The mammalian kidney has an outer cortex and inner medulla.
The paired kidneys of mammals are organized into two layers, an outer layer called the cortex and a deeper layer, surrounded by the cortex, called the medulla (Fig. 41.15). Nephrons are organized into wedge-
887
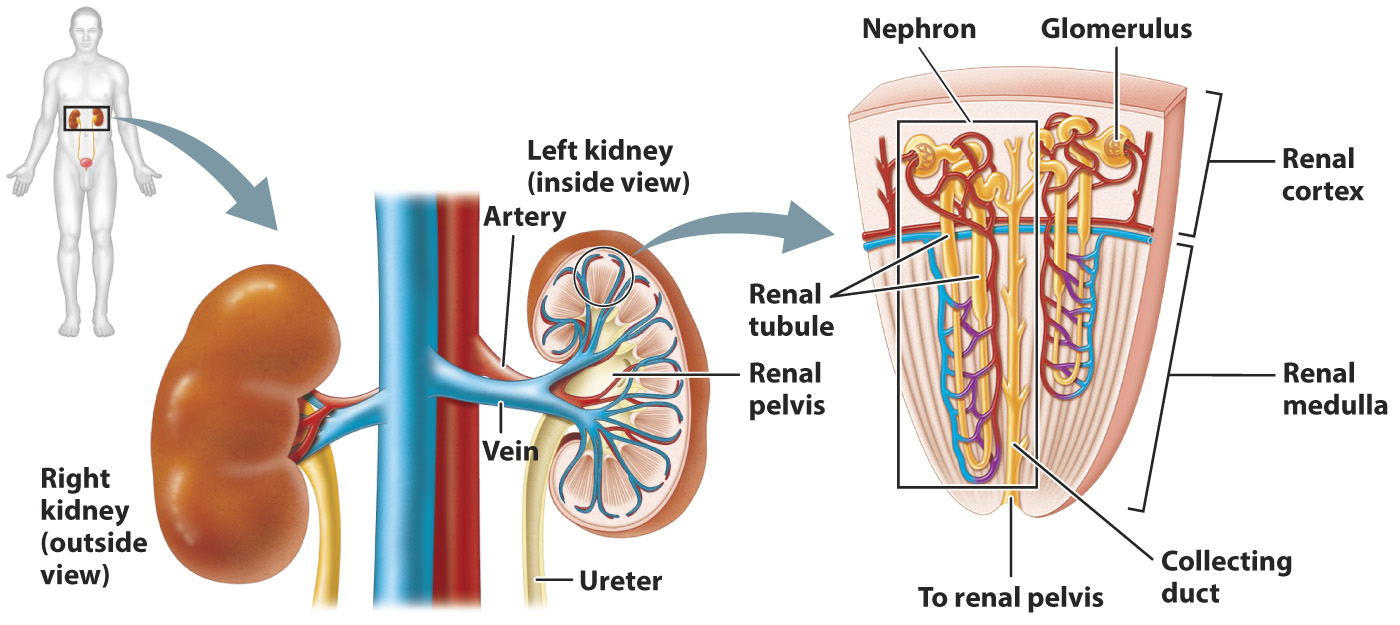
FIG. 41.15 The organization of the mammalian kidney and nephron.