DNA damage can affect both DNA backbone and bases.
Most mutations are spontaneous and occur naturally. However, mutations can also be induced by radiation or chemicals. Mutagens are agents that increase the probability of mutation. The presence of a mutagen can increase the probability of mutation by a factor of 100 or more.
304
Some of the most important types of DNA damage induced by mutagens are illustrated in Fig. 14.16, which shows a highly damaged DNA molecule. Some types of damage affect the structure of the DNA double helix. These include breaks in the sugar–
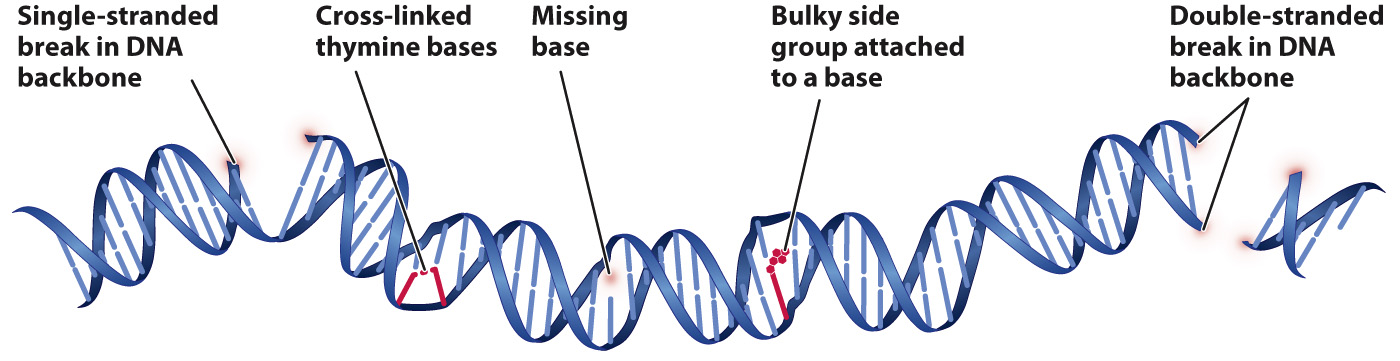
Yet another type of structural damage is loss of a base from one of the deoxyribose sugars, resulting in a gap in one strand where no base is present. Spontaneous loss of a purine base is one of the most common types of DNA damage, occurring at the rate of about 13,000 purines lost per human cell per day. Most of these mutations result from the interaction between DNA and normal metabolic by-
Other types of damage affect the bases themselves. Bases that are chemically damaged tend to mispair. Some bases are damaged spontaneously when reaction with a water molecule replaces an amino group (–NH2) with an atom of oxygen (=O), which interferes with the base’s ability to form hydrogen bonds with a complement. Some naturally occurring molecules mimic bases and can be incorporated into DNA and cause nucleotide substitutions. Caffeine mimics a purine base, for example (although to be mutagenic, the amount of caffeine required is far more than any normal person could possibly consume).
Chemicals that are highly reactive tend to be mutagenic, often because they add bulky side groups to the bases that hinder proper base pairing. The main environmental source of such chemicals is tobacco smoke. Other chemicals can perturb the DNA replication complex and cause the insertion or deletion of one or occasionally several nucleotides.
Quick Check 3 Earlier, we described the Lederbergs’ experiment, which demonstrated that mutations are not directed by the environment. But mutagens, which are environmental, can lead to mutations. What’s the difference?
Quick Check 3 Answer
Mutations are random; they are not directed by the environment. This does not mean that the environment cannot affect the rate of mutation. Mutagens increase the rate of the mutation, but they cannot induce specific mutations that would be beneficial to the organism in response to the environment.