Unit 6: Showtime
C-21
Lesson 117
Both HIn (red) and In− (blue) are present.
H+ + In– → HIn
Lesson 118
Possible answer: evaporation and condensation of water
freezing and melting, evaporation and condensing
C12H22O11(s) ⇌ C12H22O11(aq)
Forward
reverse
Lesson 119
C-22
Dynamic equilibrium means that the rate of a forward process and the rate of its reverse process are equal.
Artificial sweetener is sweeter than the same amount of sucrose. Answer: Many more artificial sweetener molecules bind to the sweet receptors than do the same number of sucrose molecules. So AB is more favored for the artificial sweetener compared with sucrose.
Much more sodium chloride, NaCl, dissolves in 1 L of water compared with silver chloride, AgCl. Answer: More products form for NaCl, whereas AgCl remains mostly as the starting substance. So AB is more favored for AgCl compared with NaCl.
Lesson 120
A large value of K indicates that there are more products in the equilibrium mixture, while a small value of K indicates that more starting substance is present.
The binding of CO to hemoglobin has the larger equilibrium constant because [hemoglobin:CO] is greater than [hemoglobin:O2].
Each particle view should show a hemoglobin binding to a particle. The view with oxygen should have more free oxygen and hemoglobin particles than the view for carbon monoxide.
CO is toxic because it takes up binding sites in hemoglobin so that they are not available to oxygen. Because the [hemoglobin:CO] product is favored, fewer free hemoglobin molecules are available to bind oxygen.
Lesson 121
You can rearrange the equilibrium constant equation to solve for hydrogen ion concentration. Once you have the hydrogen ion concentration, you can solve for

Solution 1: 1.4 × 10–3, Solution 2: 1.8 × 10–4, Solution 3: 1.8 × 10–5, Solution 4: 1.8 × 10–5
Chapter 23 Review Exercises
HCl(aq) → H+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
The particle view should show 10 H+ and 10 Cl– ions and no HCl molecules.
HF(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + F–(aq)
The particle view should show mostly HF molecules as well as a few H+ and F– ions.
K = [C][D]/[A][B]
K = [CO][Cl2]/[COCl2]
K = [Pb2+][Cl–]2
Lesson 122
Add more of one of the products. Remove some of the starting substance.
More Cu(NH3)62+(aq) forms to reduce the concentration of NH3.
Since this is an endothermic process, heating favors products. Therefore more products will form to relieve the stress.
Lesson 123
Indicator molecules have a bright color that changes to a different color when the HIn molecules dissociate into H+ and In–. When the solution is more acidic, the color of HIn molecules is observed. In basic solution, the solution displays the color of In–.
In order of increasing solubility, AgCl, CuCl, TlCl, the most soluble is TlCl. A small Ksp indicates mostly undissolved solid.
CuCl(s) will precipitate.
yellow, due to the large amount of HIn
blue, due to the large amount of In–
yellow, due to large amount of In–
orange, due to presence of both HIn and In–
pH ~ 10
Chapter 24 Review Exercises
No more solid will dissolve. Excess solid remains. In a saturated solution, no more solid can be dissolved. Excess solid will remain at the bottom of the container.
More CaCl2 precipitates.
More CaCl2 precipitates.
More CaCl2 precipitates.
More CaCl2 dissolves.
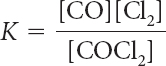
8.6 × 10–2 M
More COCl2 forms to minimize the effect of adding one of the products.
0.14 M
Unit 6 Review Exercises
General Review
Cl2(g) ⇌ Cl2(l)
2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g)
Ag+(aq) + Cl–(aq) ⇌ AgCl(s)
H2O(l) ⇍ H2O(g)
Possible answers: The reaction is reversible. The equilibrium constant does not change as the concentrations of products and reactants change.
1.2 × 10–5 M
Standardized Test Preparation
| 1. C | 3. B | 5. C |
| 7. A | 9. D | 11. B |
| 13. A | 15. A | 17. A |
| 19. B |