Fungi transport materials within their hyphae.
Fungi can transport food and signaling molecules across long distances in mycelia. As a result, they are able to grow between resource patches and to produce reproductive structures such as mushrooms that rise up above the ground. Molecules taken up actively from the environment drive water into the cell by osmosis and thus increase turgor pressure. At the same time, growth and respiration consume these molecules, resulting in a decrease in turgor pressure. Such differences in turgor pressure along hyphae drives bulk flow in a manner similar to phloem transport in plants (Chapter 29). Bulk flow carries materials obtained in a nutrient-rich location so that they can fuel hyphal elongation across nutrient-poor locations. Transport by bulk flow also allows fungi to build relatively large reproductive structures aboveground. All the raw materials used to build a mushroom must be transported from hyphae in contact with a source of nutrients, such as the soil or a rotting log.
A continuous stream of cytoplasm, not divided by barriers, is essential for the long-distance movement of materials within mycelia. In early-diverging groups, the hyphae have many nuclei but no cell walls to separate them. In later-diverging groups, nuclear divisions are accompanied by the formation of septa (singular, septum), walls that partially divide the cytoplasm into separate cells (Fig. 34.2). Each septum contains one or more pores that allow water and solutes to move freely between cells. Septa play an important role when hyphae are damaged. Injury activates sealing mechanisms that plug pores in the septa, preventing the loss of pressurized cytoplasm.
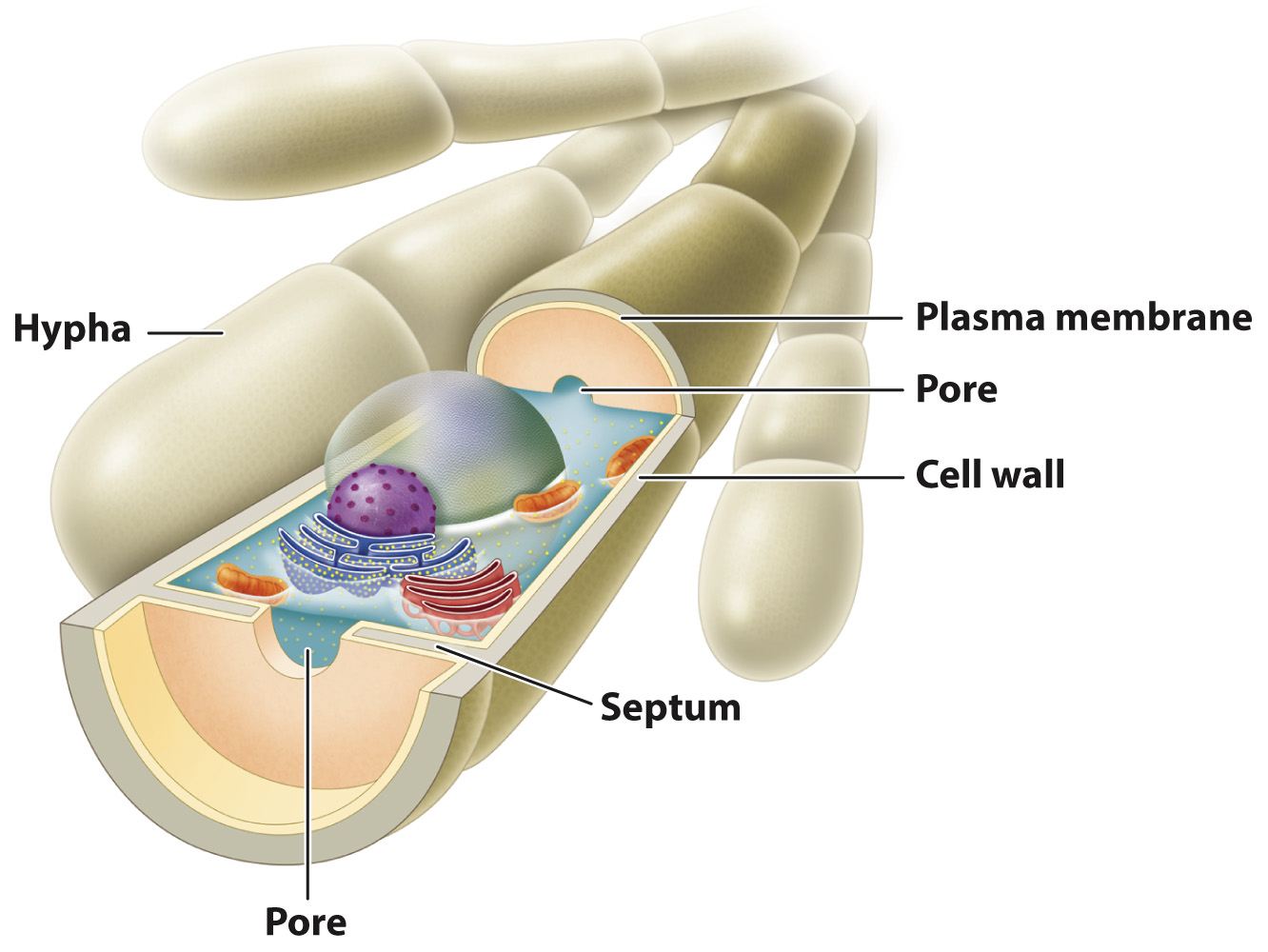
FIG. 34.2 Septa separating individual cells in fungi. Septa, partitions between cells, have pores that allow transport of solutes along the hypha.
Quick Check 1 Name two roles of hyphae.
Quick Check 1 Answer
Hyphae enable fungi to seek out new food resources; they are able to penetrate large food bodies such as rotting logs or animal carcasses. Hyphae also transport nutrients from one part of the fungus to another.
