LESSON 88: Neutral Territory: Neutralization Reactions
447
THINK ABOUT IT
There are many advertisements on television about products that are designed to treat “acid indigestion.” Some of these substances claim to neutralize extra acid that may have built up in your stomach.
What happens when acids and bases are mixed?
To answer this question, you will explore
Neutralization Reactions
Predicting the Products of Neutralization Reactions
Neutralization Reactions
EXPLORING THE TOPIC
Neutralization Reactions
Pure water is neutral because it has equal numbers of H+ and OH− ions.
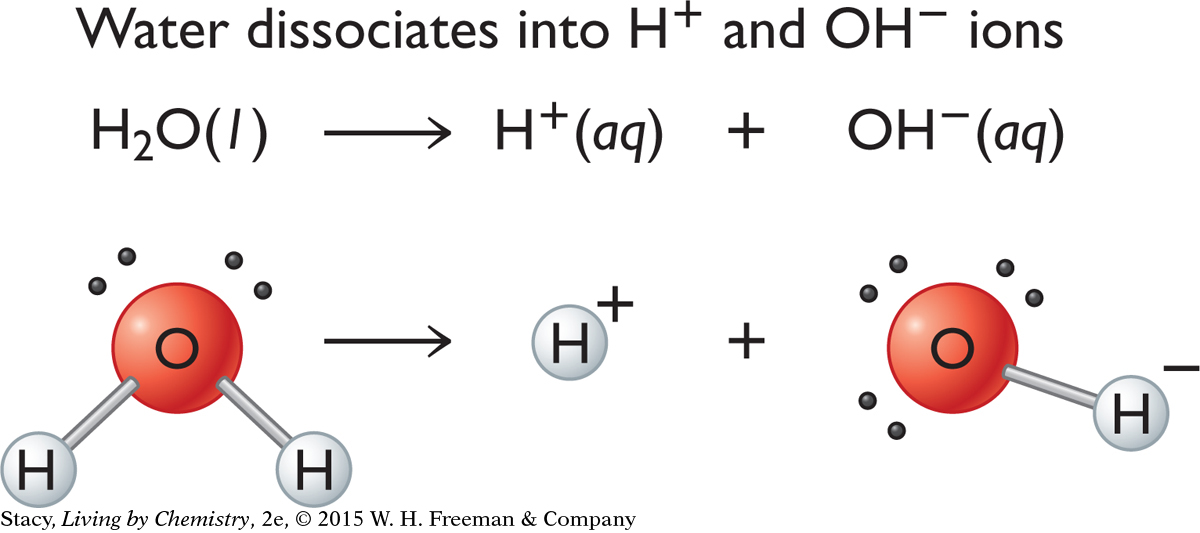
In pure water at 25 °C, [H+] and [OH−] are both 1.0 × 10−7 mol/L. But if an acid or a base is added to water, it upsets the balance of ions in solution. Acidic solutions have an excess of H+ and basic solutions have an excess of OH−.
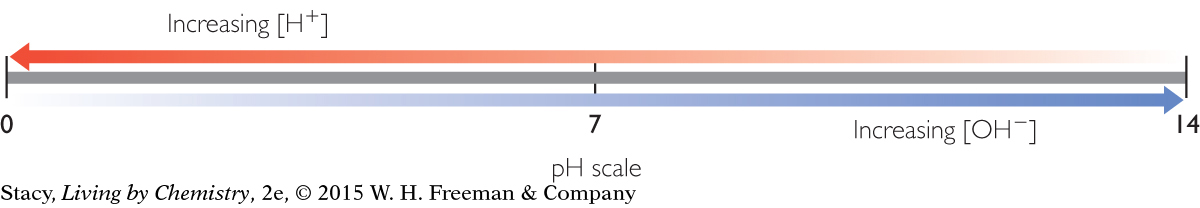
One way to reduce the toxicity of an acidic or basic solution is by dilution. If you add enough water, you can reduce the concentration of the acid or base. Extremely dilute acids and bases have a pH of 7 at 25 °C because this is the pH of pure water.
However, there is another way you can reduce the toxicity of an acidic or a basic solution. To counteract the effects of an acid in solution, you can add a base. Likewise, to counteract the effects of a base in solution, you can add an acid.
448
The acid and base react in solution and neutralize each other. The chemical equation for the reaction between an acid and base is shown below.
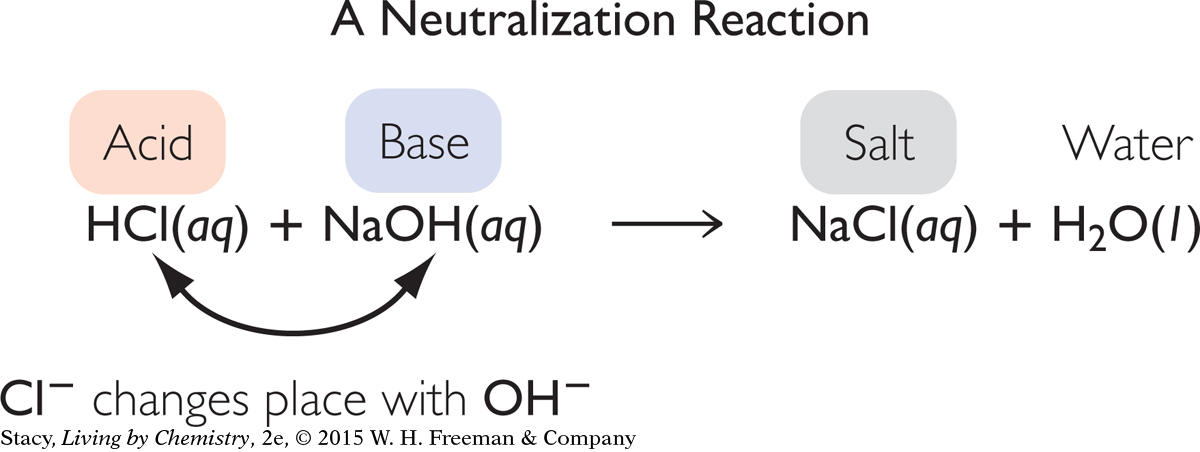
Notice that this reaction is a double exchange reaction. The H+ and Na+ cations exchange anions. The result is the production of a salt, NaCl, and water. The excess H+ from the acid combines with OH− from the added base to form H2O. The reaction is referred to as a neutralization reaction.
Big Idea
Big Idea
Acids and bases neutralize each other, producing a salt and water.
So, one way to make an acidic solution safe is by adding a base. Likewise, you can make a basic solution safe by adding an acid.
Not all neutralization reactions produce neutral solutions. For example, if you use an acidic solution that is very concentrated and a basic solution that is not very concentrated, there will be leftover H+ ions after mixing. There will not be enough OH− ions to neutralize all of the H+ ions. But some neutralization will have taken place. As a result of mixing, the solution will be closer to neutral than either of the starting solutions.
Predicting the Products of Neutralization Reactions
Predicting the Products of Neutralization Reactions
HEALTH CONNECTION
HEALTH
CONNECTION
Some antacids are made of calcium carbonate. Calcium carbonate is the main component of eggshells and seashells and can also be used as an inexpensive calcium supplement.

Several neutralization reactions are shown. Notice the patterns in the products of the reactions.
HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) → KCl(aq) + H2O(l)
HNO3(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaNO3(aq) + H2O(l)
H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
2HCl + Mg(OH)2(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
H2SO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) → CaSO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Each reaction results in the production of an ionic compound (a salt) plus water. The salt consists of the cation of the base and the anion of the acid. For example, the cation in potassium hydroxide, KOH, is potassium, K+. The anion in nitric acid, HNO, is nitrate, NO3−. The K+ and NO3− produce the ionic compound, potassium nitrate, KNO3, which is a salt.
Some acids transfer more than one H+ ion. For example, each mole of sulfuric acid, H2SO4, transfers two moles of H+ ions. This is because there are two hydrogen ions in solution for every one sulfate anion, SO42−. Likewise, each mole of calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, transfers two moles of OH− ions. There are two hydroxide ions in each formula unit of calcium hydroxide to balance the charge on the calcium cations, Ca2+.
449
Example
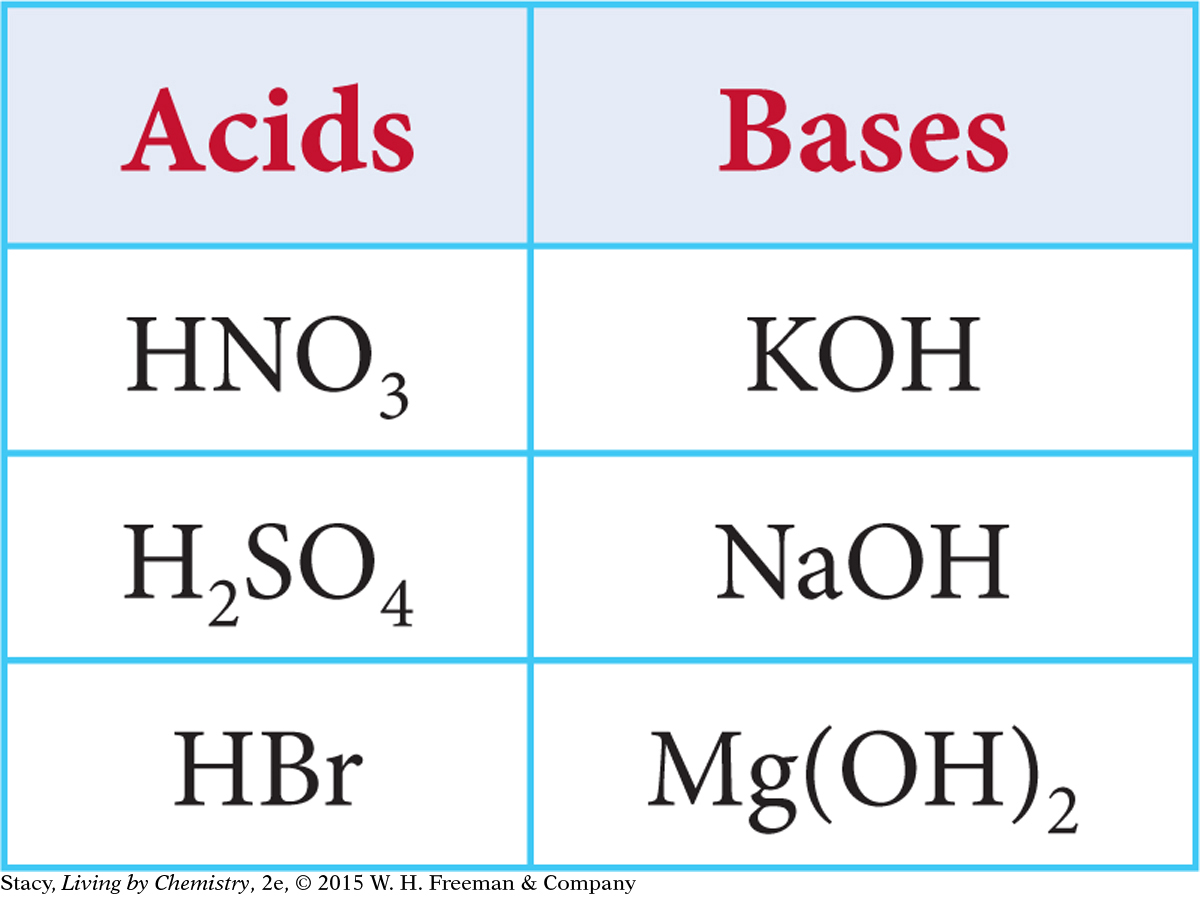
Producing Potassium Sulfate, K2SO4
Which of the acids and bases in this table could you mix to make potassium sulfate, K2SO4? Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
Solution
One way to use a neutralization reaction to make potassium sulfate is
H2SO4(aq) + 2KOH(aq) → K2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Notice that you need 2 mol of KOH to balance the equation properly.
STOMACH ACID RELIEF
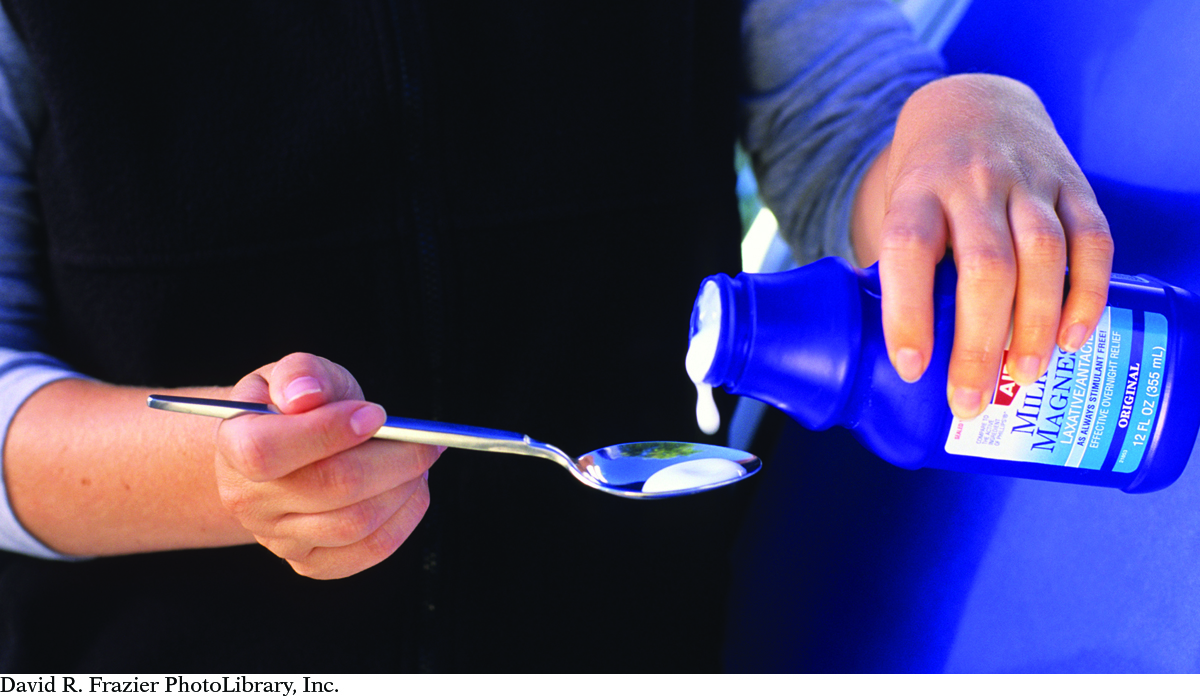

A common over-the-counter remedy for excess stomach acid uses a neutralization reaction. Milk of magnesia is a white mixture containing magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2. The mixture looks like milk because magnesium hydroxide, a white solid, does not dissolve completely in water. Instead, the white solid is suspended in the liquid.
Magnesium hydroxide is a base. It neutralizes stomach acid, HCl, to produce a salt and water as shown by this reaction.
2HCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
stomach acid + milk of magnesia → magnesium chloride + water
LESSON SUMMARY
LESSON SUMMARY
What happens when acids and bases are mixed?
KEY TERM
neutralization reaction
A neutralization reaction is a reaction in which an acid and a base react in aqueous solution to produce an ionic compound (a salt) and water. The pH approaches 7 because the H+ from the acid and the OH− from the base combine to form H2O. It is relatively easy to predict the products of a neutralization reaction. The salt that forms is made from the cation of the base and the anion of the acid.
Exercises
Reading Questions
Describe two ways to make a strong acidic solution safer.
What is a neutralization reaction?
450
Reason and Apply
Lab Report Complete a lab report for the Lab: Neutralization Reactions. In your report, give the title of the experiment, purpose, procedure, observations, and conclusion. In your conclusion, explain how you can use chemical equations to predict the products of the reactions you carried out.

Predict the products for the reactions given below. Be sure to balance each equation.
HF(aq) + NaOH(aq) →
HCl(aq) + Mg(OH)2(aq) →
HF(aq) + NH4OH(aq) →
CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) →
HNO3(aq) + Mg(OH)2(aq) →
HNO3(aq) + NH4OH(aq) →
CH3COOH(aq) + Mg(OH)2(aq) →
CH3COOH(aq) + NH4OH(aq) →
H2SO4(aq) + HNO3(aq) →
H2SO4(aq) + Mg(OH)2(aq) →
Suppose you mix 1 mol of sulfuric acid, H2SO4, with 1 mol of sodium hydroxide, NaOH. Why does the pH of the solution remain below 7?
Suppose you mix 1 mol of sodium hydroxide, NaOH, with 1 mol of magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2. Why does the pH of the solution remain above 7?
Which of these substances might be useful in neutralizing a lake damaged by acid rain?
H2SO4
CH3COOH
CaCl2
Ca(OH)2
Which combination of reactants would result in a neutralization reaction with sodium nitrate, NaNO3, as one of the products?
Mg(NO3)2 + NaOH
HNO3 + NaOH
CH3OH + NaOH
HNO3 + NaCl