Fungi evolved from aquatic, unicellular, and flagellated ancestors.
Fungi are opisthokonts, members of the eukaryotic superkingdom that includes animals (Chapter 27). Among fungi, the Chytridiomycota (commonly referred to as chytrids) were the first groups to diverge. Molecular clock analysis estimates that chytrids began to diversify 800 to 700 million years ago. Today, there are about 1000 species of chytrids found in aquatic or moist environments (Fig. 34.16). Many chytrids are single cells with walls of chitin. They may also form short multinucleate structures, but they lack the well-
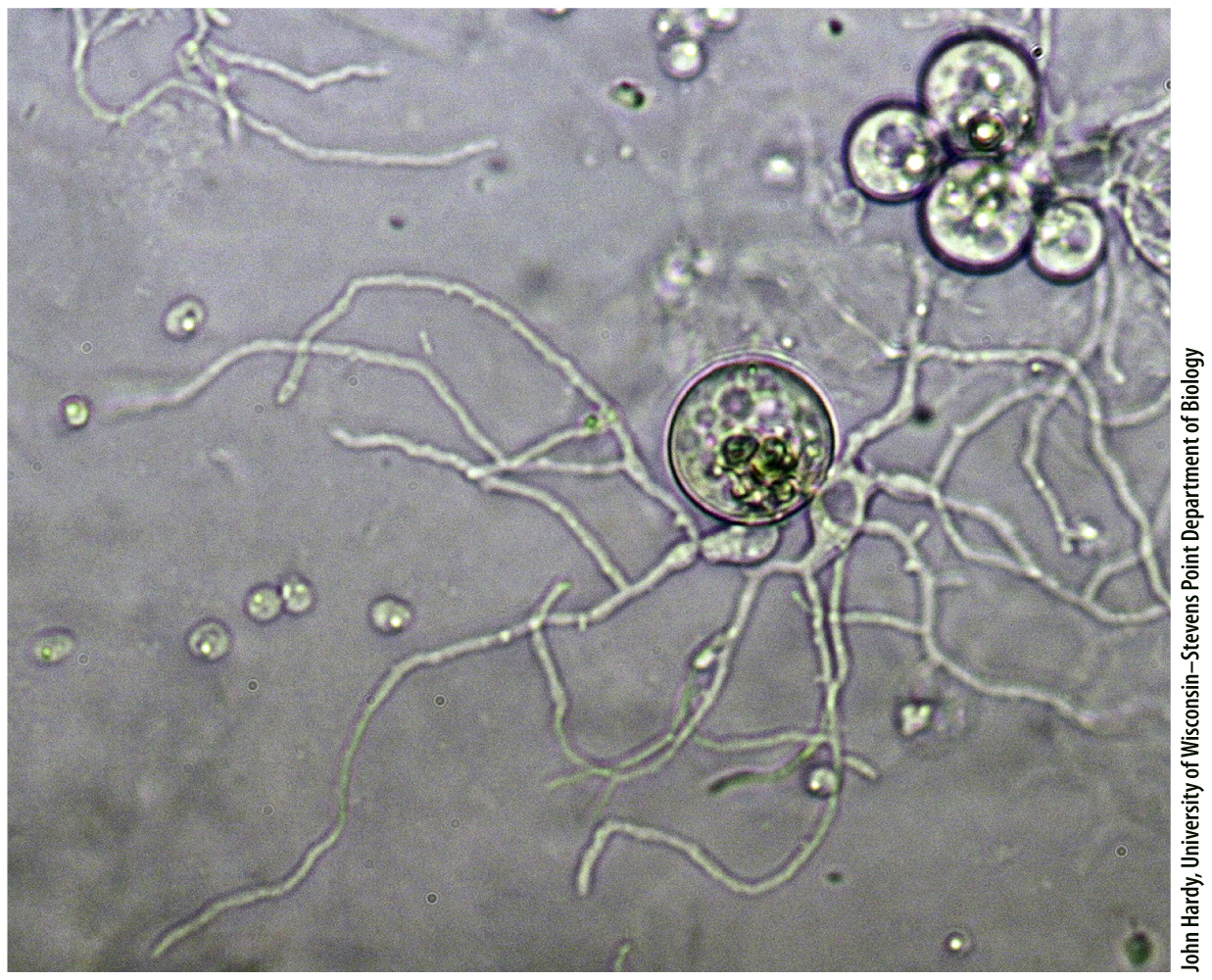
Chytrids generally disperse by flagellated spores. Sexual reproduction appears to be rare, but there is substantial life-
Most chytrids are decomposers, and a few of them are pathogenic. Notably, infection by the chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis may be a cause of a widespread decline in amphibian populations (Chapter 49).