DNA is a linear polymer of nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds.
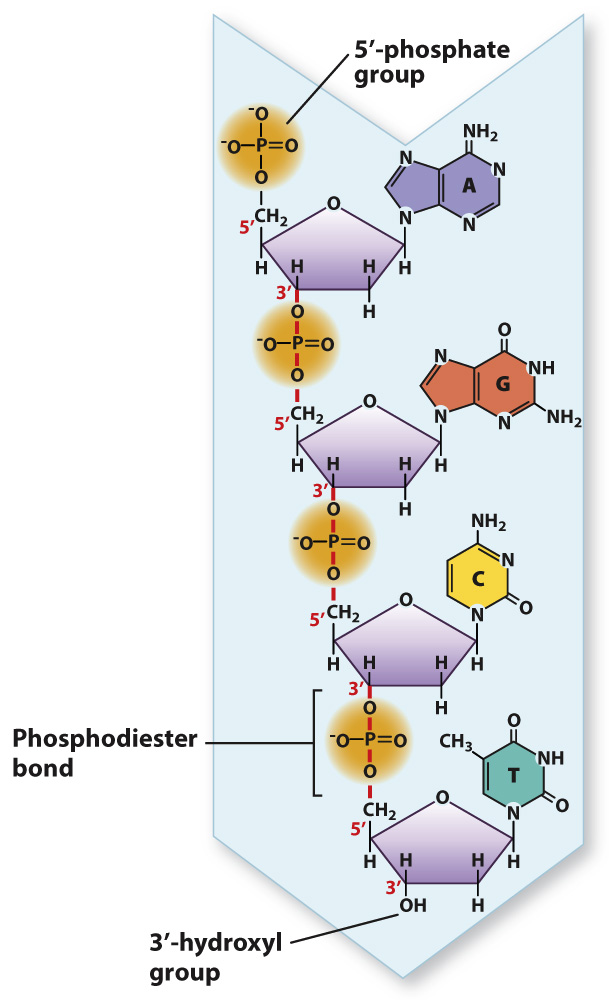
Not only were the nucleotide building blocks of DNA known before the structure was discovered, it was also known how they were linked into a polymer. The chemical linkages between nucleotides in DNA are shown in Fig. 3.7. The characteristic covalent bond that connects one nucleotide to the next is indicated by the vertical red lines that connect the 3′ carbon of one nucleotide to the 5′ carbon of the next nucleotide in line through the 5′-phosphate group. This C–
55
The phosphodiester linkages in a DNA strand give it polarity, which means that one end differs from the other. In Fig. 3.7, the nucleotide at the top has a free 5′ phosphate, and is known as the 5′ end of the molecule. The nucleotide at the bottom has a free 3 hydroxyl and is known as the 3′ end. The DNA strand in Fig. 3.7 has the sequence of bases AGCT from top to bottom, but because of strand polarity we need to specify which end is which. For this strand of DNA, we could say that the base sequence is 5′-AGCT-