STANDARDIZED TEST PREPARATION
Multiple Choice
Choose the best answer.
Question 1
1. Based on its name and chemical formula, predict the smell of formic acid, CH2O2.
Sweet
Minty
Fishy
Putrid
Question 2
2. Which of the following compounds are covalent molecules? (Choose all that apply.)
NH4C2H3O2
C(CH3)4
CH2BrF
Na2CO3
Question 3
3. Which statement best describes what happens to the valence electrons in a covalent bond?
Valence electrons are shared between two metal atoms.
Valence electrons are shared between two nonmetal atoms.
Valence electrons are transferred from a metal atom to a nonmetal atom.
Valence electrons are transferred from a nonmetal atom to a metal atom.
Question 4
4. Which of the following best describes how two different compounds made up of molecules that are isomers of each other might smell?
The two compounds will most likely smell different from each other because isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
The two compounds will most likely smell the same because isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
The two compounds will most likely smell the same because isomers have the same molecular formula and the same structural formulas.
The two compounds will most likely smell different from each other because isomers have different molecular formulas and the same structural formulas.
Question 5
5. Which of the following statements best describes the molecule below?
254
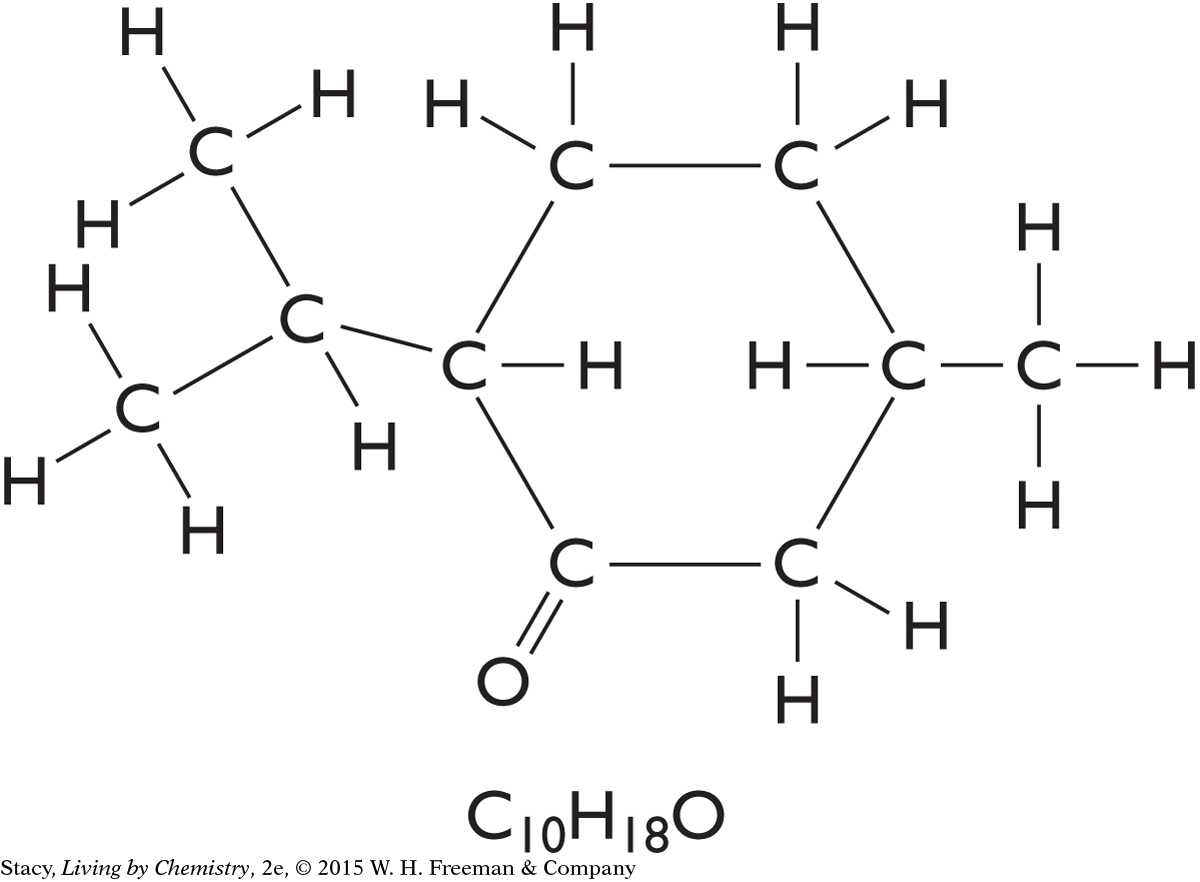
The molecular formula for the molecule is C9H15O.
The functional group is an ester.
The shape around all of the carbon atoms is linear.
The name of the compound will most likely end with “-one.”
Question 6
6. Which statement about the Lewis dot symbol of an element is true?
The total number of dots surrounding the symbol is the number of valence electrons for that element.
The number of dots surrounding the symbol will be the same for all elements of the same group on the periodic table.
For elements in the same period on the periodic table, the number of dots surrounding the element symbol will increase as you move from left to right on the periodic table.
All of the above statements are true.
Question 7
7. Which statement correctly describes the Lewis dot structure of CF4?
The Lewis structure for CF4 has a total of 40 dots in the structure because there are 5 atoms.
In the Lewis structure for CF4, carbon is the central atom with four bonded pairs of electrons, and each fluorine atom has a total of three bonded pairs of electrons.
In the Lewis structure for CF4, carbon is the central atom with four bonded pairs of electrons, and each fluorine atom has three lone pairs of electrons.
In the Lewis structure for CF4, the fluorine atom shares seven electrons with each carbon atom.
Question 8
8. Which statement best describes water, H2O?
Water is a bent molecule that has two lone pairs around the central oxygen atom.
Water is a linear molecule that has two lone pairs around the central oxygen atom.
Water is a bent molecule with no lone pairs around the central oxygen atom.
Water is a bent molecule with no lone pairs around the central hydrogen atom.
Question 9
9. Which of the molecules below have a double bond in their structural formula?
H2, N2, O2, Cl2, C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, H2CO
H2, N2, O2, Cl2
C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, H2CO
O2, C2H4, H2CO
H2, N2, Cl2, C2H6
Question 10
10. How many electrons are shared between the carbon and nitrogen in hydrogen cyanide, HCN?
Six electrons
Five electrons
Four electrons
Three electrons
Question 11
11. Based on the functional group, what is the predicted smell for the compound below?
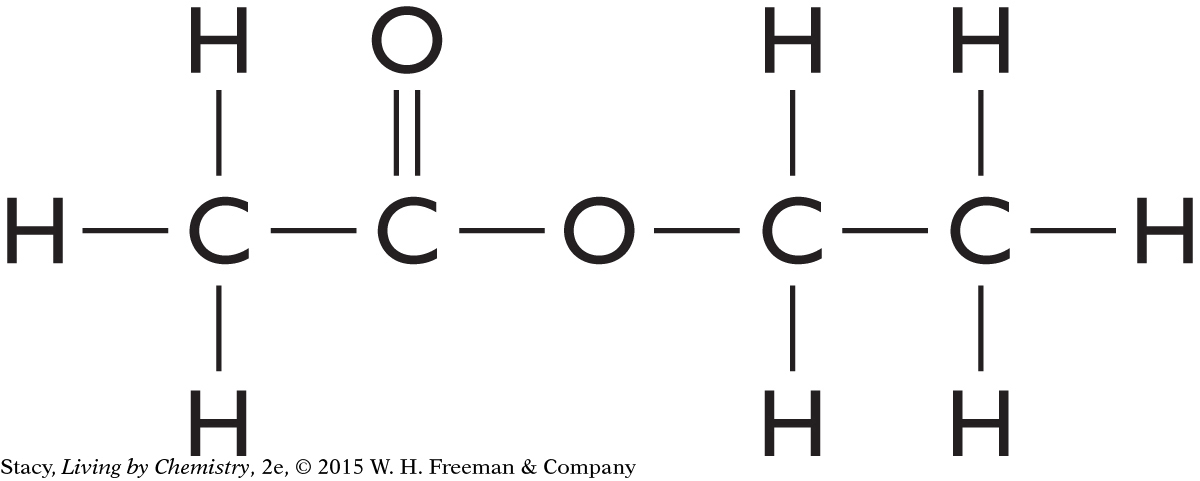
The molecule has a carboxyl group, so it likely smells putrid.
The molecule has a carboxyl group, so it likely smells minty.
The molecule has an ester group, so it likely smells sweet.
The molecule has a ketone group, so it likely smells minty.
255
Question 12
12. Which of the following correctly describes electron domains and molecular shape?
Only bonded pairs of electrons affect the shape of a molecule.
Only lone pairs of electrons affect the shape of a molecule.
Electron pairs have a tendency to repel one another due to their negative charge.
Electron pairs have a tendency to be as close to one another as possible.
Question 13
13. What molecular shapes are represented in this picture of ethanol, C2H5OH?
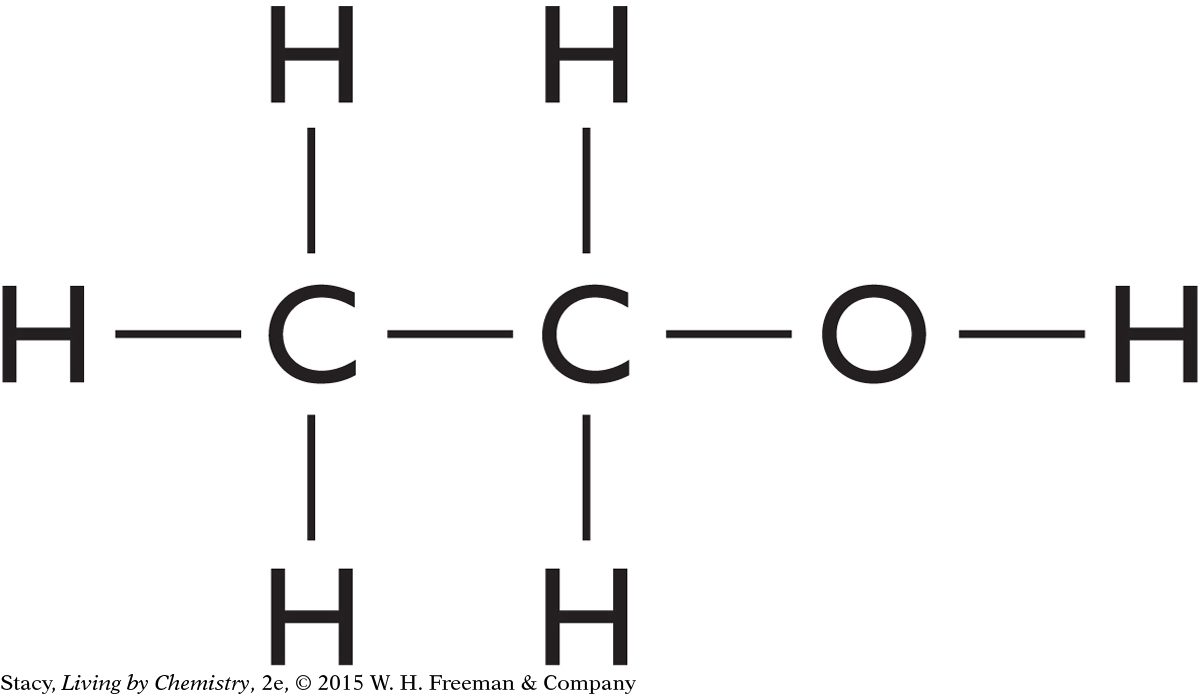
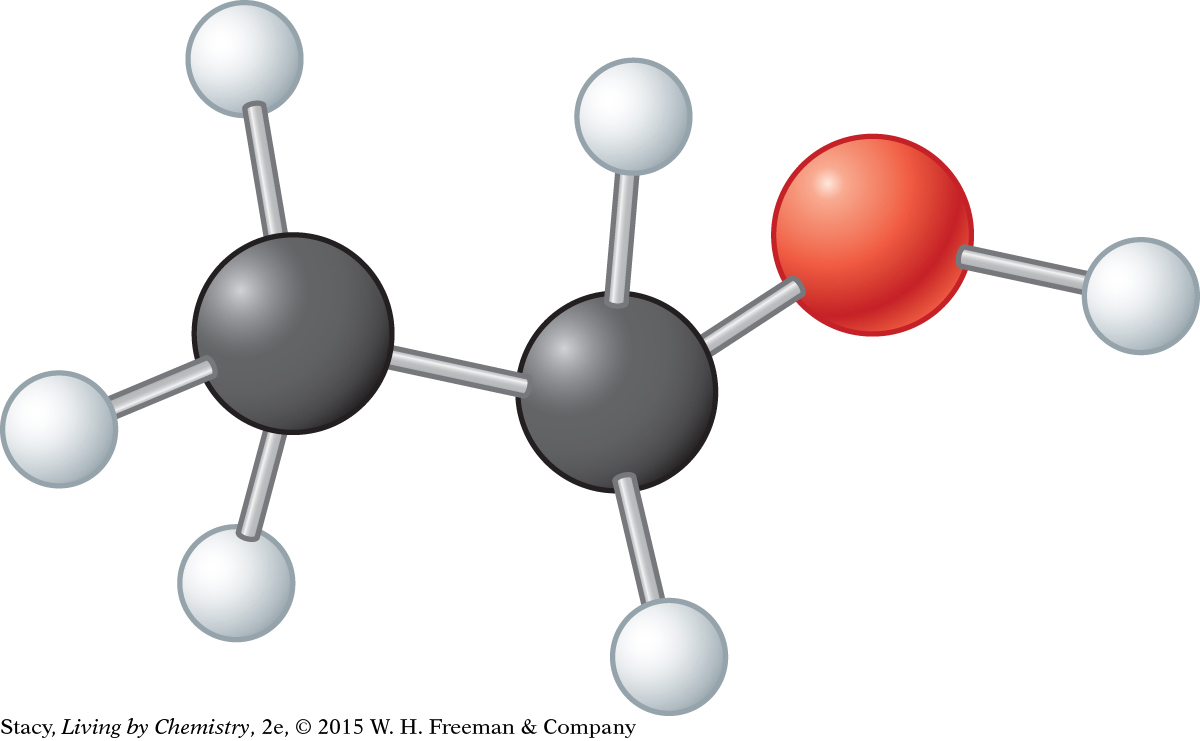
Pyramidal and bent
Tetrahedral and pyramidal
Tetrahedral and bent
Pyramidal and linear
Question 14
14. Aspects of the receptor site theory are given below. What can you conclude about smell molecules from the receptor site theory?
Smell molecules come in a variety of molecular shapes.
Smell molecules change phase to become a gas or vapor that floats through the air to enter your nose and be detected.
Smell molecules “dock” in receptor sites that match their molecular shapes.
Nerves are stimulated when the molecules dock and send messages to the brain, which are interpreted as a particular smell.
Smell molecules must break apart into individual atoms when they become a gas.
Smell molecules must lose their functional groups when they become a gas.
Smell molecules must change their shape to fit the “dock” in the receptor sites.
Smell molecules must keep their same structural formula when they become a gas.
Question 15
15. What is the bond polarity of the C–H bonds in methane, CH4? Refer to the electronegativity scale at the beginning of Lesson 44 to answer.
The C–H bonds are nonpolar covalent bonds because the electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen is large.
The C–H bonds are polar covalent bonds because the electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen is large.
The C–H bonds are ionic bonds because the electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen is large.
The polarity of C–H bonds is small because the electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen is small.
Question 16
16. Which of these molecules are polar? (Choose all that apply.)
NH3
CCl4
C2H6
CH3OH
Question 17
17. Which of the choices below illustrates the concept “like dissolves like?”
Iodine, I2, is more soluble in water than in oil.
Iodine, I2, is more soluble in oil than in water.
Vinegar, CH3COOH, is more soluble in oil than in water.
Sodium chloride, NaCl, is more soluble in oil than in water.
256
HISTORY CONNECTION
HISTORY
CONNECTION
In 2004, Richard Axel and Linda Buck shared a Nobel prize for their advances in understanding the mechanism of smell. Axel and Buck found that mammals have approximately 1000 different genes for olfactory receptors, which led to a better understanding of smell.

Question 18
18. Which of the following cannot be explained by describing the intermolecular forces between molecules?
Water molecules form drops rather than spreading out on wax paper.
Water is a liquid at room temperature while methane is a gas at room temperature, even though both water and methane have similar molecular mass.
The O–H bond in water is polar because of differences in electronegativity of the atoms.
Oil tends to float on water while ethanol tends to dissolve in water.
Question 19
19. Which group of elements has the highest electronegativity values?
C, H, O
O, Cl, F
Ne, H, C
Cl, Br, I
Question 20
20. Which of the following molecules has a mirror-image isomer?
CH(CH3)FBr
CHF3
CH2F2
CF4