Chapter 3 Summary
CHAPTER 3
A World of Particles
SUMMARY
KEY TERMS
atom
atomic theory
model
nucleus
proton
neutron
electron
atomic number
isotope
mass number
average atomic mass
radioactive isotope
nuclear reaction
radioactive decay
alpha decay
alpha particle
beta decay
beta particle
half-life
radiation
gamma ray
fission
fusion
nuclear equation
parent isotope
daughter isotope
nuclear chain reaction
Alchemy Update
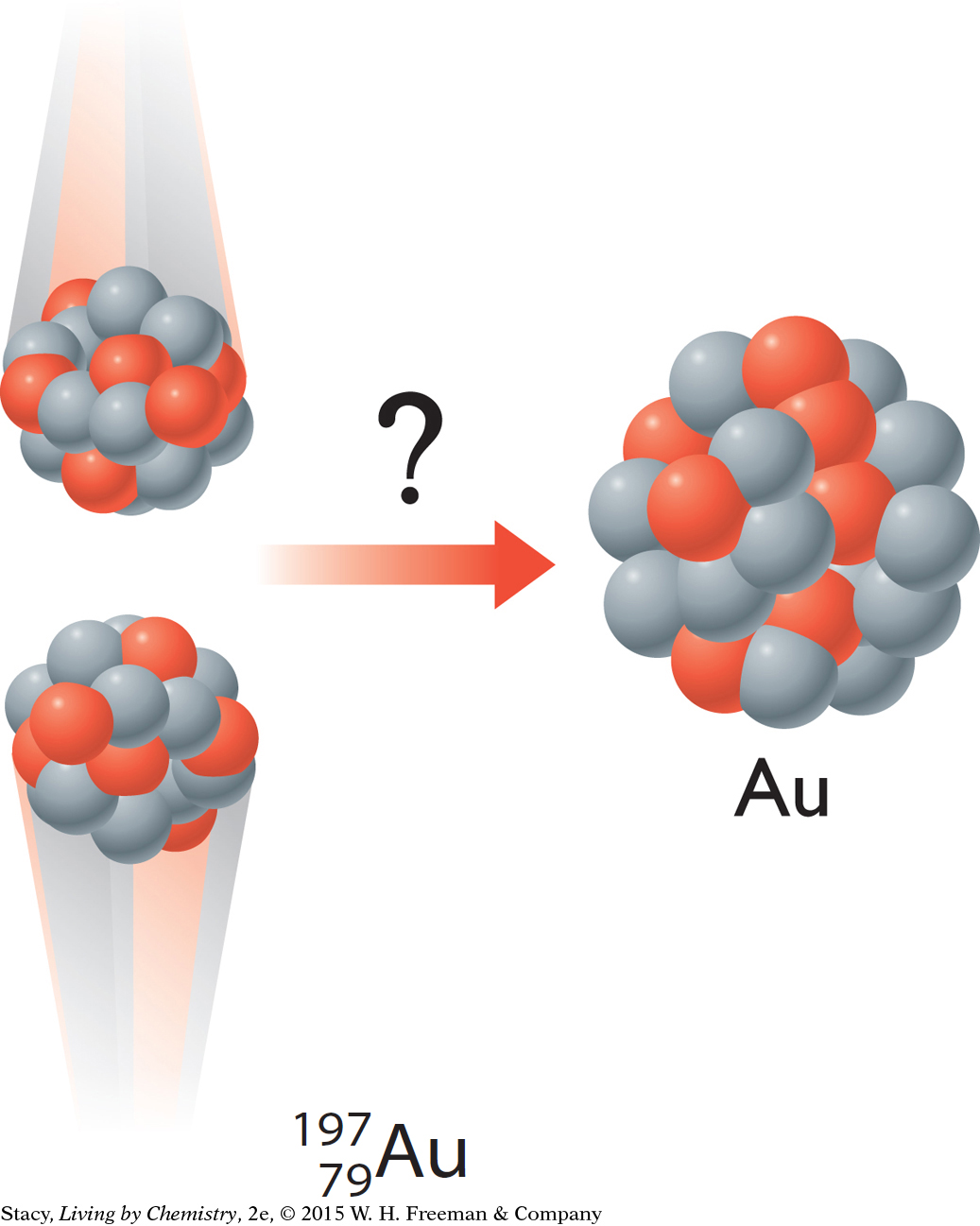
Can a copper atom be transformed into a gold atom through nuclear processes?
Elements are collections of similar atoms. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the identity of an atom. For instance, all atoms of gold have 79 protons. However, atoms of an element may have different numbers of neutrons. The number of neutrons is related to the stability of the atom. Stable gold atoms have 118 neutrons.
Nuclear fission, nuclear fusion, and radioactive decay can result in new elements. But nuclear fusion and nuclear fission are difficult processes to control and often involve large amounts of energy. Nuclear reactions do take place in the stars where atoms are created. So far it is not yet possible or practical to create gold atoms through nuclear reactions here on Earth.
REVIEW EXERCISES
Question 3.1
1. Describe the different processes that might result in a change in atomic identity.
Question 3.2
2. Give an example of evidence used by scientists to revise the atomic model.
Question 3.3
3. Explain how to use the periodic table to deduce the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons of an atom of a specified element.
Question 3.4
4. Write a nuclear equation for the hypothetical fusion of a copper atom with another nucleus to make gold. Can this happen? Why or why not?