The rigid bones of vertebrate endoskeletons are jointed for motion and can be repaired if damaged.
Endoskeletons first evolved about 350–
800
A bony or cartilaginous endoskeleton lies internal to most of an animal’s soft tissues. In contrast to exoskeletons, the endoskeletons of vertebrate animals can grow extensively and, when broken, can be repaired. Endoskeletons also provide protection for certain key internal organs, such as the brain, lungs, and heart.
The bones of vertebrate skeletons consist of a variety of tubular, rodlike, and platelike elements that form a scaffold to which the muscles attach. Because bones are rigid and hard, there are joints between adjacent bones to enable movement. Muscles attach to the skeleton by connective tissue and specialized tendons made of collagen. Tendons transmit muscle forces, allowing the forces to be redirected and transmitted over a wide range of joint motion. Tendons, like a spring, also store and recover elastic energy.
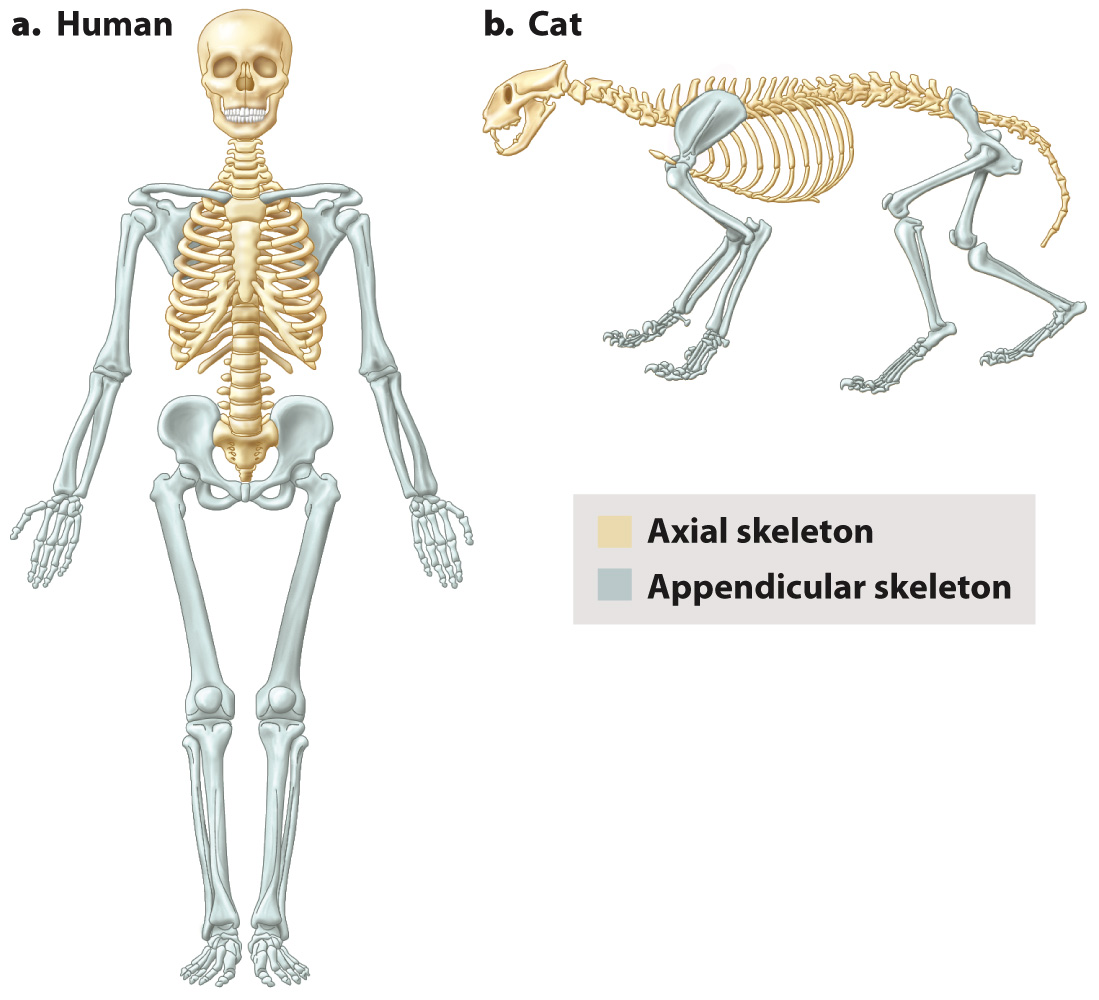
The vertebrate skeleton can be divided into axial and appendicular regions (Fig. 37.17). The axial skeleton consists of the skull and jaws of the head, the vertebrae of the spinal column, and the ribs. Bones of the skull protect the brain and sense organs of the head. The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of the limbs, including the shoulder and pelvis. The axial and appendicular regions reflect the evolutionary ancestry of vertebrates. The axial skeleton formed first, to protect the head and provide support and movement of the animal’s body by bending its body axis. As a result, the axial skeleton is the main skeletal component of fishes. The appendicular skeleton includes the pectoral and pelvic fins of fish, which evolved into limbs when vertebrate animals first moved onto land. In a special group of lobed-
Skeletal tissues have relatively few cells for their volume because they consist mostly of an extensive extracellular matrix that is secreted by specialized cells, forming connective tissue external to the cells (Chapter 10). In addition to tendon, three main extracellular tissues are produced in the formation of the vertebrate skeleton: bone, tooth enamel, and cartilage.
Bone tissue–
Articular cartilage located at the joint surfaces of a bone forms a cushion between bones meeting at a joint. The cartilage is a gel-
Quick Check 5 Glass is strong and rigid but can be easily broken. In contrast, a bone is strong and rigid but hard to break. How can this be?
Quick Check 5 Answer
Glass is composed of a single material (silica), which is rigid but can crack easily. Bone is a composite material, built of crystalline mineral reinforced by the protein collagen, enabling bone to absorb much more energy before breaking.