STANDARDIZED TEST PREPARATION
Multiple Choice
Choose the best answer.
Question 1
1. Which of these is best classified as energy as opposed to matter?
safety match
potassium chlorate, KClO3(s)
fireworks
light
Use the following to answer Exercises 2 and 3.
A solution of sodium bicarbonate is mixed with a solution of hydrochloric acid in a beaker. A solution of sodium chloride and carbonic acid then forms. A thermometer inside the beaker indicates that the temperature decreased from 24 ºC to 17 ºC.
NaHCO3(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2CO3(aq)
Question 2
2. What evidence would indicate that energy was transferred from the surroundings to the products of the reaction in the beaker?
The products are aqueous. No precipitate formed.
Both the products and reactants include acids.
The beaker would feel cold to the touch.
The beaker would feel hot to the touch.
Question 3
3. Which correctly names this process?
endothermic process
exothermic process
equilibrium process
combustion process
Question 4
4. Water condenses on the outside of a cold glass of lemonade on a warm day. Which of the following correctly describes this process?
When water vapor condenses, energy is transferred from the surroundings to the gaseous water molecules, thereby lowering the temperature.
When water vapor condenses, energy is transferred to the surroundings, thereby lowering the temperature of the water molecules.
Condensation is a cooling process because hydrogen and oxygen react to form water molecules.
Condensation is a cooling process because gaseous water molecules collide with one another during the phase change.
Question 5
5. Choose the best description of the final temperature if 100 mL of water at 20 ºC is mixed with 50 mL of water at 80 ºC.
The final temperature will be 50 ºC because this is the average temperature.
The final temperature will less than 50 ºC because the 100 mL sample has the greater volume.
The final temperature will greater than 50 ºC because the 50 mL sample has the higher temperature.
The final temperature cannot be determined with the information given.
Question 6
6. Which cup of water gets the hottest, if the initial temperature is the same?
160 calories of energy are transferred to 32 mL of water.
525 calories of energy are transferred to 105 mL of water.
2375 calories of energy are transferred to 475 mL of water.
Each cup of water will reach the same final temperature.
604
Question 7
7. The specific heat capacities for several substances are listed in the following table.
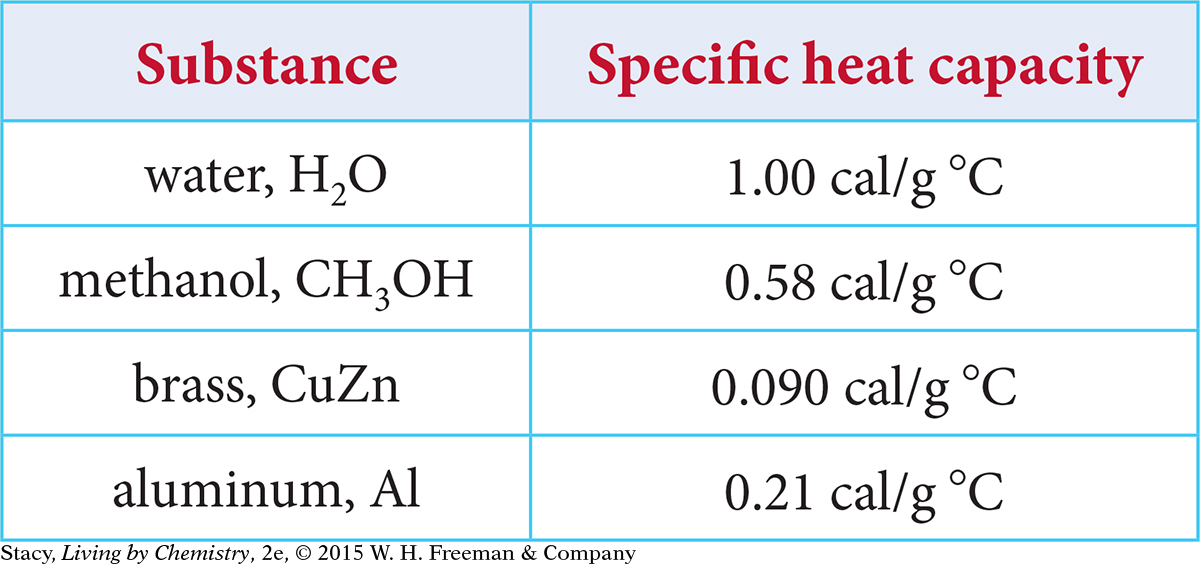
Which substance would require the most energy to be tranferred to raise the temperature from 20 ºC to 30 ºC?
water
methanol
brass
aluminum
Question 8
8. If the specific heat capacity is 0.49 cal/g ºC for ice and 1.0 cal/g ºC for liquid water, how much energy must be transferred to a 32 g sample of ice to raise its temperature from –4.0 ºC to 24 ºC? The heat of fusion of water is 79.9 cal/g ºC.
770 cal
820 cal
3300 cal
3400 cal
Question 9
9. The heating curve shows what happens as heat is added to water at a constant rate, starting with a piece of ice. What is present during time D?
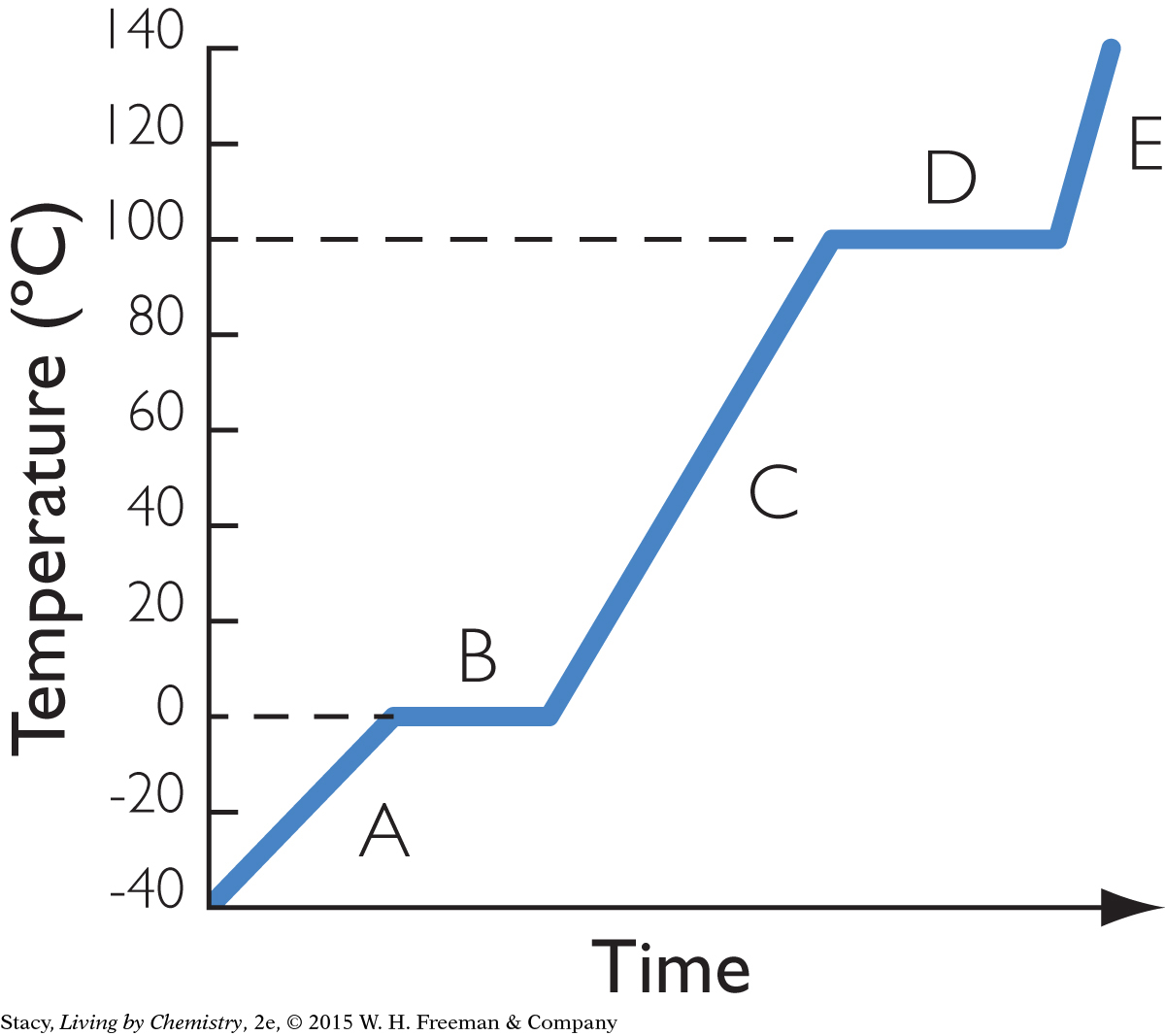
both liquid water and ice
both liquid water and water vapor
only water vapor
only liquid water
Question 10
10. Which of the following describes a plausible combustion reaction with a balanced chemical equation?
C6H14(l) + 6 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 7 H2O(l)
C2H4O2(l) + 2 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l)
2 Li(s) + O2(g) → Li2O(s)
2 MgO(s) + O2(g) → 2 MgO2(s)
Question 11
11. A student performed a calorimetry experiment where 1.3 g of crushed potato chips were burned to warm 25.0 mL of water. If the temperature of the water increased by 6.00 ºC, how much energy per gram was released by the combustion of the crushed chips?
0.416 cal/g
115 cal/g
150 cal/g
195 cal/g
Question 12
12. The combustion of 2.6 g of octane transferred energy to 926 mL of water. If the temperature of the water increased from 22 ºC to 54 ºC, how many kilojoules of energy were transferred to the water?
0.083 kJ
0.35 kJ
29 kJ
120 kJ
605
Use the following table to answer Exercises 13 and 14.
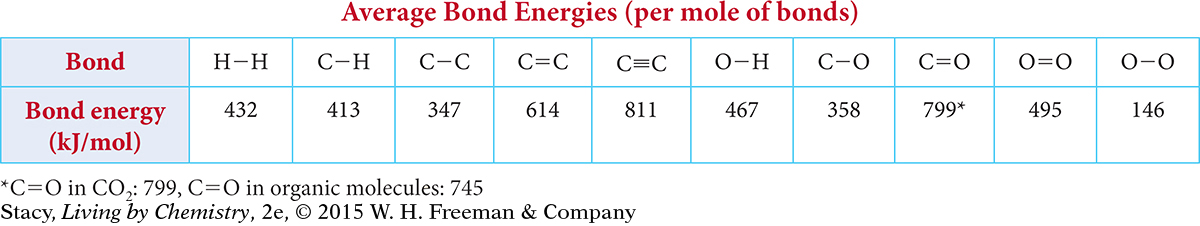
Question 13
13. What is the total energy required to break all the bonds in 1 mole of ethanol, C2H6O?
880 kJ/mol
1120 kJ/mol
3240 kJ/mol
4150 kJ/mol
Question 14
14. Based on bond energies, what is the energy change for the combustion of propane?
C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g)
22060 kJ/mol
2060 kJ/mol
215,000 kJ/mol
15,000 kJ/mol
Question 15
15. Which process could be represented correctly by the energy diagram?
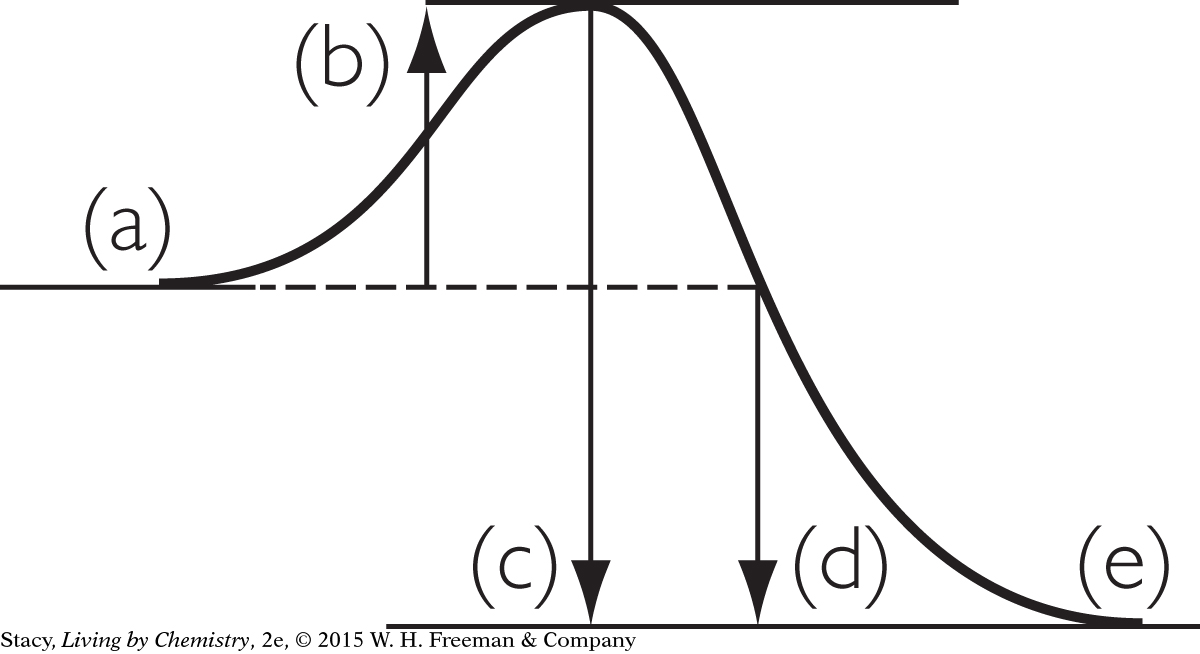
An ice cube is melting at 0 ºC.
H2O(g) → H2(g) + O2(g) ΔH = +482 kJ
2 C4H10(g) + 13 O2(g) → 8 CO2(g) + 10 H2O(g)
Ammonium chloride is dissolved in water. The temperature cools by 16 ºC.
Question 16
16. Which of these processes will result in an increase of the speed of the process?
Use cool water to dissolve sugar crystals.
Crush charcoal into smaller pieces before lighting.
Decrease the concentration of detergent to remove a stain.
Put a rusty nail in a small container sealed with a lid.
Question 17
17. What would you expect to observe if you added aluminum metal to a solution of copper (II) chloride? Use the activity series diagram below to answer.
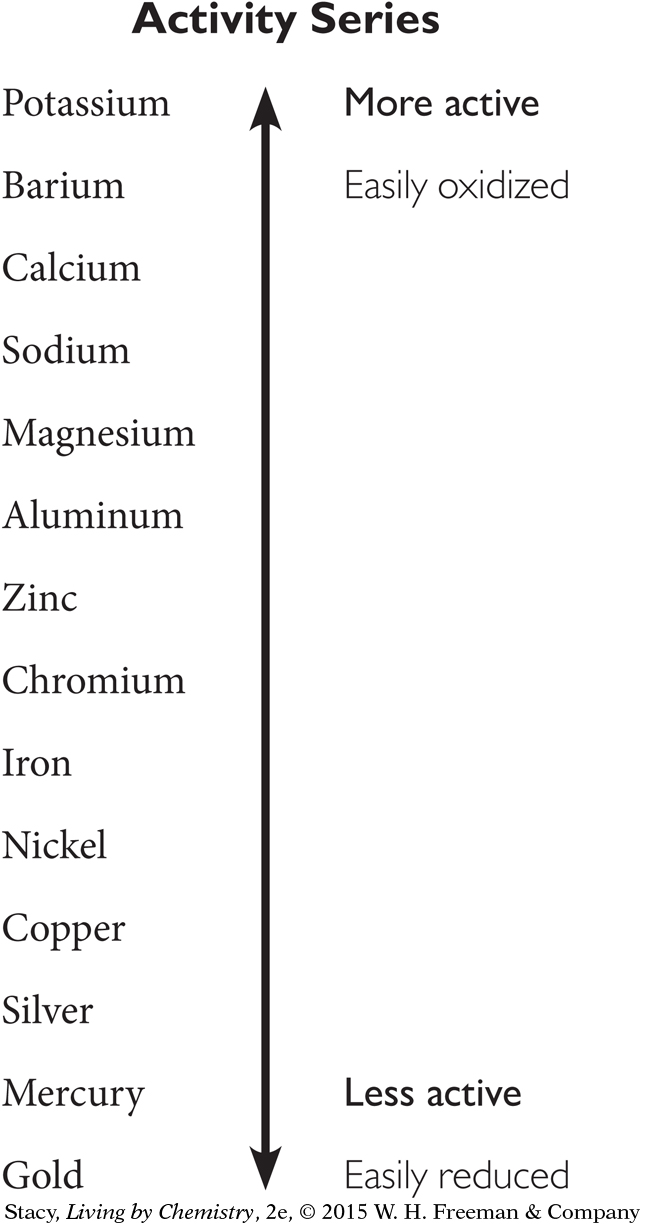
Aluminum would dissolve as copper oxidized.
Copper would dissolve as aluminum oxidized.
Copper would precipitate as copper oxidized.
Copper would precipitate as aluminum oxidized.
606
Question 18
18. What occurs in an electrochemical cell using the two half-reactions shown below?
| Li+ + e– → Li | –3.05 V |
| Zn2+ + 2e– → Zn | –0.76 V |
Li is reduced; Zn is oxidized; cell is 2.29 V.
Li is reduced; Zn is oxidized; cell is 3.81 V.
Zn is reduced; Li is oxidized; cell is 2.29 V.
Zn is reduced; Li is oxidized; cell is 3.81 V.
Question 19
19. When visible light strikes a mirror, the light is mostly
Absorbed by the mirror.
Transmitted by the mirror.
Absorbed and transmitted by the mirror.
Reflected by the mirror.
Question 20
20. Red light has a wavelength of 7.5 × 10–7 m and a frequency of 4.0 × 1014 Hz. Blue light has a shorter wavelength. Which statement is true about blue light?
Blue light has a higher frequency compared with red light.
Blue light has a greater speed compared with red light.
Blue light has a lower energy compared with red light.
Blue light has the same speed as red light but a lower frequency.
Question 21
21. The wavelength of a radio wave is 300 m. What is the frequency of this wave?
10 Hz
1,000 Hz
1,000,000 Hz
100,000,000 Hz
Question 22
22. Spectroscopy is a method that can be used to determine
The speed of light.
The density of a substance.
The concentration of a solution.
The mass of a substance.