8.2 The Calvin Cycle
157
The Calvin cycle consists of 15 chemical reactions that synthesize carbohydrates from CO2. These reactions can be grouped into three main steps: (1) carboxylation, in which CO2 is added to a 5-
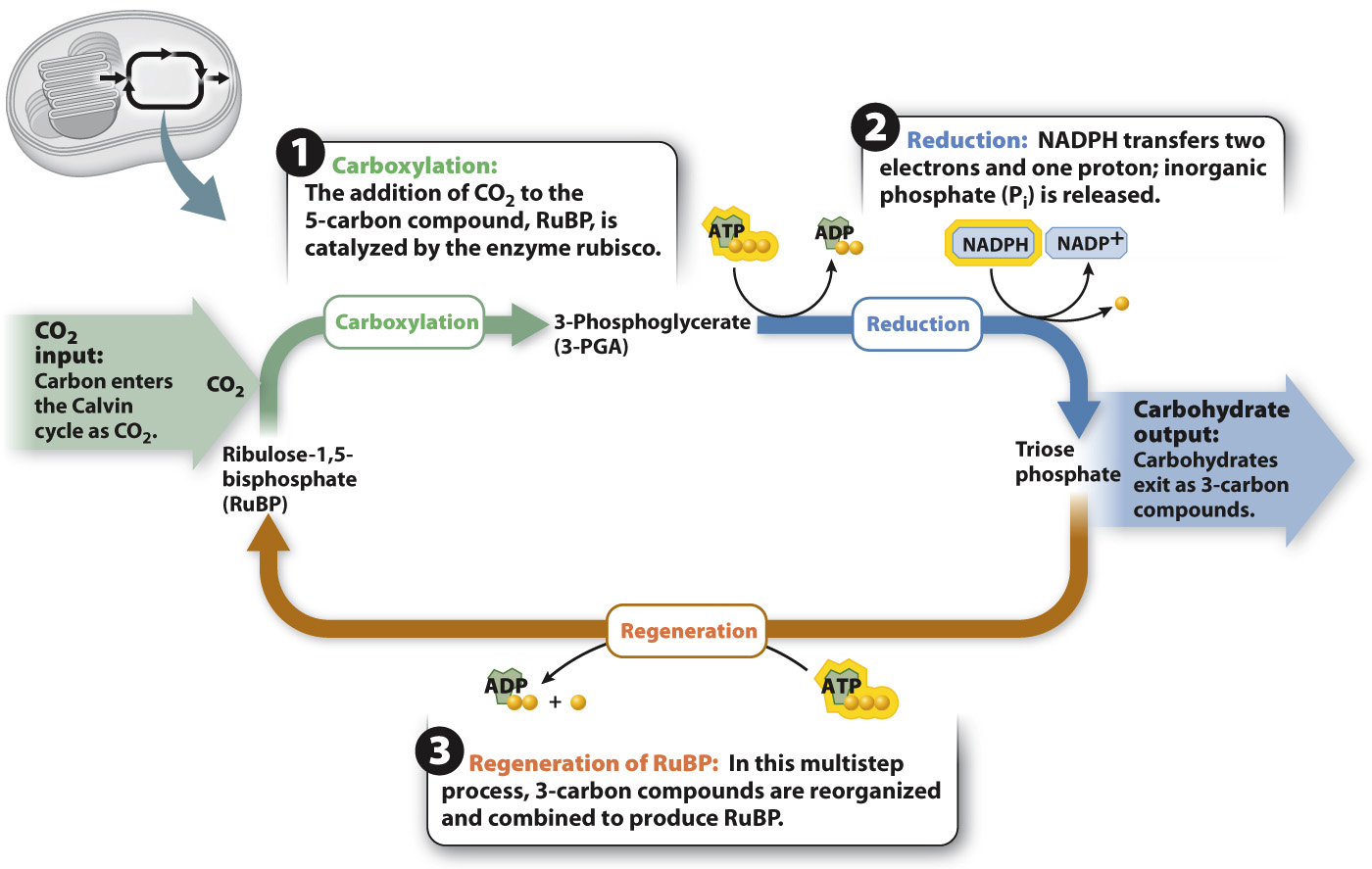
FIG. 8.5 The Calvin cycle. CO2 is the input and triose phosphate is the output of the Calvin Cycle.