Indicating verb tenses
Contents:
Using present-tense forms
Using past-tense forms
Using future-tense forms

In English, you must clearly indicate the time of the action in every verb or verb phrase by using the correct tense form. Tenses show when the action or condition expressed by a verb occurs. The three simple tenses are present tense, past tense, and future tense.
| PRESENT TENSE | I ask, I write |
| PAST TENSE | I asked, I wrote |
| FUTURE TENSE | I will ask, I will write |
More complex aspects of time are expressed through progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive forms of the simple tenses. (Although this terminology may sound complicated, native English speakers regularly use all these tense forms.)
| PRESENT PROGRESSIVE | she is asking, she is writing |
| PAST PROGRESSIVE | she was asking, she was writing |
| FUTURE PROGRESSIVE | she will be asking, she will be writing |
| PRESENT PERFECT | she has asked, she has written |
| PAST PERFECT | she had asked, she had written |
| FUTURE PERFECT | she will have asked, she will have written |
| PRESENT PERFECT PROGRESSIVE | she has been asking, she has been writing |
| PAST PERFECT PROGRESSIVE | she had been asking, she had been writing |
| FUTURE PERFECT PROGRESSIVE | she will have been asking, she will have been writing |
The simple tenses locate an action only within the three basic time frames of present, past, and future. Progressive forms express continuing actions; perfect forms express actions completed before another action or time in the present, past, or future; perfect progressive forms express actions that continue up to some point in the present, past, or future.
 Using present-tense forms
Using present-tense forms
The present tense includes simple, progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive forms.
Simple present
The simple present tense indicates actions or conditions occurring now and those occurring habitually.
They are very angry about the decision.
I eat breakfast every day at 8:00 AM.
Love conquers all.
The simple present can also indicate a scheduled future event if the sentence explains when the event will take place.
Classes begin next week.
Write about general truths or scientific facts in the simple present, even when the predicate of the sentence is in the past tense.

Use the simple present, not the past tense, when writing about action in literary works.

In general, use the simple present when you are quoting, summarizing, or paraphrasing someone else’s writing.
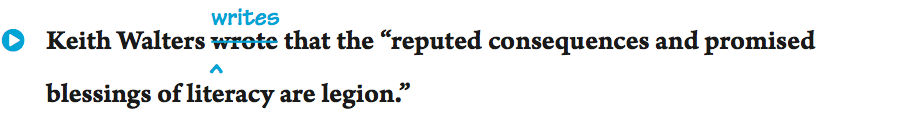
But in an essay using APA (American Psychological Association) style, report your experiments or another researcher’s work in the past tense (wrote, noted) or the present perfect (has reported).

Present progressive
Use the present progressive form when an action is in progress now. The present progressive uses a present form of be (am, is, are) and the -ing form of the main verb.
He is directing a new film.
In contrast, use the simple present tense for actions that frequently occur during a period that might include the present, but that is not necessarily happening now.

With an appropriate expression of time, you can use the present progressive to indicate a scheduled event in the future.
We are having friends over for dinner tomorrow night.
Some verbs are rarely used in progressive forms in formal writing. These verbs are said to express unchanging conditions or mental states: believe, belong, hate, know, like, love, need, own, resemble, understand. However, in spoken and informal written English, progressive forms like I’m loving this and You’re not understanding me correctly are becoming increasingly common.
Present perfect
The present perfect tense indicates actions begun in the past and either completed at some unspecified time in the past or continuing into the present. To form the present perfect, use a present form of have (has, have) and a perfect participle such as talked.
Uncontrolled logging has destroyed many tropical forests.
Present perfect progressive
Use the present perfect progressive form to indicate continuous actions begun in the past and continuing into the present. To form the present perfect progressive, use the present perfect form of be (have been, has been) and the -ing form of the main verb.
The two sides have been trying to settle the case out of court.
Since September, he has been writing a novel in his spare time.
 Using past-tense forms
Using past-tense forms
In the past tense, you can use simple past, past progressive, past perfect, and past perfect progressive forms.
Simple past
Use the simple past to indicate actions or conditions that occurred at a specific time and do not extend into the present.
Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939.
Past progressive
Use the past progressive when an action was in progress in the past. It is used relatively infrequently in English, and it focuses on duration or calls attention to a past action that went on at the same time as something else. The present progressive uses a past form of be (was, were) and the -ing form of the main verb.
Lenin was living in exile in Zurich when the tsar was overthrown.
Past perfect
Use the past perfect to indicate actions or conditions completed by a specific time in the past or before some other past action occurred. To form the past perfect, use had and a perfect participle such as talked.
By the fourth century, Christianity had become the state religion.
Past perfect progressive
Use the past perfect progressive form to indicate a continuing action or condition in the past that had already been happening when some other past action happened. (You will probably need the simple past tense for the other past action.) To form the past perfect progressive, use the past perfect form of be (had been) and the -ing form of the main verb.
Carter had been planning a naval career until his father died.
 Using future-tense forms
Using future-tense forms
The future tense includes simple, progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive forms.
Simple future
Use the simple future (will plus the base form of the verb) to indicate actions or conditions that have not yet begun.
The exhibition will come to Washington in September.
Future progressive
Use the future progressive to indicate continuing actions or conditions in the future. The future progressive uses the future form of be (will be) and the -ing form of the main verb.
The loans will be coming due over the next two years.
Future perfect
Use the future perfect to indicate actions or conditions that will be completed by or before some specified time in the future. To form the future perfect, use will have and a perfect participle such as talked.
By next summer, she will have published the results of the research study.
Future perfect progressive
Use the future perfect progressive to indicate continuing actions or conditions that will be completed by some specified time in the future. To form the future perfect progressive, use the future perfect form of be (will have been) and the -ing form of the main verb.
As of May 1, I will have been living in Tucson for five years.