Atoms consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
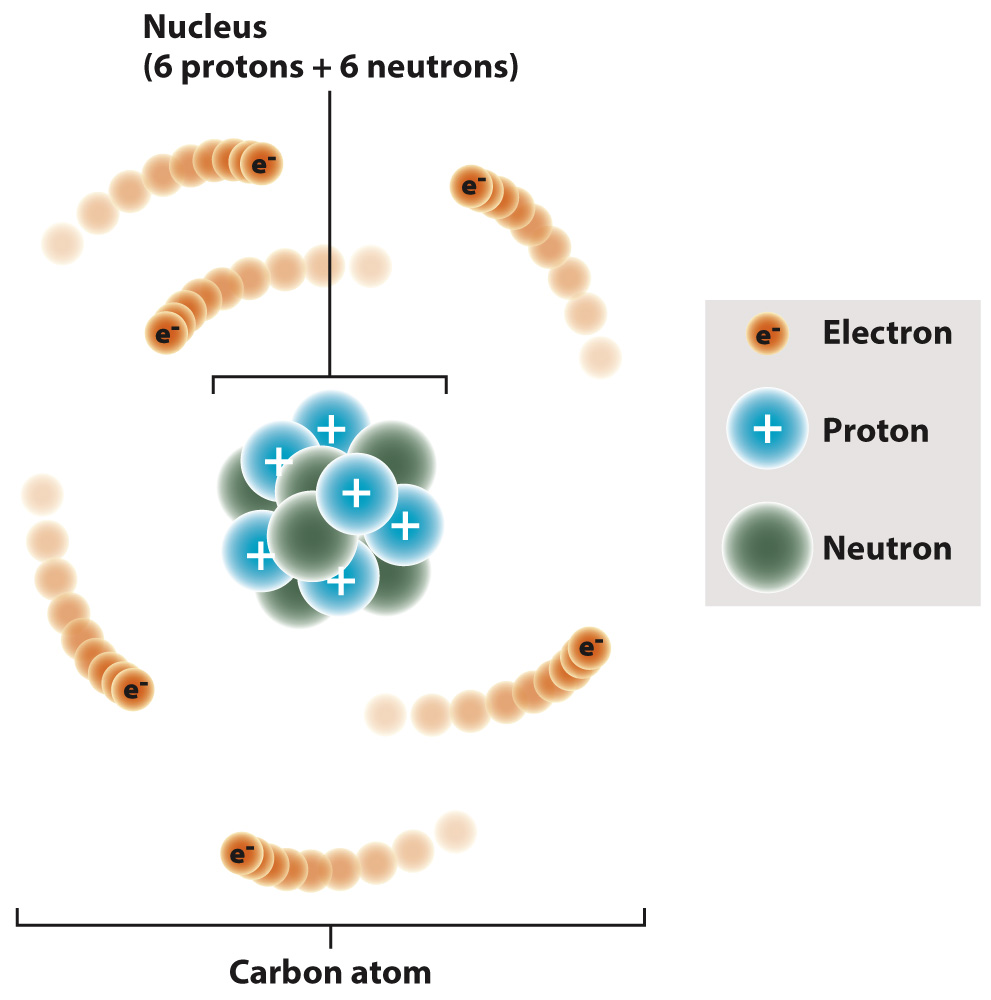
Elements are composed of atoms. The atom contains a dense central nucleus made up of positively charged particles called protons and electrically neutral particles called neutrons. A third type of particle, the negatively charged electron, moves around the nucleus at some distance from it. Carbon, for example, typically has six protons, six neutrons, and six electrons (Fig. 2.1). The number of protons, or the atomic number, specifies an atom as a particular element. An atom with one proton is hydrogen, for example, and an atom with six protons is carbon.
Together, the protons and neutrons determine the atomic mass, the mass of the atom. Each proton and neutron, by definition, has a mass of 1, whereas an electron has negligible mass. The number of neutrons in atoms of a particular element can vary, changing its mass. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. For example, carbon has three isotopes: About 99% of carbon atoms have six neutrons and six protons, for an atomic mass of 12; about 1% have seven neutrons and six protons, for an atomic mass of 13; and only a very small fraction have eight neutrons and six protons, for an atomic mass of 14. The atomic mass is sometimes indicated as a superscript to the left of the chemical symbol. For instance, 12C is the isotope of carbon with six neutrons and six protons.
Typically, an atom has the same number of protons and electrons. Because a carbon atom has six protons and six electrons, the positive and negative charges cancel each other out and the carbon atom is electrically neutral. Some chemical processes cause an atom to either gain or lose electrons. An atom that has lost an electron is positively charged, and one that has gained an electron is negatively charged. Electrically charged atoms are called ions. The charge of an ion is specified as a superscript to the right of the chemical symbol. Thus, H+ indicates a hydrogen ion that has lost an electron and is positively charged.