Communicating junctions allow the passage of molecules between cells.
Not all cell junctions are involved in the adhesion of cells to each other or in sealing a layer of cells. Gap junctions (Fig. 10.14) of animal cells and plasmodesmata of plant cells (see Fig. 5.17b) permit materials to pass directly from the cytoplasm of one cell to the cytoplasm of another. Gap junctions are a complex of integral membrane proteins called connexins arranged in a ring. The ring of connexin proteins connects to a similar ring of proteins in the membrane of an adjacent cell. Ions and signaling molecules pass through these junctions, allowing cells to communicate. In the heart, for example, ions pass though gap junctions connecting cardiac muscle cells. This rapid electrical communication allows the muscle cells to beat in a coordinated fashion (Chapter 39).
Plasmodesmata (the singular form is plasmodesma) are passages through the cell walls of adjacent plant cells. They are similar to gap junctions in that they allow cells to exchange ions and small molecules directly, but the similarity ends there. In plasmodesmata, the plasma membranes of the two connected cells are actually continuous. The size of the opening is considerably larger than that of gap junctions, large enough for cells to transfer RNA molecules and proteins, an ability that is especially important during embryonic development. Plasmodesmata allow plant cells to send signals to one another despite being enclosed within rigid cell walls.
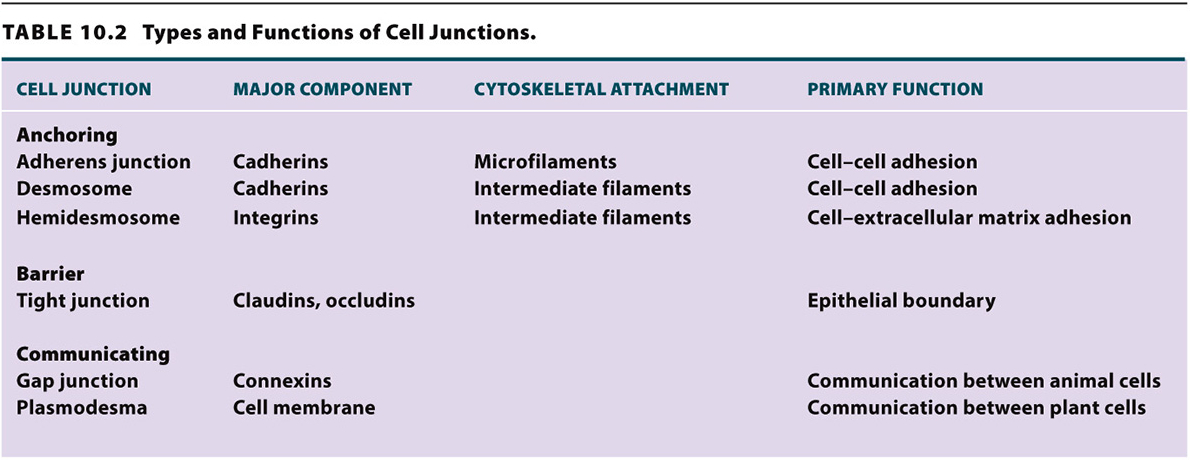
From this discussion, we see that cell junctions interact to create stable communities of cells in the form of tissues and organs. These cell junctions are important for the functions of tissues, allowing cells to adhere to each other and the extracellular matrix, act as a barrier, and communicate rapidly. The types and functions of the cell junctions are summarized in Table 10.2.
Quick Check 3 Which type(s) of cell junction prevent(s) substances from moving through the space between cells? Which type(s) of cell junction attach(es) cells to one another?
Quick Check 3 Answer
Tight junctions prevent the passage of materials through the space between cells. Adherens junctions and desmosomes attach cells to one another.