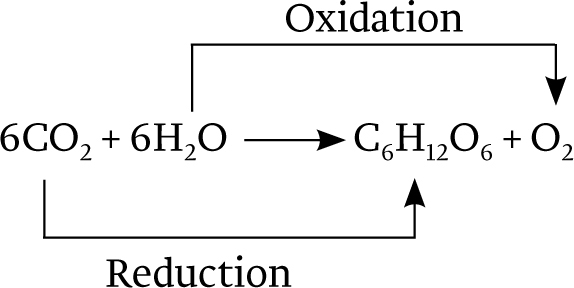
Photosynthesis is a redox reaction.
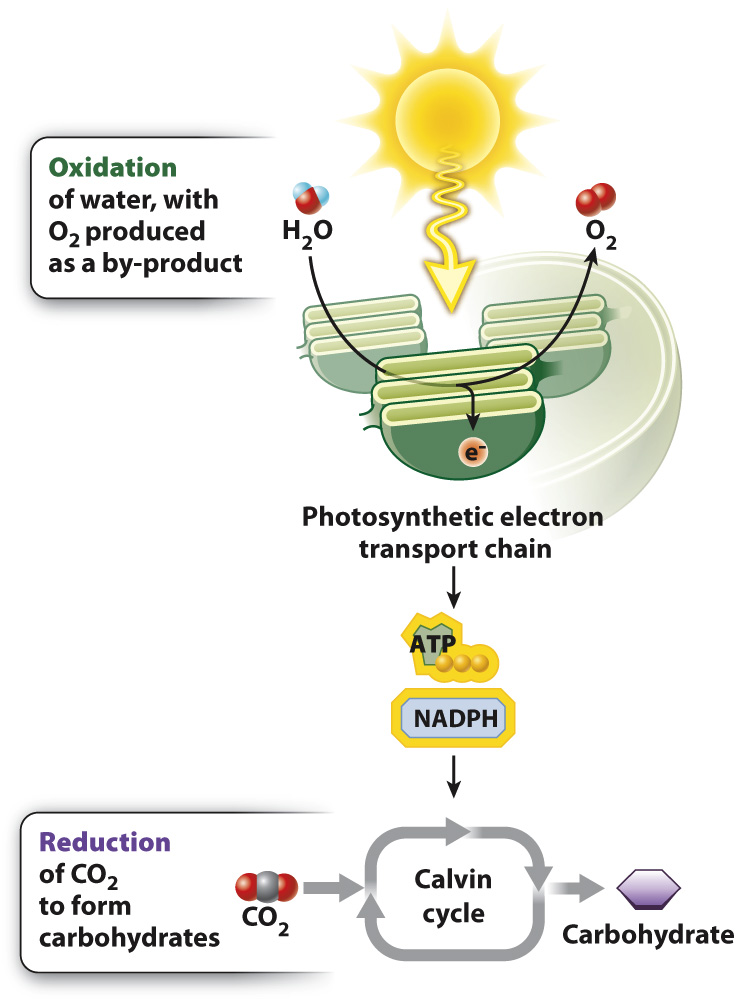
Carbohydrates are synthesized from CO2 molecules during photosynthesis, yet they have more energy stored in their chemical bonds than is contained in the bonds of CO2 molecules. Therefore, to build carbohydrates using CO2 requires an input of energy. This energy comes from sunlight.
How does energy from sunlight become incorporated into chemical bonds? The answer to this question arises from the fact that the synthesis of carbohydrates from CO2 and water is a reduction–
Where do the electrons used to reduce CO2 come from? In photosynthesis carried out by plants and many algae, the ultimate electron donor is water. The oxidation of water results in the production of electrons, protons, and O2. Thus, oxygen is formed in photosynthesis as a by-
HOW DO WE KNOW?
FIG. 8.3
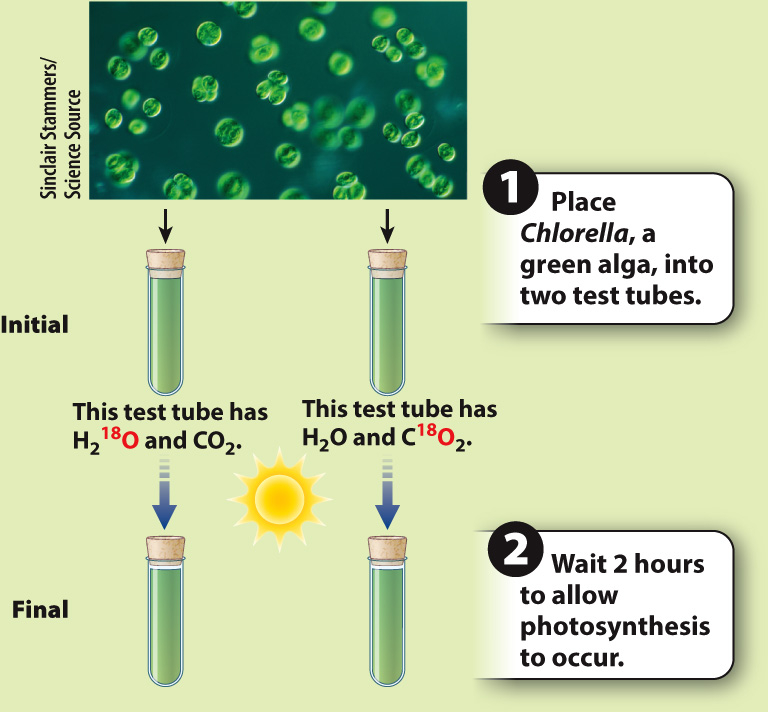
Does the oxygen released by photosynthesis come from H2O or CO2?
BACKGROUND The reactants in photosynthesis are water and carbon dioxide. Both contain oxygen, so it is unclear which one is the source of the oxygen that is produced in the reaction.
METHOD Most of the oxygen in the atmosphere is 16O, a stable isotope containing 8 protons and 8 neutrons. A small amount (0.2%) is 18O, a stable isotope with 8 protons and 10 neutrons. The relative abundance of molecules containing 16O versus 18O can be measured using a mass spectrometer. H2O and CO2 containing a high percentage of 18O can be used to determine whether the oxygen produced in photosynthesis comes from water or carbon dioxide.
EXPERIMENT
RESULT
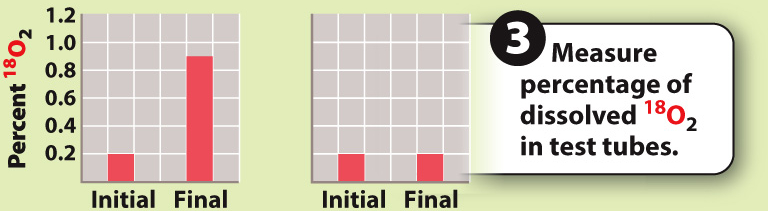
CONCLUSION The percentage of 18O increases only when water contains 18O, but not when carbon dioxide contains 18O. This finding indicates that the oxygen produced in photosynthesis comes from water, not carbon dioxide.
FOLLOW-
SOURCE Adapted from Ruben, S., M. Randall, M. Kamen, and J. L. Hyde. 1941. “Heavy Oxygen (O18) as a Tracer in the Study of Photosynthesis.” Journal of the American Chemical Society 63:877–
Overall, then, the equation for photosynthesis leading to the synthesis of glucose (C6H12O6) can be described as follows:
The oxidation of water is linked with the reduction of CO2 through a series of redox reactions in which electrons are passed from one compound to another. This series of reactions constitutes the photosynthetic electron transport chain. The process begins with the absorption of sunlight by protein–
Quick Check 1 If you want to produce carbohydrates containing the heavy oxygen (18O) isotope, should you water your plants with H218O or inject C18O2 into the air?
Quick Check 1 Answer
You should label the oxygen in CO2 (that is, inject C18O2) because the entire CO2 molecule is used in synthesizing carbohydrates, whereas H2O donates only the electron needed for the reduction step of the Calvin cycle. The extraction of electrons from water releases O2 as a by-