Excess glucose is stored as glycogen in animals and starch in plants.
Glucose is a readily available form of energy in organisms, but it is not always broken down immediately. Excess glucose can be stored in cells and then mobilized—
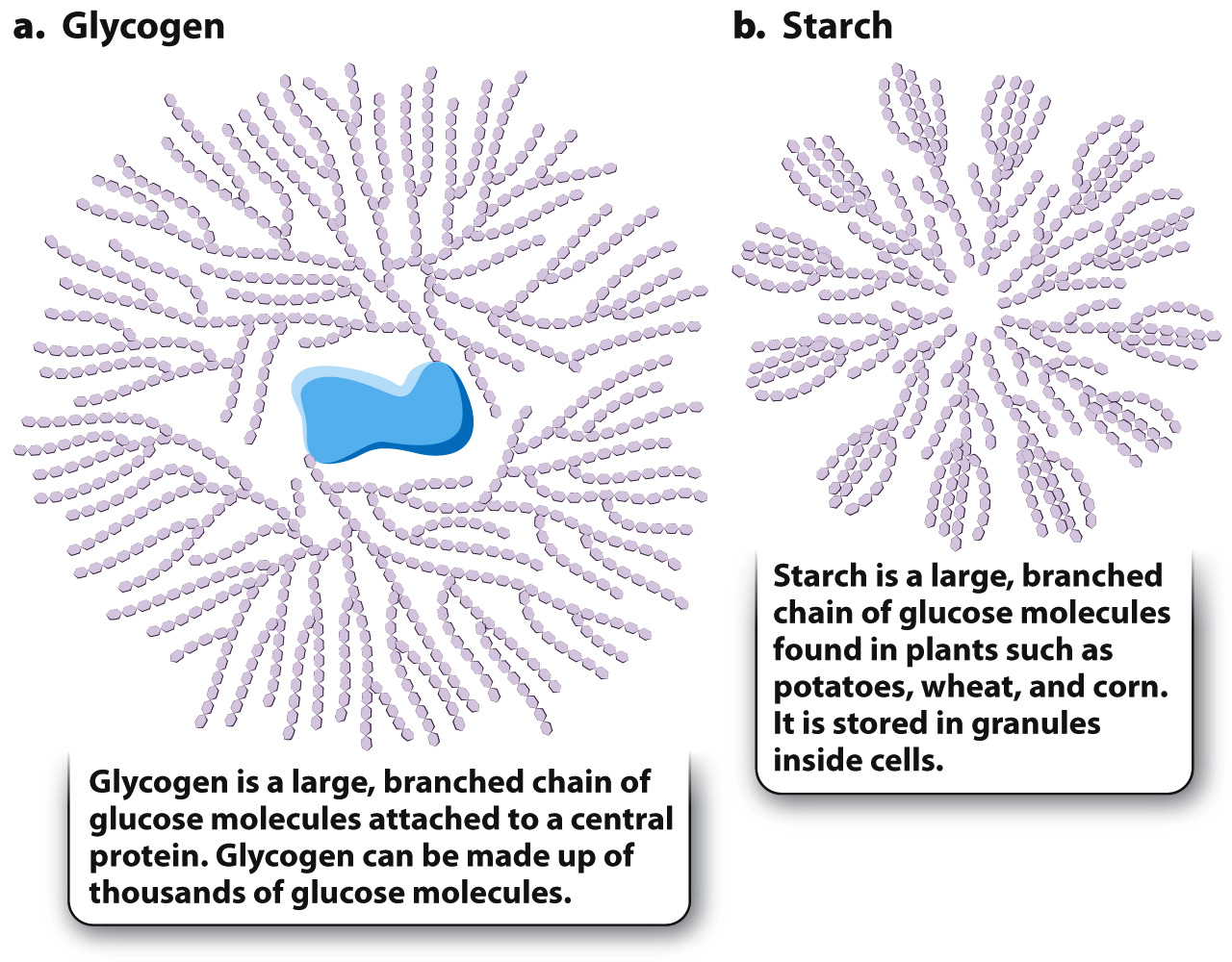
Carbohydrates that are consumed by animals are broken down into simple sugars and circulate in the blood. The level of glucose in the blood is tightly regulated. When the blood glucose level is high, as it is after a meal, glucose molecules that are not consumed by glycolysis are linked together to form glycogen in liver and muscle. Glycogen stored in muscle is used to provide ATP for muscle contraction. By contrast, the liver does not store glycogen primarily for its own use, but is a central glycogen storehouse for the whole body, able to release glucose into the bloodstream when it is needed elsewhere. Glycogen provides a source of glucose 6-