Metternich and Conservatism
The political ideals of conservatism, often associated with Austrian foreign minister Prince Klemens von Metternich (1773–1859), dominated Great Power discussions at the Congress of Vienna. Austrian foreign minister from 1809 to 1848, the cosmopolitan and conservative Metternich had a pessimistic view of human nature, which he believed was ever prone to error, excess, and self-serving behavior. The disruptive events of the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Wars confirmed these views, and Metternich’s conservatism would emerge as a powerful new political ideological force in response to the revolutionary age.
Metternich firmly believed that liberalism, as embodied in revolutionary America and France, bore the responsibility for the untold bloodshed and suffering caused by twenty-five years of war. Like Edmund Burke (see "The International Response" in Chapter 19) and other conservatives, Metternich blamed liberal middle-class revolutionaries for stirring up the lower classes. Authoritarian governments, he concluded, were necessary to protect society from the baser elements of human behavior. Organized religion was another pillar of strong government; Metternich maintained that Christian morality was a vital bulwark against radical change.
Metternich defended his class and its rights and privileges with a clear conscience. The church and nobility were among Europe’s most ancient and valuable institutions, and conservatives regarded tradition as the basic foundation of human society.
The threat of liberalism appeared doubly dangerous to Metternich because it generally went with aspirations for national independence. Liberals believed that each people, each national group, had a right to establish its own independent government and fulfill its own destiny. The idea of national self-determination under constitutional government was repellent to Metternich because it threatened to revolutionize central Europe and destroy the Austrian Empire.
After centuries of war, royal intermarriage, and territorial expansion, the vast Austrian Empire of the Habsburgs included many peoples within its borders (Map 21.2). The peoples of the Austrian Empire spoke at least eleven different languages, observed vastly different customs, and lived with a surprising variety of regional civic and political institutions. The multiethnic state Metternich served had strengths and weaknesses. A large population and vast territories gave the empire economic and military clout, but its potentially dissatisfied nationalities undermined political unity. In these circumstances, Metternich virtually had to oppose liberalism and nationalism — if Austria was to remain intact and powerful, it could hardly accommodate ideologies that supported national self-determination.
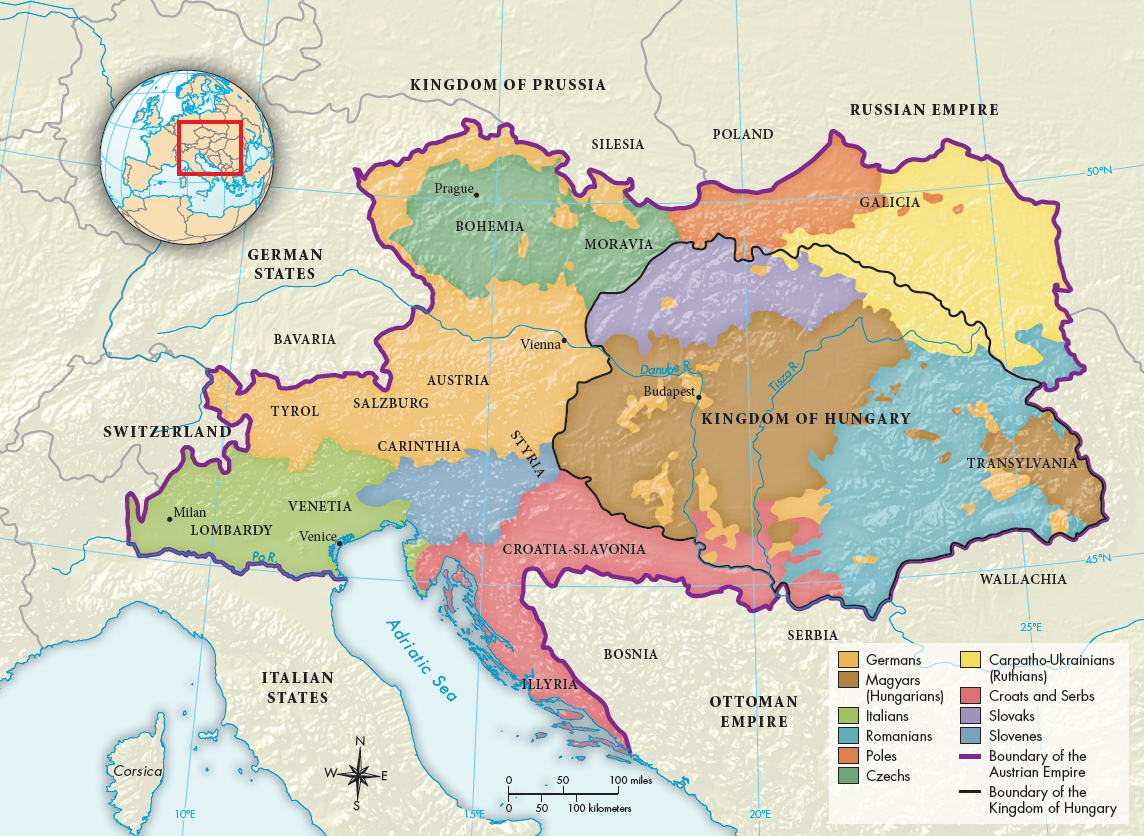
MAP 21.2
Peoples of the Habsburg Monarchy, 1815The old dynastic state ruled by the Habsburg monarchy was a patchwork of nationalities and ethnic groups, in which territorial borders barely reflected the diversity of where different peoples actually lived. Note especially the widely scattered pockets of Germans and Hungarians. How do you think this ethnic diversity might have led to the rise of national independence movements in the Austrian Empire?
On Austria’s borders, Russia and, to a lesser extent, the Ottoman Empire supported and echoed Metternich’s efforts to hold back liberalism and nationalism. These far-flung empires were both absolutist states with powerful armies and long traditions of expansion and conquest. Because of those conquests, both were also multinational empires with many peoples, languages, and religions. After 1815, both of these multinational absolutist states worked to preserve their respective traditional conservative orders. Only after 1840 did each in turn experience a profound crisis and embark on a program of fundamental reform and modernization, as we shall see in Chapter 23.
