LESSON 49: Weather or Not: Weather Science
259
THINK ABOUT IT
You have probably seen a weather forecast, either on television or in the newspapers. You may have wondered—what are highs and lows? What are fronts? What does the jet stream have to do with the weather?
What causes the weather?
To begin to answer this question, you will explore
Earth, Air, Water, and Sun
Weather Maps
Earth, Air, Water, and Sun
EXPLORING THE TOPIC
Earth, Air, Water, and Sun

© Dex Image/Corbis
|

© 68/GK Hart/Vikki Hart/Ocean/Corbis
|
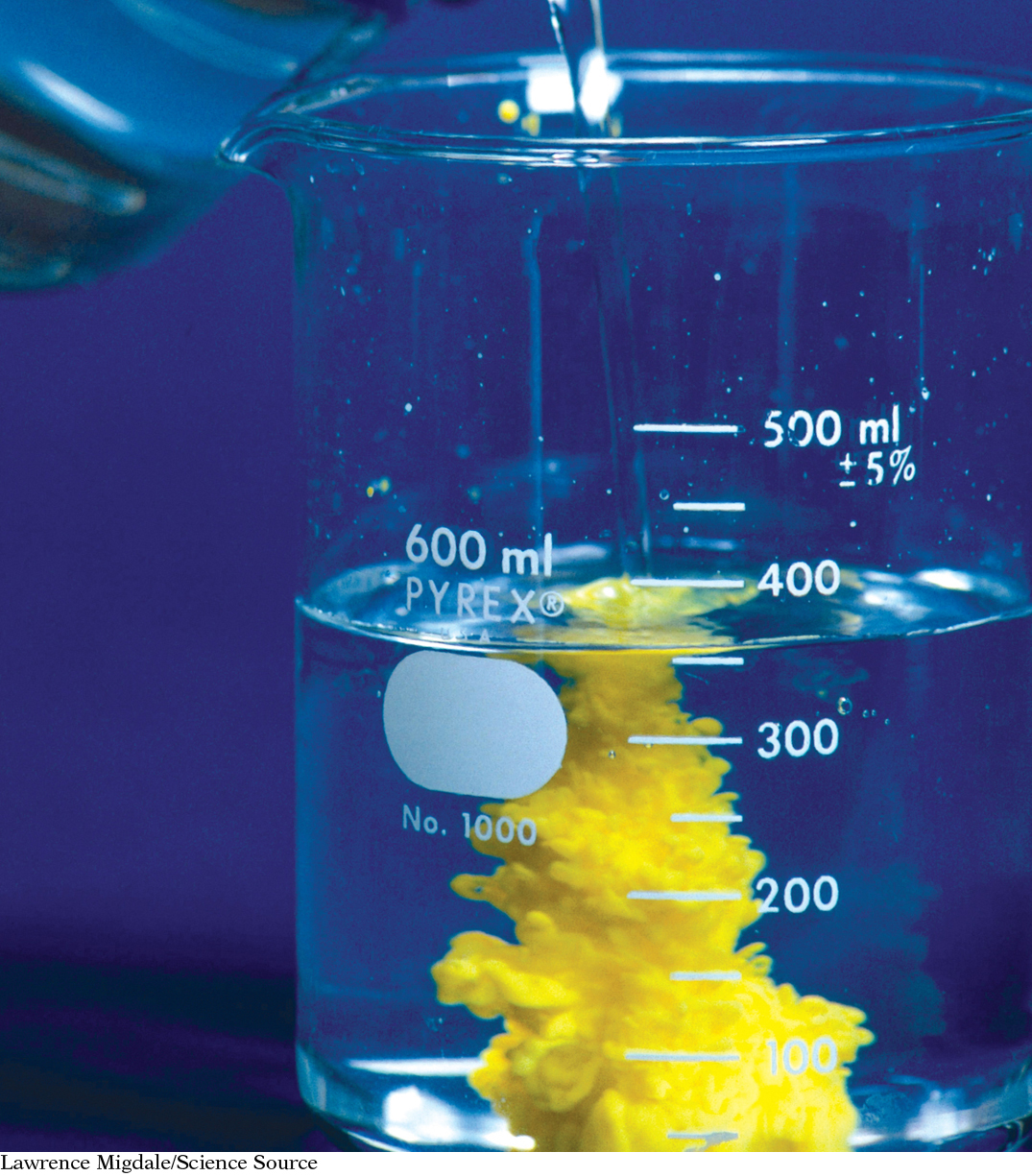
Heating and reshaping a substance are both physical changes. Mixing chemicals to form a new compound is a chemical change.
Lawrence Migdale/Science Source
|

This lesson launches an investigation into the connection between chemistry and weather. Weather refers to clouds, winds, temperature, and precipitation in a region at any given time. It differs from climate, which describes the overall weather trends of a region over long periods of time. Weather is caused by the interaction of Earth, the atmosphere, water, and the Sun. It is about the movement of matter.
A planet must have an atmosphere to have weather. An atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the planet. In contrast, the Moon has no weather because it barely has any atmosphere. The atmosphere on Earth is often referred to as air. Air is composed of a mixture of gases. Earth’s atmosphere consists of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (1%), carbon dioxide (0.04%), and traces of other gases. There is some water vapor, H2O(g), in the atmosphere, but the amount varies from place to place, from day to day, and even from hour to hour. On average, it makes up about 1% of the atmosphere.
The weather we experience is caused by physical changes in the atmosphere. Physical changes alter the form a substance takes but do not change the identity of the substance. Examples of physical changes are changes in volume, temperature, shape, size, and pressure. These are different from chemical changes, which produce new substances. The heating of Earth by the Sun is the root cause of most of the physical changes in Earth’s atmosphere.
260
The phase changes of water between solid, liquid, and gas are types of physical changes that play an important role in weather. For example, rain is evidence that a phase change from gas to liquid has taken place.
Big Idea
Big Idea
Weather is the result of physical changes to matter.
Weather Maps
Weather Maps
Meteorologists use maps to keep track of atmospheric conditions and to predict the weather. Weather information for a specific day is shown on the maps here. What patterns do you observe as you compare the six maps?
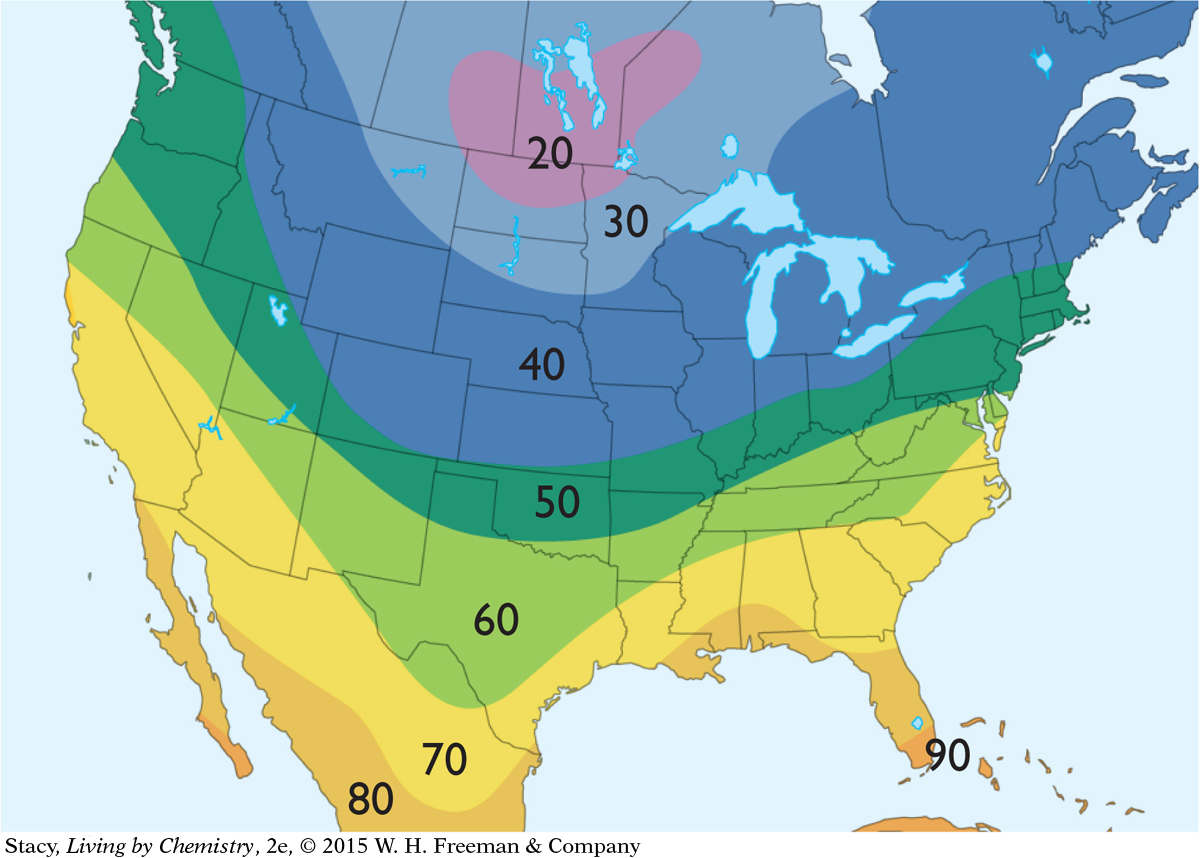
Temperature highs in degrees Fahrenheit
|
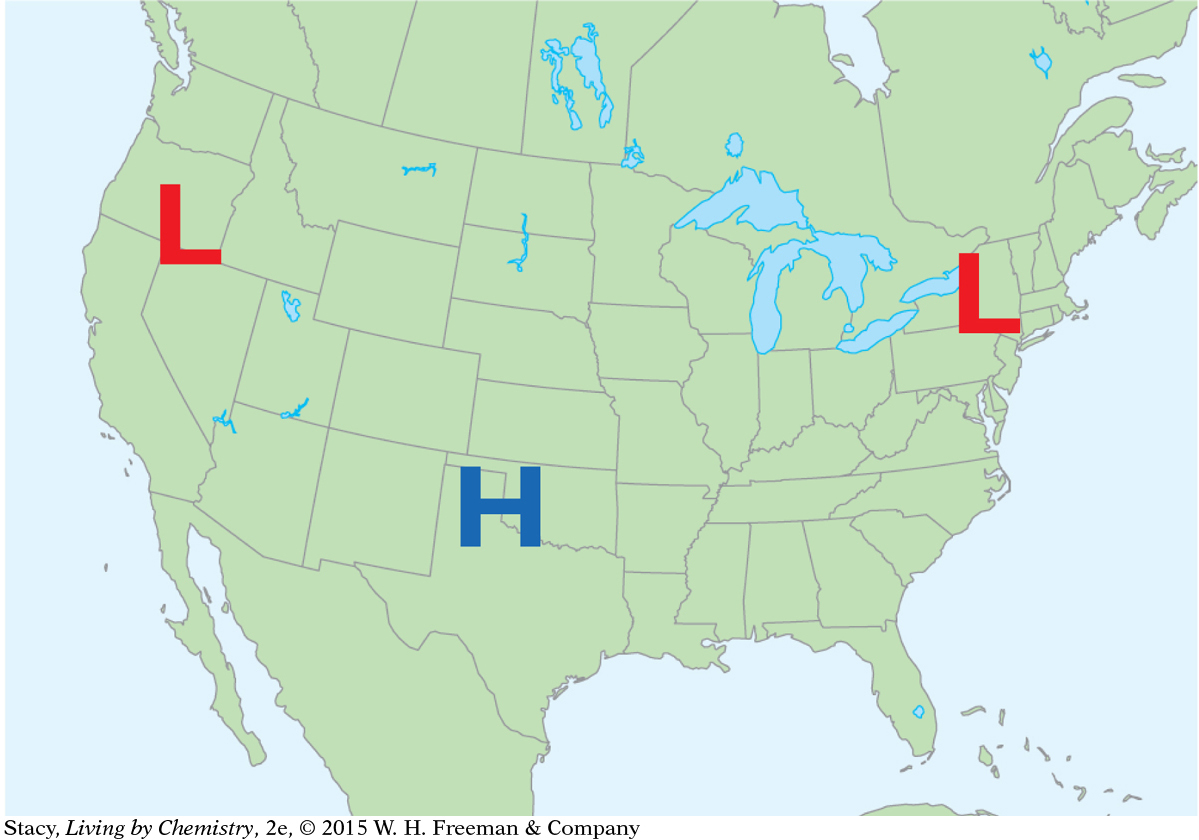
Air pressure highs and lows
|
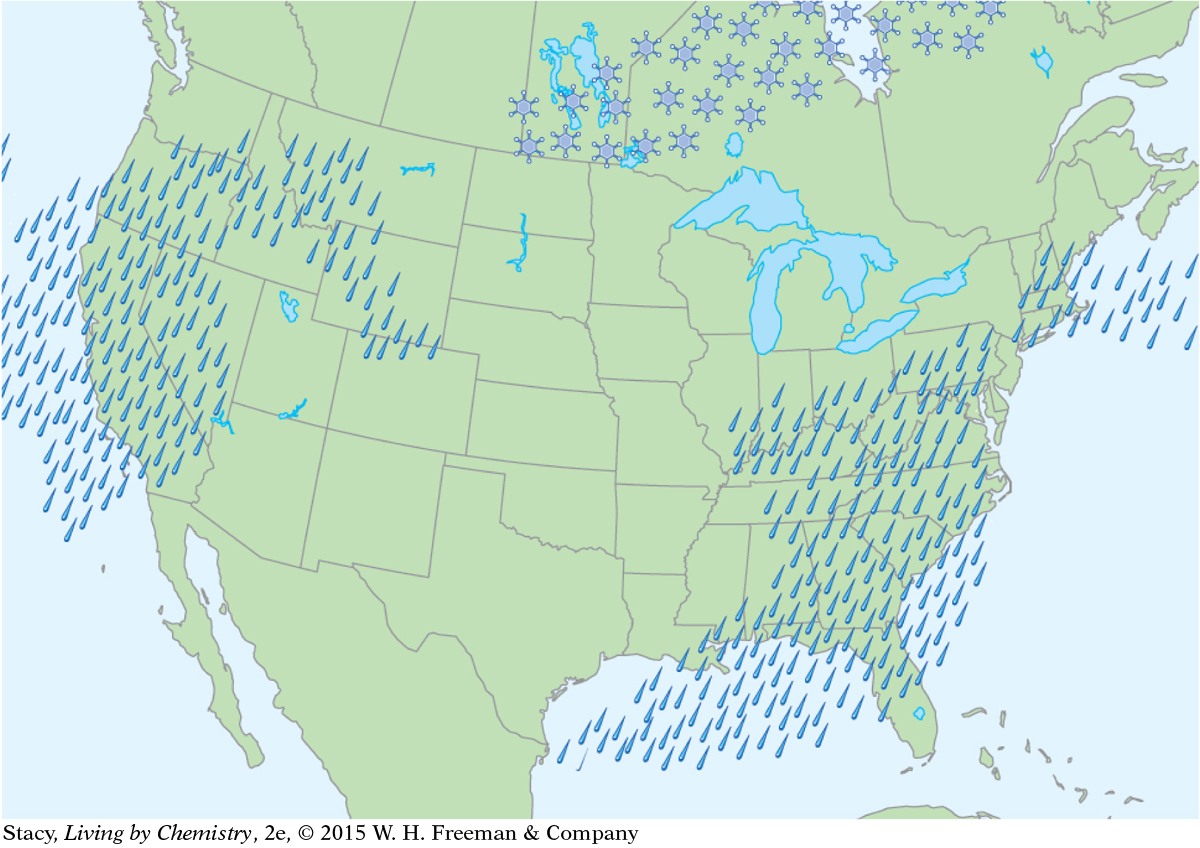
Precipitation: rain and snow
|
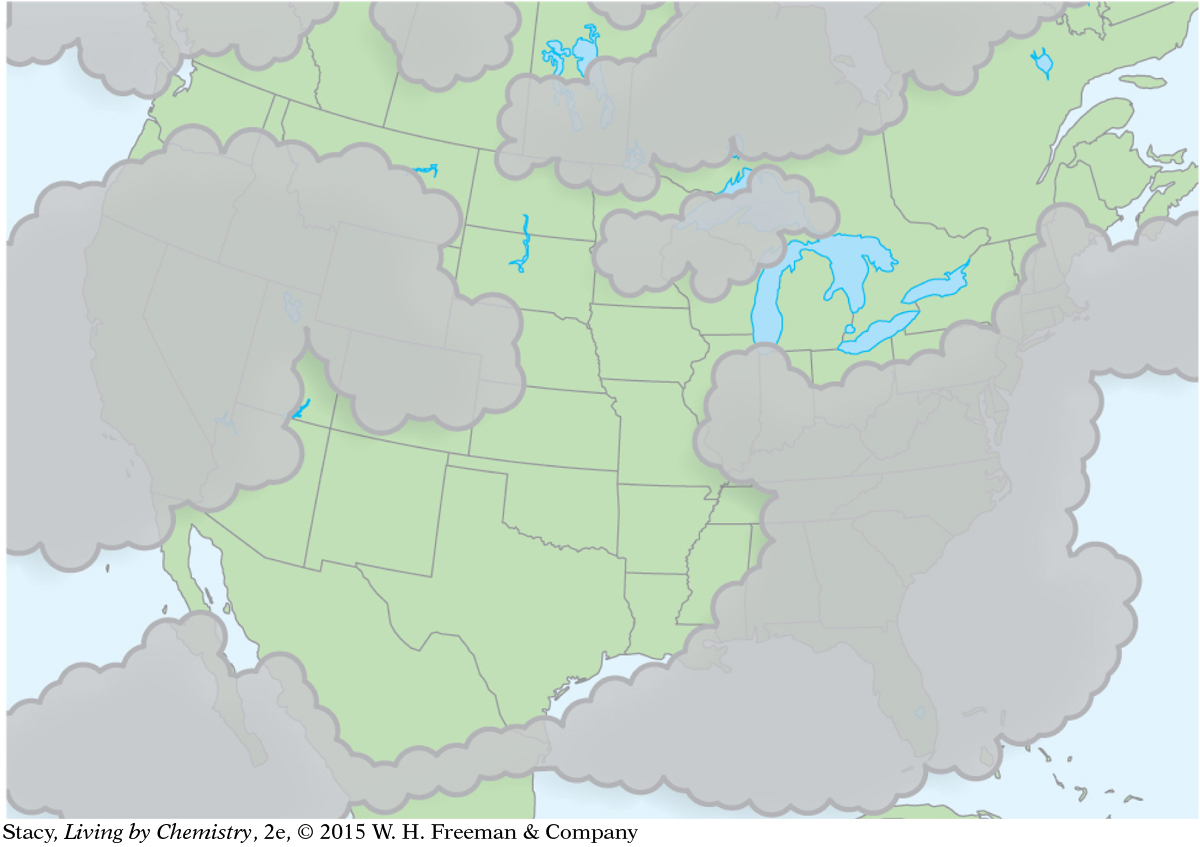
Cloud cover
|
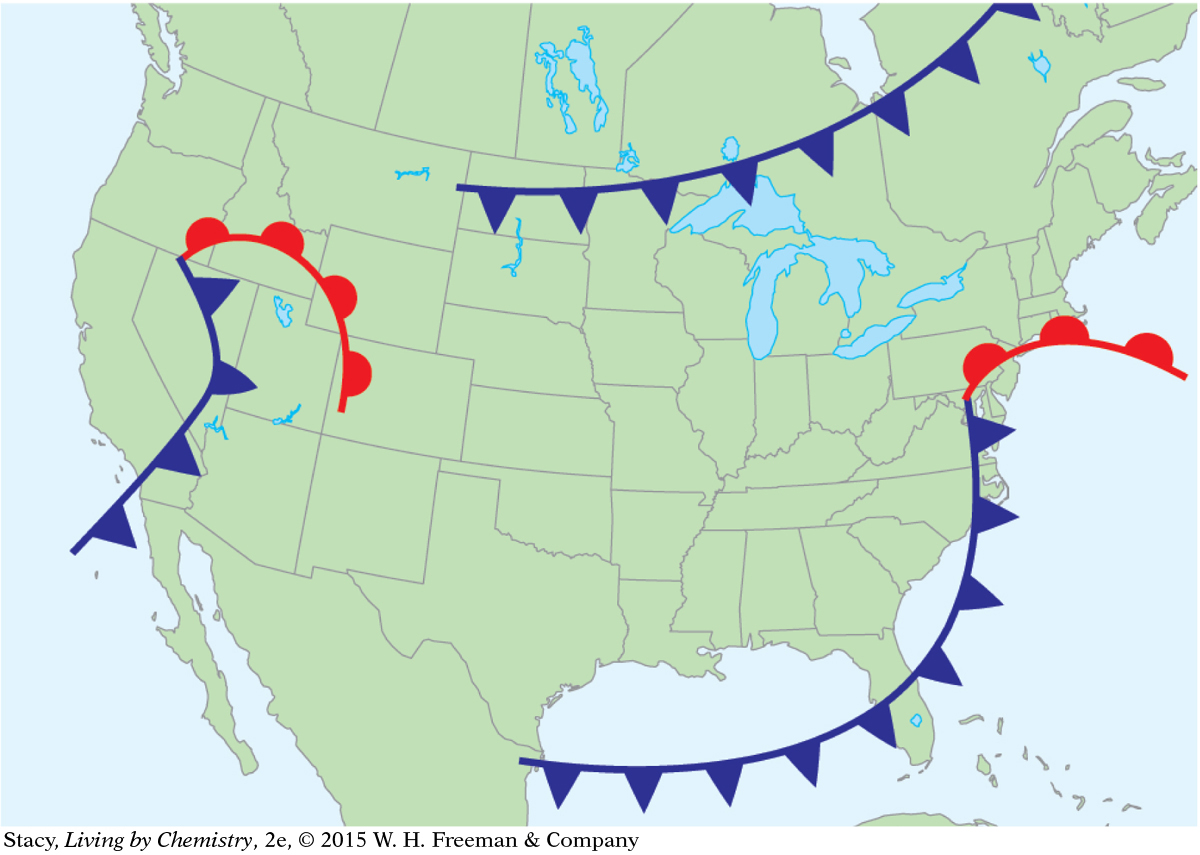
Fronts
|
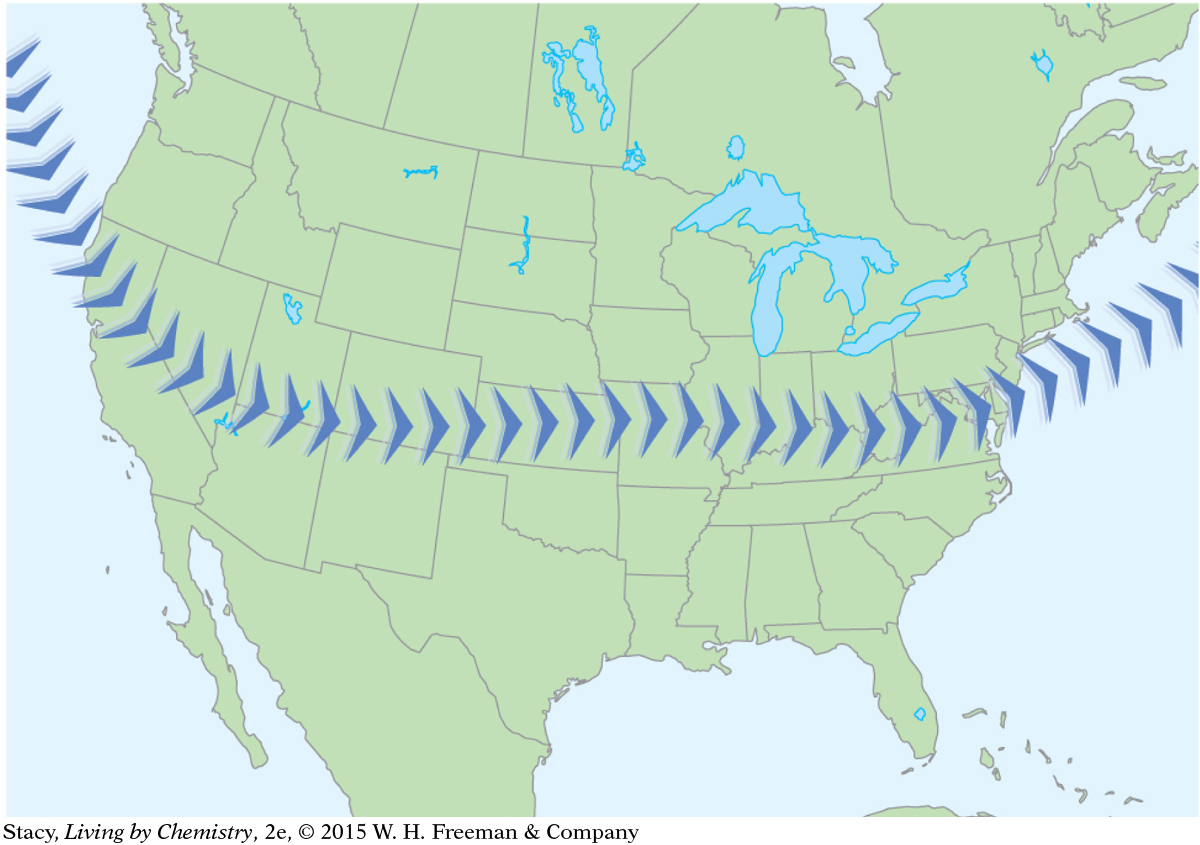
Jet stream
|
261
GEOLOGY CONNECTION
GEOLOGY
CONNECTION
Earth’s atmosphere is divided into several distinct layers. Almost all of the weather on the planet takes place in the layer of atmosphere closest to Earth. This layer is called the troposphere and is about 14 kilometers high (that’s about 9 miles).

In addition to familiar features such as temperature and precipitation, weather maps often show a curve called the jet stream. The jet stream shows the location of high-altitude winds. These winds are at least 57 miles per hour (up to 190 mi/h) and are in the upper atmosphere above 20,000 feet in altitude (that’s 4 miles up). These winds have a great effect on what happens in the air below them and generally “steer” storms.
Here are some features to take note of:
In North America, temperatures are colder in the north and warmer in the south.
The shape of the jet stream coincides with the contour lines on the temperature map.
If it is raining or snowing, then clouds must be present, but clouds do not necessarily mean it will rain or snow.
Fronts are located in areas of low pressure.
Clouds are more likely to form near fronts, so it is more likely to rain and snow there.
Warm fronts and cold fronts are associated with low-pressure systems.
There is no precipitation for regions with high pressure. High pressure is associated with sunny days. A region with high pressure can be either hot or cold.
Example
Weather Maps
Describe the weather in these areas using the six weather maps in this lesson. Include the temperature, air pressure, cloud cover, precipitation, and storm fronts.
West Coast
middle of the United States
Solution
West Coast: The temperature is about 60 °F, slightly colder to the north. The air pressure is low. There are storm fronts and it is cloudy, with rain to the south and clearing to the north.
Middle of the United States: It is about 40 °F and sunny. The air pressure is high, there are no clouds, and there is no precipitation.
LESSON SUMMARY
LESSON SUMMARY
What causes the weather?
KEY TERMS
weather
physical change
phase change
Weather is about the movement of air and water. The gases in our atmosphere and the water on Earth’s surface undergo physical changes and move around the planet. Water exists in all three phases (solid, liquid, and gas) on Earth. Water shows up as snow, ice, rain, clouds, fog, and water vapor. Meteorologists use detailed maps to monitor the physical changes taking place in our atmosphere and to keep track of the movement of moisture and air around the planet. Information on weather maps includes temperature, air pressure, cloud cover, precipitation, warm and cold fronts, and the location of the jet stream.
262
ENVIRONMENTAL CONNECTION
ENVIRONMENTAL
CONNECTION
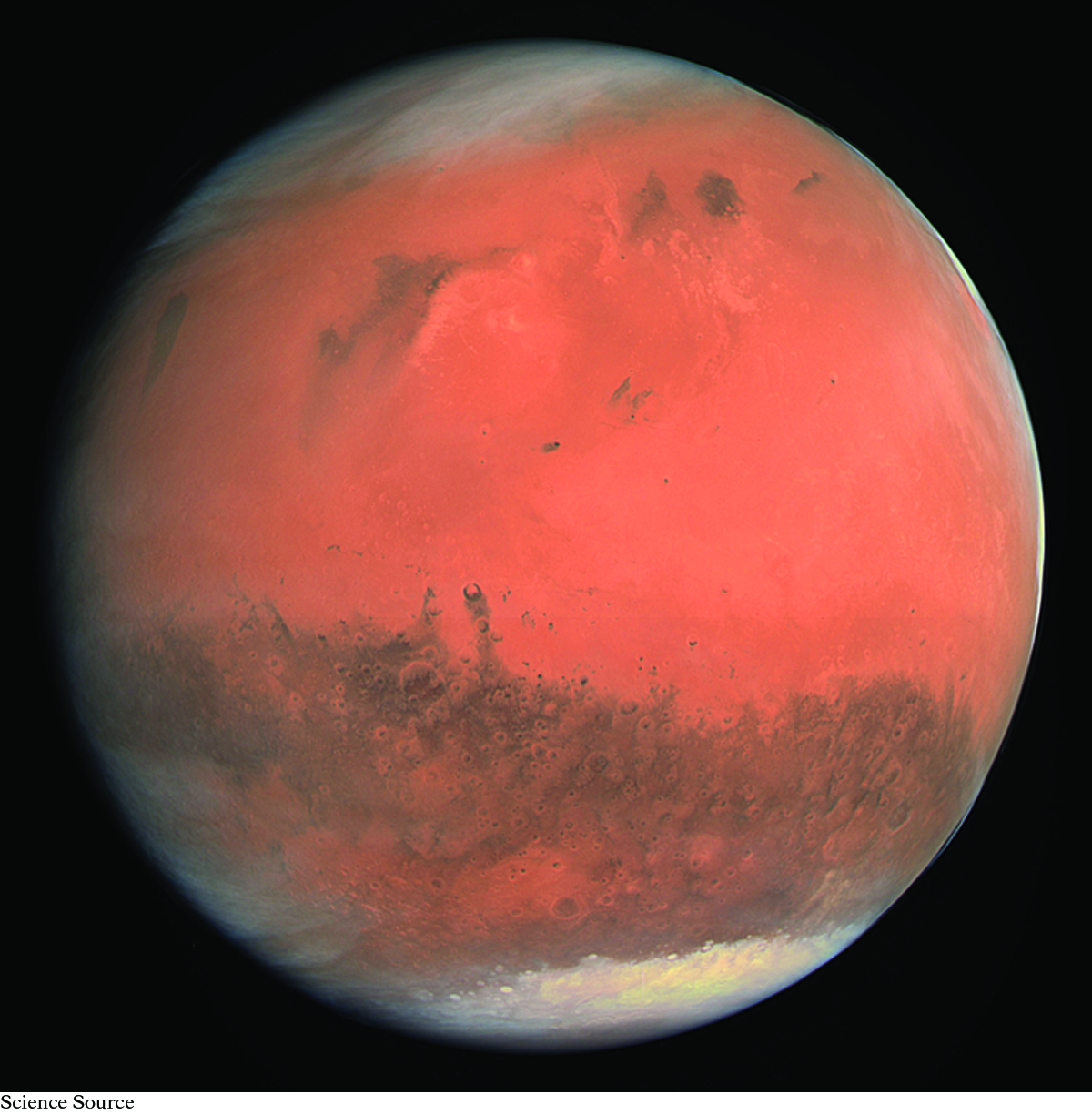
On other planets, the compounds that are involved in the weather may be quite different from those found on Earth. The atmosphere of Mars is mostly carbon dioxide. The polar ice caps on Mars are made of frozen carbon dioxide.

Exercises
Reading Questions
What substances are necessary for a planet to have weather?
Describe three variables that meteorologists study to make weather predictions.
What is a physical change?
Reason and Apply
Name three types of maps that meteorologists use. Describe the maps and the information that they contain.
Consult a newspaper, the Internet, or a weather report on television.
Name three states that are currently experiencing a cold front (or warm front) moving through.
Which states are experiencing high-pressure systems? What is the weather forecast in those states?
If you were traveling to New York tomorrow, would you pack a raincoat? Explain.
Nitrogen, N2(g), oxygen, O2(g), carbon dioxide, CO2(g), and water vapor, H2O(g), are all gases found in the atmosphere.
Draw the structural formula for each and include lone pair electrons.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for water.
Which molecules are polar and which molecules are nonpolar?
Which one of the four substances is naturally found as a liquid, a solid, and a gas on Earth?