The Tsar and His People
Developments in Russia took a chaotic turn with the reign of Ivan IV (r. 1533–
As landlords demanded more from the serfs who survived the persecutions, growing numbers of peasants fled toward wild, recently conquered territories to the east and south. There they joined free groups and warrior bands known as Cossacks. Ivan responded by tying peasants more firmly to the land and to noble landholders. Simultaneously, he ordered that urban dwellers be bound to their towns and jobs so that he could tax them more heavily. These restrictions checked the growth of the Russian middle classes and stood in sharp contrast to economic and social developments in western Europe.
After the death of Ivan and his successor, Russia entered a chaotic period known as the Time of Troubles (1598–
Although the new tsar successfully reconsolidated central authority, he and his successors did not improve the lot of the common people. In 1649, a law extended serfdom to all peasants in the realm, giving lords unrestricted rights over their serfs and establishing penalties for harboring runaways. Social and religious uprisings among the poor and oppressed continued through the seventeenth century.
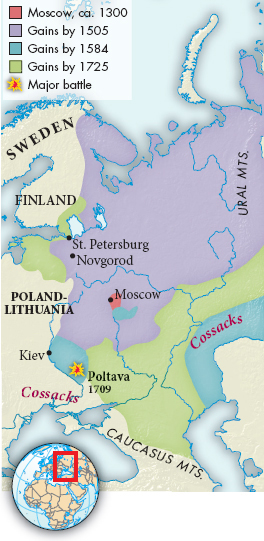
Despite the turbulence of the period, the Romanov tsars, like their Western counterparts, made several important achievements during the second half of the seventeenth century. After a long war, Russia gained land in Ukraine from Poland in 1667 and completed the conquest of Siberia by the end of the century. Territorial expansion was accompanied by growth of the bureaucracy and the army. The tsars employed foreign experts to reform the Russian army, and they enlisted Cossack warriors to fight Siberian campaigns. Russian imperialist expansion to the east paralleled the Western powers’ exploration and conquest of the Atlantic world in the same period.