LESSON 43: Polar Bears and Penguins: Electronegativity and Polarity
223
THINK ABOUT IT
NATURE CONNECTION
NATURE
CONNECTION
Polar bears and penguins live on opposite poles, so they do not encounter each other in the wild. Polar bears inhabit the Arctic, while penguins live exclusively in the southern hemisphere.
Hydrogen chloride, HCl, is a colorless but very toxic gas. Its smell is described as a suffocating, acrid odor. Like most other small molecules that smell, HCl molecules are polar. But what makes an HCl molecule polar? Where do the partial charges come from on the atoms in a polar molecule?
What makes a molecule polar?
To answer this question, you will examine
Electronegativity
Nonpolar Molecules
Electronegativity and Bonding
Electronegativity
EXPLORING THE TOPIC
Electronegativity
The hydrogen atom and the chlorine atom in hydrogen chloride, HCl, form a covalent bond by sharing a pair of electrons. This cartoon represents HCl as a penguin and a polar bear. The bonded pair of electrons is represented as two scoops of ice cream. Although the penguin and the polar bear are sharing the ice cream, they are not sharing it equally.
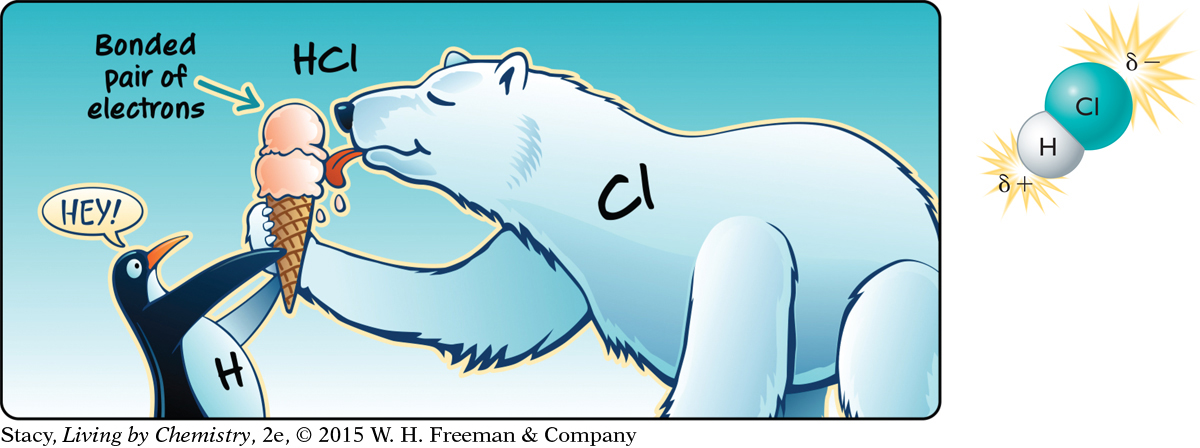
Similarly, the hydrogen atom and the chlorine atom in a hydrogen chloride molecule do not share the bonded pair of electrons equally. The chlorine atom attracts the shared electrons much more strongly than the hydrogen atom does. As a result, the shared electrons spend more time near the chlorine atom than they do near the hydrogen atom. Because of this displacement of the electrons, the hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge and the chlorine atom has a partial negative charge.
224
The tendency of an atom to attract shared electrons is called electronegativity. An atom that has a large electronegativity value strongly attracts shared electrons. In this case, the chlorine atom, like the polar bear, is stronger in attracting electrons, so it is more electronegative than the hydrogen atom. The atoms that are more electronegative are the ones that end up with a partial negative charge. The atoms that are less electronegative end up with a partial positive charge. The result is a polar bond.
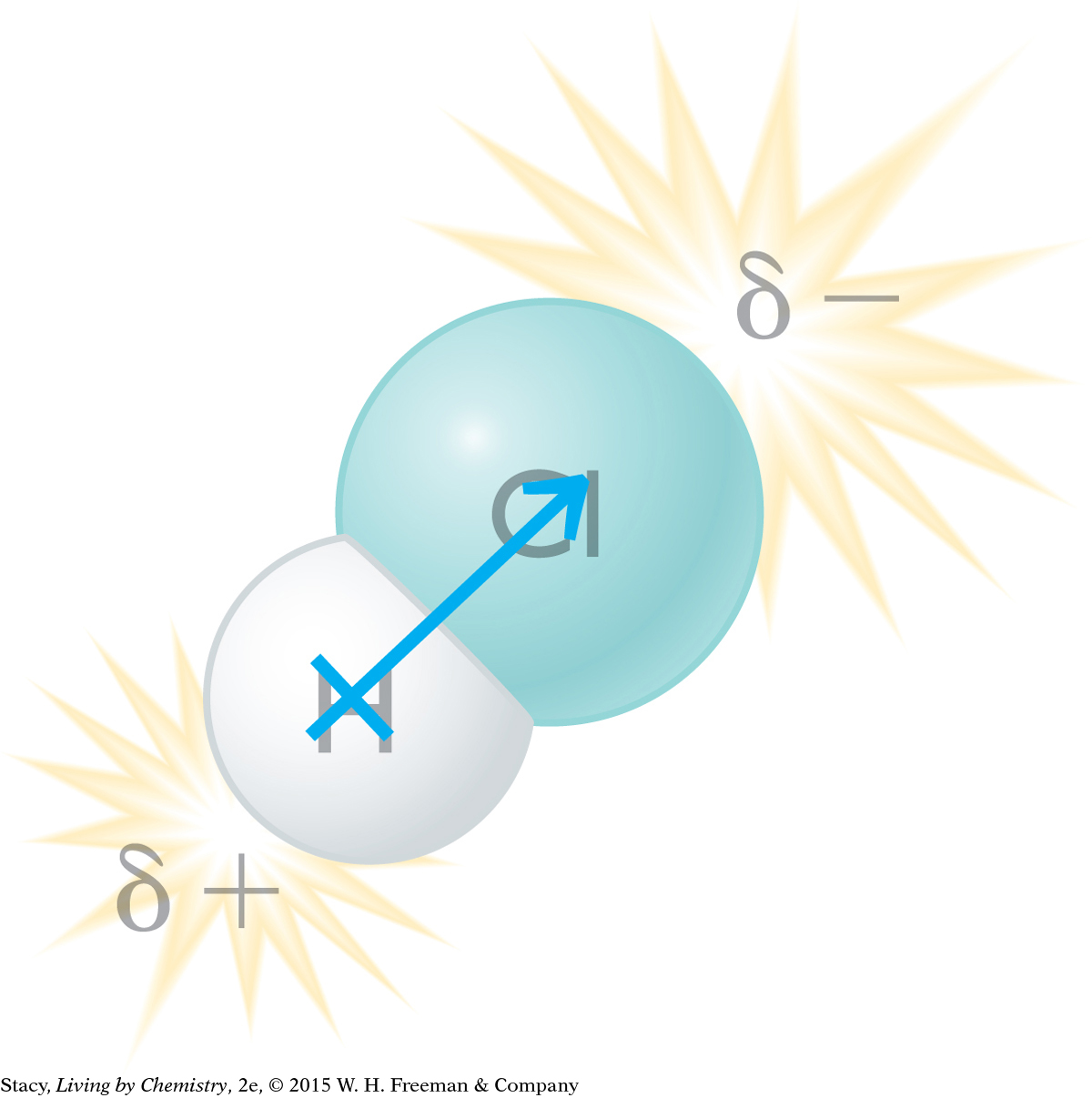
A polar molecule is called a dipole, because it has two poles: a positive end and a negative end. A dipole can be shown with an arrow starting at the positive end and pointing to the negative end of the molecule. The polar bond itself is also called a dipole.
Nonpolar Molecules
Nonpolar Molecules
When two atoms with identical electronegativities bond together, the attraction of the shared electrons is identical. As a result, the molecule is nonpolar. For example, H2 and Cl2 are both nonpolar molecules. They have no partial charges.

There is another way to end up with a nonpolar molecule. Examine the next illustration. Why is carbon dioxide, CO2, a nonpolar molecule?
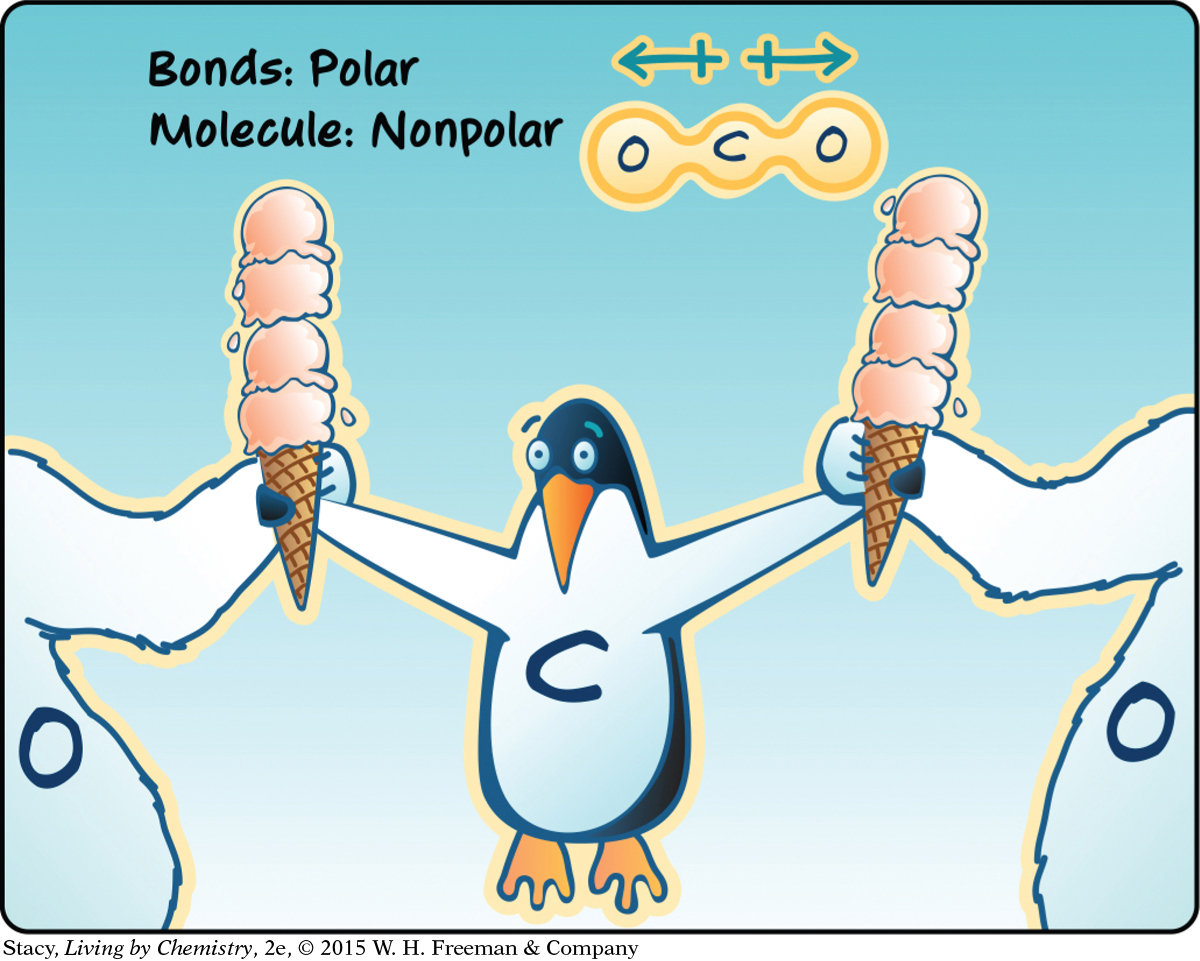
The two dipoles in CO2 balance each other, and there is no partial positive end to the molecule. So the overall molecule is nonpolar.
Electronegativity and Bonding
Electronegativity and Bonding
225
There are two types of covalent bonds: polar covalent bonds and nonpolar covalent bonds. When two atoms with different electronegativities bond together, the result is a polar covalent bond.
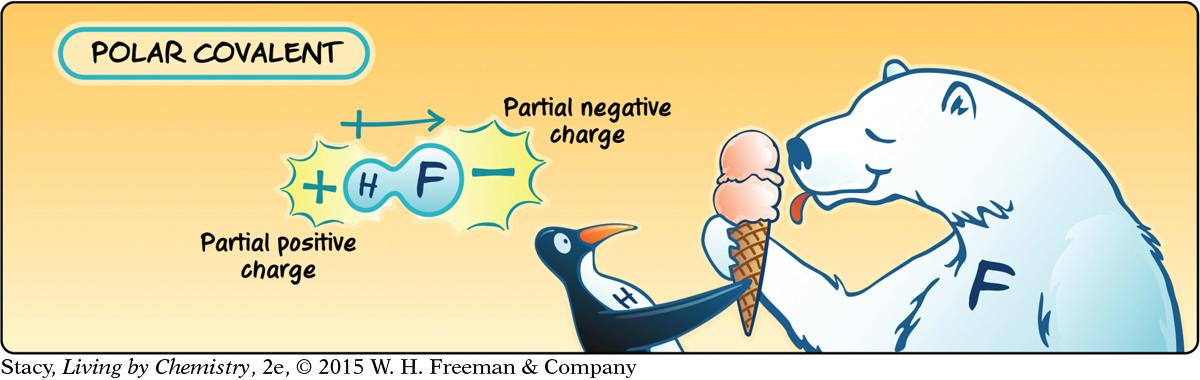
When the electronegativities of the atoms that bond are identical, the result is a nonpolar covalent bond.
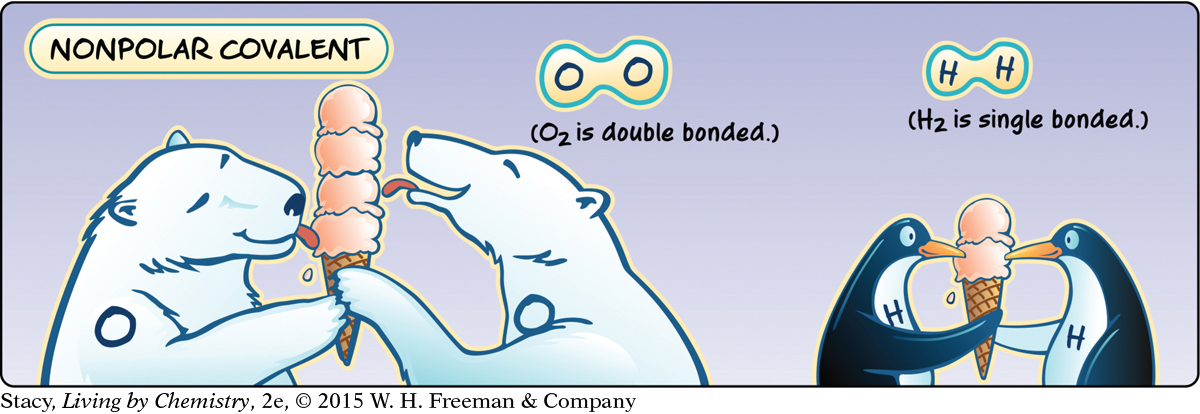
If the electronegativities of the two atoms differ greatly, it is possible for electrons to be pulled entirely toward one of the atoms in a bond. The result is an ionic bond.
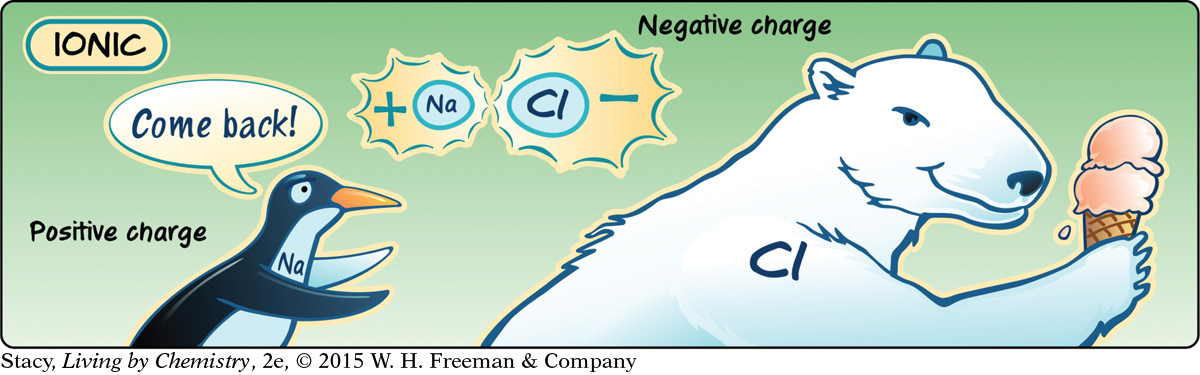
Ionic compounds represent the extreme of polar bonds, in which electrons are transferred to the more electronegative atom in the pair.
226
LESSON SUMMARY
LESSON SUMMARY
What makes a molecule polar?
KEY TERMS
electronegativity
dipole
Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract the electrons that are involved in a bond. Different atoms have different electronegativities. When two different kinds of atoms bond together, they do not attract the bonding electrons equally. The electrons are attracted to the atom with greater electronegativity. The result is a polar covalent bond. When atoms with identical electronegativities bond together, the electrons are shared equally, and the result is a nonpolar covalent bond. If the two atoms involved in a bond differ greatly in electronegativity, the result is electron transfer and an ionic bond.
Exercises
Reading Questions
What is the difference between a polar covalent bond and a nonpolar covalent bond?
What is the difference between a polar covalent bond and an ionic bond?
Explain why carbon dioxide is a nonpolar molecule even though its bonds are polar.
Reason and Apply
Are these molecules polar covalent or nonpolar covalent?
N2
HF
F2
NO
FCl
Using polar bears and penguins, create an illustration showing an ammonia, NH3, molecule. (Hint: You may wish to start with a Lewis dot structure.)
Is the molecule HOCl polar or nonpolar? Use a Lewis dot structure to explain your thinking.
Use electronegativity to explain why some molecules are attracted to a charged wand.