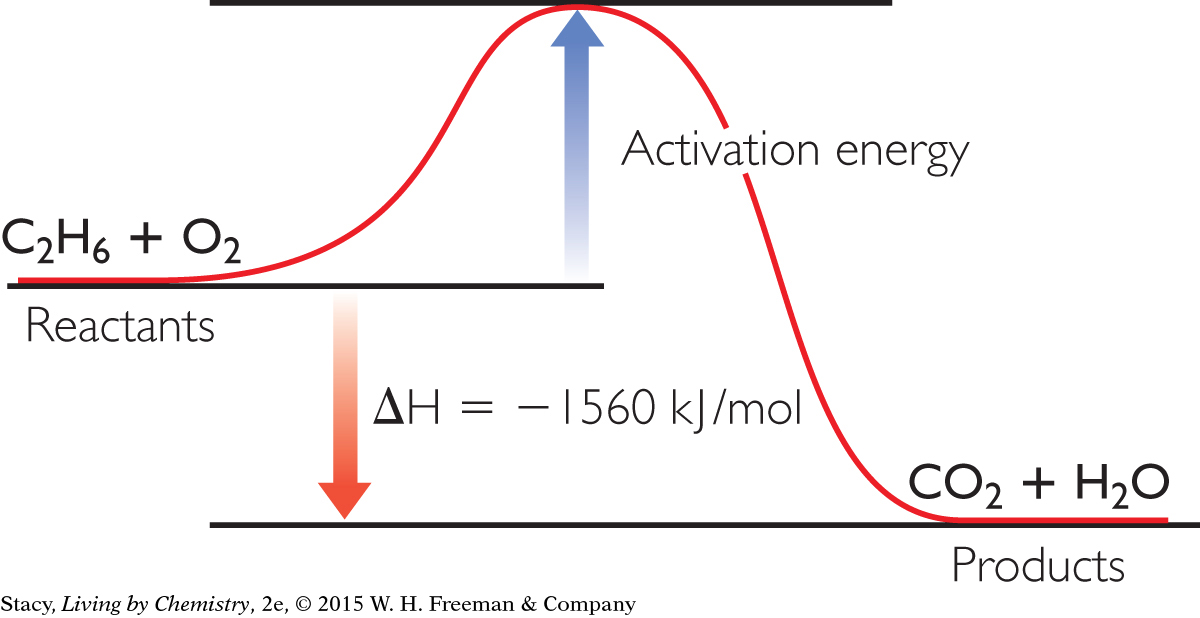
The net energy exchange of the reverse reaction is 1560 kJ/mol. Conservation of energy requires that the amount of energy used to make ethane and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water is equal to the amount of energy released when ethane and oxygen are converted into carbon dioxide and water.
C-20
a. and b.
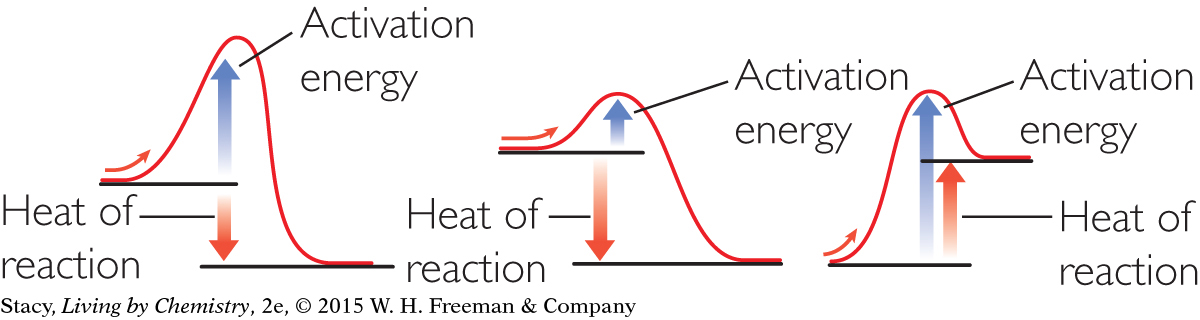
c. the second diagram
d. All of the reactions require energy to get started.
Lesson 106
Wood chips will burn faster because they have a much greater surface area than a tree, allowing the molecules in the wood chips more contact with the oxygen in the air.
The powdered iron oxidizes faster than the steel beam because the small particles have much more total surface area than the beam. Because a greater percentage of the iron is exposed to the oxygen in the air, the reaction is faster.
During an explosion, a large amount of energy is released very quickly from chemical bonds in molecules. This energy acts as activation energy to other molecules and causes the explosion to occur rapidly.
Lesson 107
Work is the result of a force acting through a distance. It is a transfer of energy, like heat.
14 atm · L
Chapter 20 Review Exercises
Paige’s answer is correct. The water will evaporate before any hydrogen-oxygen bonds are broken.
Lesson 108
2Ca(s) + O2(g) → 2CaO(s); Ca2+, O2–
4Cr(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Cr2O3(s); Cr3+, O2–
4Li(s) + O2(g) → 2Li2O(s); Li+, O2–
Calcium, Ca, is oxidized. Chromium, Cr, is oxidized. Lithium, Li, is oxidized.
Lesson 109
Possible answer: The oxidation reactions are better sources of energy than the reverse reactions because they are almost always exothermic. The metals that are the hardest to extract have the lowest (most negative) heats of formation, which means that they release the most energy into the environment. The oxidation of aluminum is the best source of energy listed in the lesson.
2180 kJ
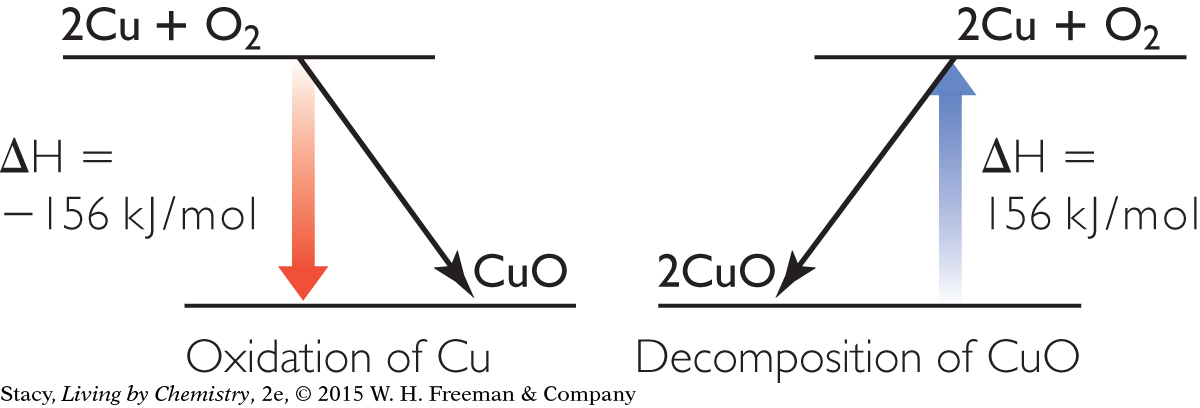
24.5 kJ
Lesson 110
In this reaction, copper is oxidized because the neutral copper atom loses the electrons and becomes a positively charged copper ion. The oxygen atom is reduced because it gains electrons and becomes a negatively charged oxygen ion.
Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Cu(s) + Zn2+(aq)
Ba2+(aq) + SO42–(aq) → BaSO4(s)
a. not a redox reaction b. not a redox reaction c. not a redox reaction d. not a redox reaction e. redox reaction, lead is oxidized and hydrogen is reduced, 2 electrons are transferred f. redox reaction, arsenic is oxidized and hydrogen is reduced, 6 electrons are transferred
Lesson 111
No change would be observed because iron is less active than zinc. Therefore, iron cannot be oxidized by the zinc nitrate solution and the iron strip would not be affected.
No reaction occurs in Exercise 3. The chemical equation for the reaction in Exercise 4 is 2Fe(NO3)2(aq) + 3Zn(s) → 2Fe(s) + 3Zn(NO3)2(aq)
2Fe3+(aq) + 3Zn(s) → 2Fe(s) + 3Zn2+(aq)
zinc
Zinc is oxidized, and iron is reduced.
Cobalt is below iron in the activity series because the iron is oxidized by the cobalt ions, making iron the more active metal.
Lesson 112
In an electrochemical cell, electrons are transferred from the more active metal to the less active metal.
Ca → Ca2+ + 2e–
Fe → Fe3+ + 3e–
Calcium is oxidized and iron is reduced.
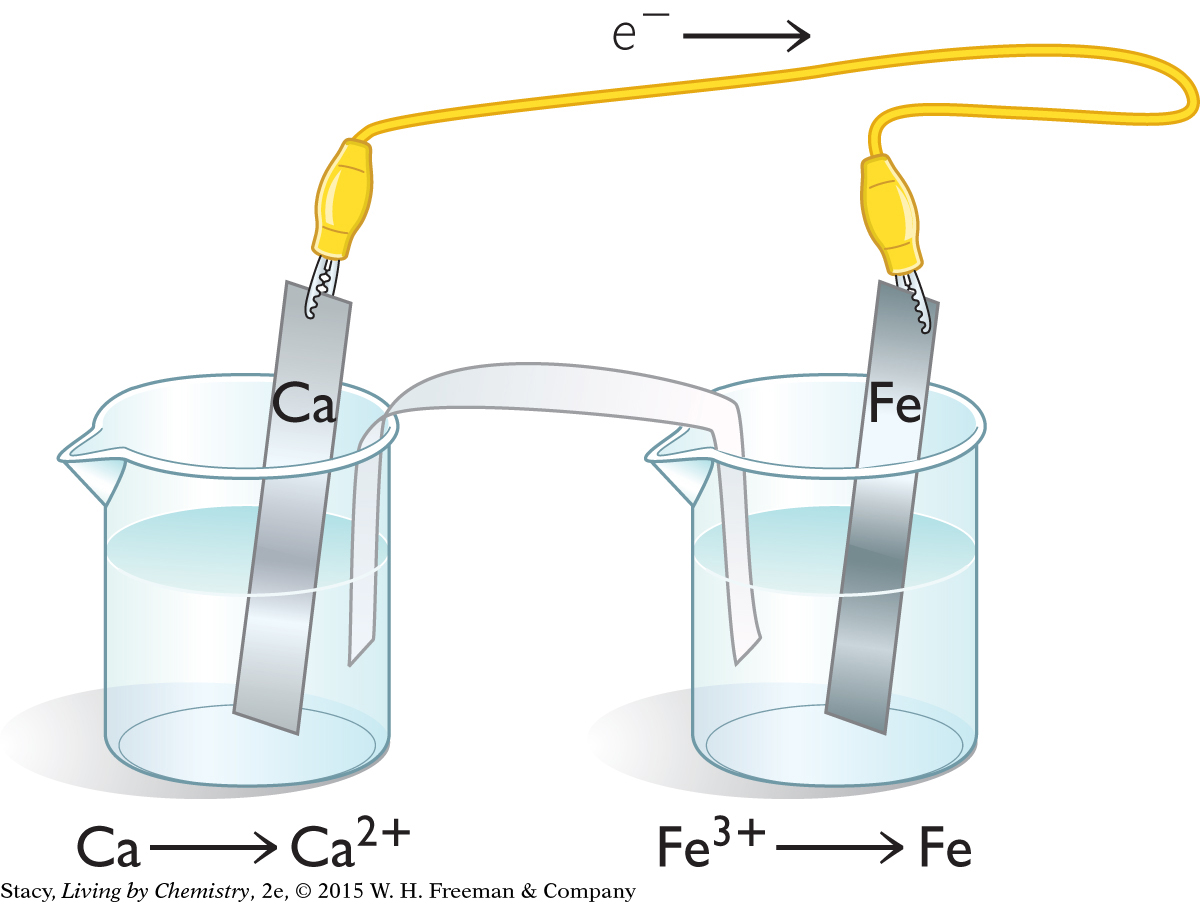
Ca(s) + Fe3+(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + Fe(s)
Chapter 21 Review Exercises
21
Possible answer: An electrochemical cell works by separating the two parts of a redox reaction. As electrons are transferred from one metal to the other, they travel through a wire connecting the two half-reactions. The electrical energy is the stream of moving electrons. The chemical energy is the voltage potential of the redox reaction.
In the extraction of metals from metal oxides table, the heat of reaction of iron (III) oxide decomposing into pure iron and oxygen gas is listed as –413 kJ/mol. Because this value is positive, the reaction is endothermic. Energy must be continuously added into the system for the reaction to occur.
Lesson 113
Light shining on matter raises its temperature.
Blue
Green
Orange, glasses transmit orange light, so an orange object would look orange.
Black, because blue light would not be transmitted.
Lesson 114
λ = c/f; you need to know the frequency of the light, f, and the speed of light, c
5.9 × 1014 Hz
Green
Lesson 115
E = hf; energy and frequency are proportional to one another
Possible answer: an insect
2 × 10–13 J
Lesson 116
A chemical reaction happens.
It remains green. No reaction occurs.
The sunglasses with UV protection will block UV light such that the UV-sensitive paper remains green. The regular reading glasses will transmit more UV light, thereby exposing the UV-sensitive paper and turning it blue.
Chapter 22 Review Exercises
Colored objects reflect the color we see and absorb other colors.
2.5 × 102 m
4.1 × 1014 Hz
Unit 5 Review Exercises
General Review
The thermal energy of an exothermic reaction is the result of bond making releasing more energy than is required for bond breaking for the reaction.
3800 cal
–7500 cal
More energy is required to raise the temperature of water than to raise the temperature of aluminum by the same amount because water has a higher specific heat capacity than aluminum.
Zn(s) + 2Mn4+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2Mn3+(aq) Zinc loses electrons, so it is oxidized. Magnesium gains electrons, so magnesium ions are reduced. 2Al(s) + 3Ca2+(aq) → 2Al3+(aq) + 3Ca(s) Aluminum loses electrons, so it is oxidized. Calcium gains electrons, so calcium ions are reduced.
Standardized Test Preparation
| 1. D | 3. A | 5. B |
| 7. A | 9. B | 11. B |
| 13. C | 15. C | 17. D |
| 19. D | 21. C |