LESSON 84: Heartburn: Acids and Bases
429
THINK ABOUT IT
Solutions have a wide variety of properties. Acetic acid, or vinegar, is used to flavor salad dressing, while citric acid gives a sour taste to lemon juice and orange juice. Ammonium hydroxide is used to clean windows, and sodium hydroxide is used to open clogged drains. All of these solutions are either acids or bases and can be classified into these categories based on their general properties.
What are the properties of acids and bases?
To answer this question, you will explore
Acids and Bases
Indicators
The pH Scale
Acids and Bases
EXPLORING THE TOPIC
Acids and Bases
GENERAL PROPERTIES
CONSUMER CONNECTION
CONSUMER
CONNECTION
Carbonic acid, H2CO3, and phosphoric acid, H3PO4, are two acids found in carbonated soft drinks. The phosphoric acid acts as a flavoring and a preservative, while the carbonic acid is a byproduct of carbonation.

Acids and bases are special categories of solutions. They are extremely useful to us in our everyday lives precisely because of their unique properties. The term acid comes from the Latin word acidus, which means sour. Many of the sour tastes in our food come from the acids found in those foods.
For much of history, the term alkaline was used instead of base. Bases are found in many household cleaners, from soaps to drain openers to oven cleaners. Bases have a bitter taste, as you may have noticed if you have ever accidentally tasted soap. Bases usually feel slippery to the touch. The slipperiness of bases arises from the fact that they are reacting with the fats in your skin and turning them into soap.
In general, acids and bases are toxic, especially large quantities of concentrated solutions. It is important that acids and bases not splash on your skin or in your eyes. Acids and bases are both corrosive and can cause a chemical burn. A chemical burn is one in which living tissue is damaged.
Indicators
Indicators
Many acidic and basic solutions are colorless and odorless, which can make them difficult to detect by their appearance alone. Because these solutions can be toxic, it is useful to be able to monitor them. Luckily, there are molecular substances called indicators that change color when they come into contact with acids and bases. If you add a drop or two of an indicator to an unknown solution, you can tell if you have an acid or a base by the color that results.
430
Cabbage juice is a natural acid-base indicator obtained by boiling or grinding up red cabbage. The cabbage juice changes color as it is added to various solutions, as shown in the illustration. Take a moment to look for patterns.
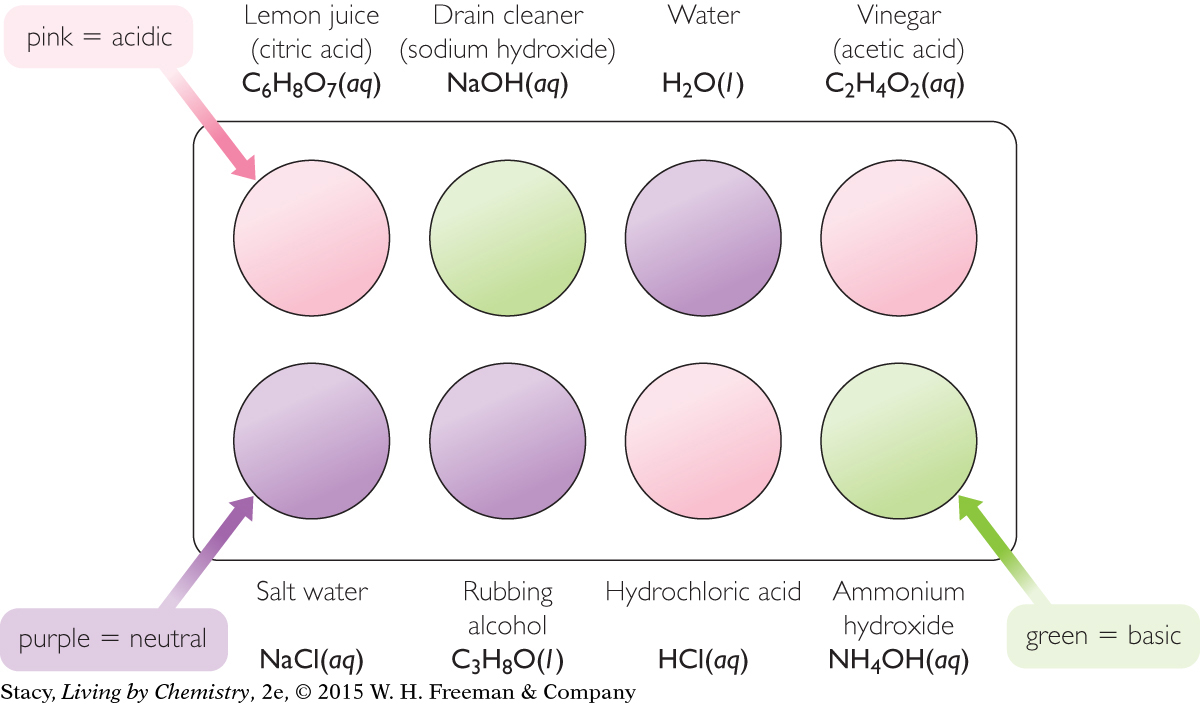
Cabbage juice turns pink when it is in contact with acids, such as citric acid, acetic acid, and hydrochloric acid. It turns green or yellow in contact with bases, such as sodium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide. And it remains purple or blue in contact with neutral substances such as pure water, salt water, and rubbing alcohol. Neutral solutions are neither acidic nor basic. So cabbage juice can be used to indicate if a solution is acidic or basic or neither.
The pH Scale
The pH Scale
HEALTH CONNECTION
HEALTH
CONNECTION
Too much acid in the stomach may result in indigestion, heartburn, or ulcers. Antacids are bases that work in the stomach to neutralize the excess acid there. Other remedies work on receptor sites in your body, preventing the secretion of excess acid in the first place.

There are dozens of different types of acid-base indicators, each with a unique color scheme. The colors associated with “universal indicator” are shown in the illustration. Notice that there is a number associated with each color. This number is referred to as the pH number, or just as the pH.
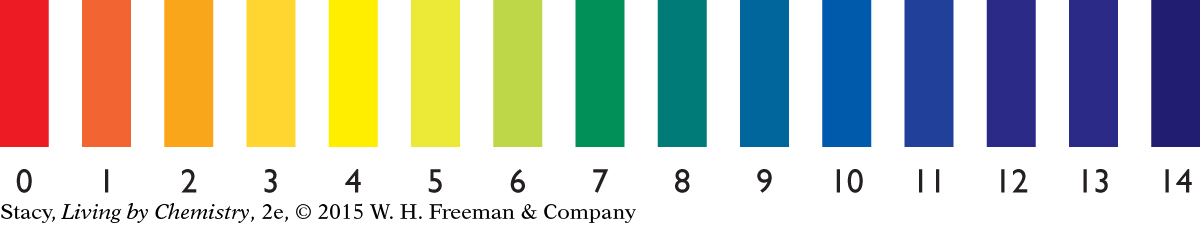
Another way to measure the pH for a solution is with paper coated with indicator, referred to as pH paper.
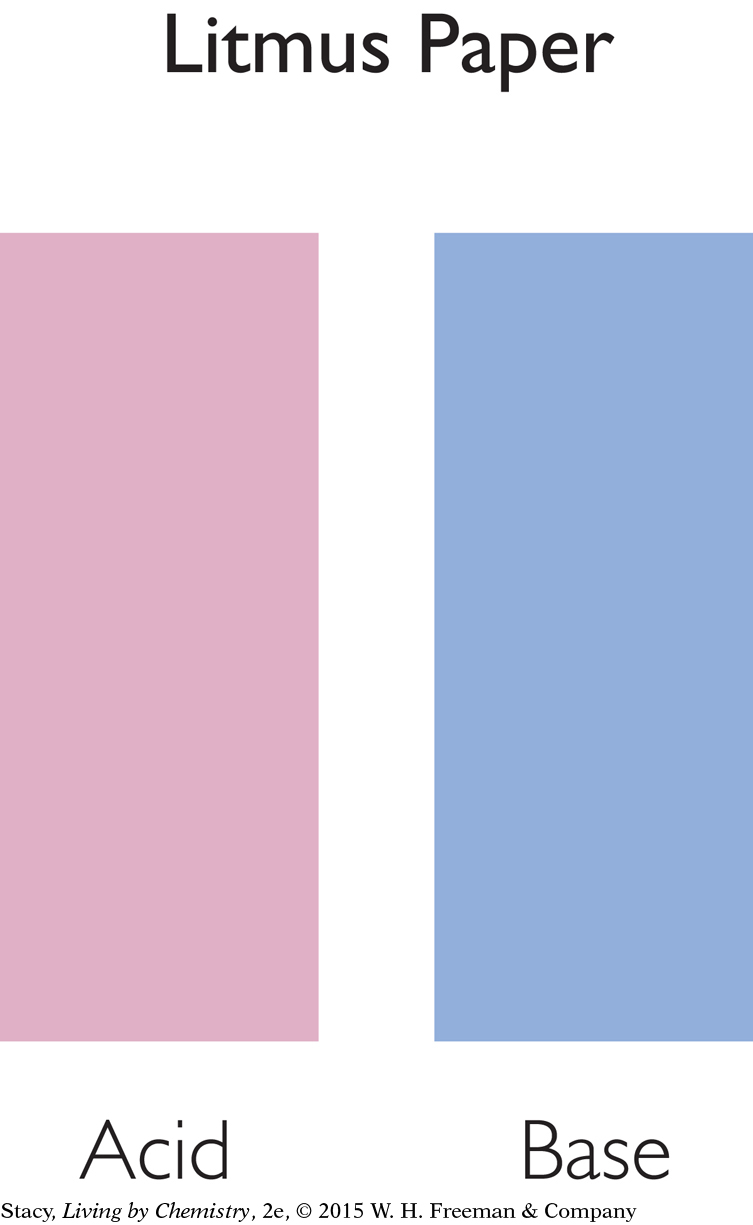

One common type of pH paper is called litmus paper. Litmus paper turns red in acidic solutions and blue in basic solutions.
The pH scale is a number line that assigns number values from 0 to 14 to acids and bases.
431
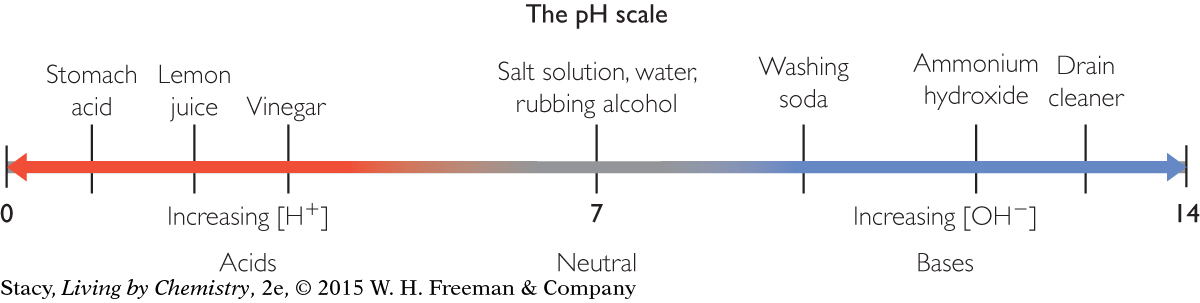
Substances with a pH below 7 at 25 °C are acids. Substances with a pH above 7 at 25 °C are bases. Substances with a pH at or near 7 at 25 °C are considered neutral. Stomach acid is extremely acidic, with a pH around 1. Lemon juice is the next most acidic substance shown here, with a pH near 2.4. The most basic substance shown here is drain cleaner. The substances on either end of the pH scale are potentially more dangerous and more toxic than substances found in the middle of the scale.
LESSON SUMMARY
LESSON SUMMARY
What are the properties of acids and bases?
KEY TERMS
indicator
pH scale
acid
base
Acids and bases are special categories of solutions. The sour tastes in our food come from the acids found in those foods. Bases cause the slippery feel of soaps and detergents. Chemical compounds called indicators help chemists to identify the presence of acids and bases in solution. Indicators change color in response to acids and bases. The pH scale is a number scale that assigns values to acids and bases, between 0 and 14. Substances with a pH below 7 at 25 °C are acids. Substances with a pH above 7 at 25 °C are bases. Substances with a pH at or near 7 at 25 °C are neutral.
Exercises
Reading Questions
What are some of the observable properties of acids and bases?
What is the pH scale?
What does it mean to say that a substance has a neutral pH?
Reason and Apply
Lab Report Write a lab report for the Lab: Acids and Bases. In your report, give the title of the experiment, purpose, procedure, observations, analysis, and conclusion.

Classify each of the following solutions at 25 °C as acidic or basic based on the information provided.
lemon juice tastes sour
a solution of washing soda turns cabbage juice green
a dilute solution of potassium hydroxide feels slippery
a sugar solution has a pH of 7
drain cleaner has a pH of 12
432
Examine the list of acids below. List three patterns that you notice in the names and chemical formulas.
hydrochloric acid, HCl nitric acid, HNO3 carbonic acid, H2CO3 acetic acid, C2H4O2 sulfuric acid, H2SO4 citric acid, C6H8O7 Examine the list of bases below. List three patterns that you notice in the names and chemical formulas.
sodium hydroxide, NaOH magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2 potassium hydroxide, KOH barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2 lithium hydroxide, LiOH ammonium hydroxide, NH4OH Find three acids and three bases used in your home. What are these acids and bases used for?
Look up the chemical name and chemical formula of each acid and base.