9.2 Cell Signaling Over Long and Short Distances
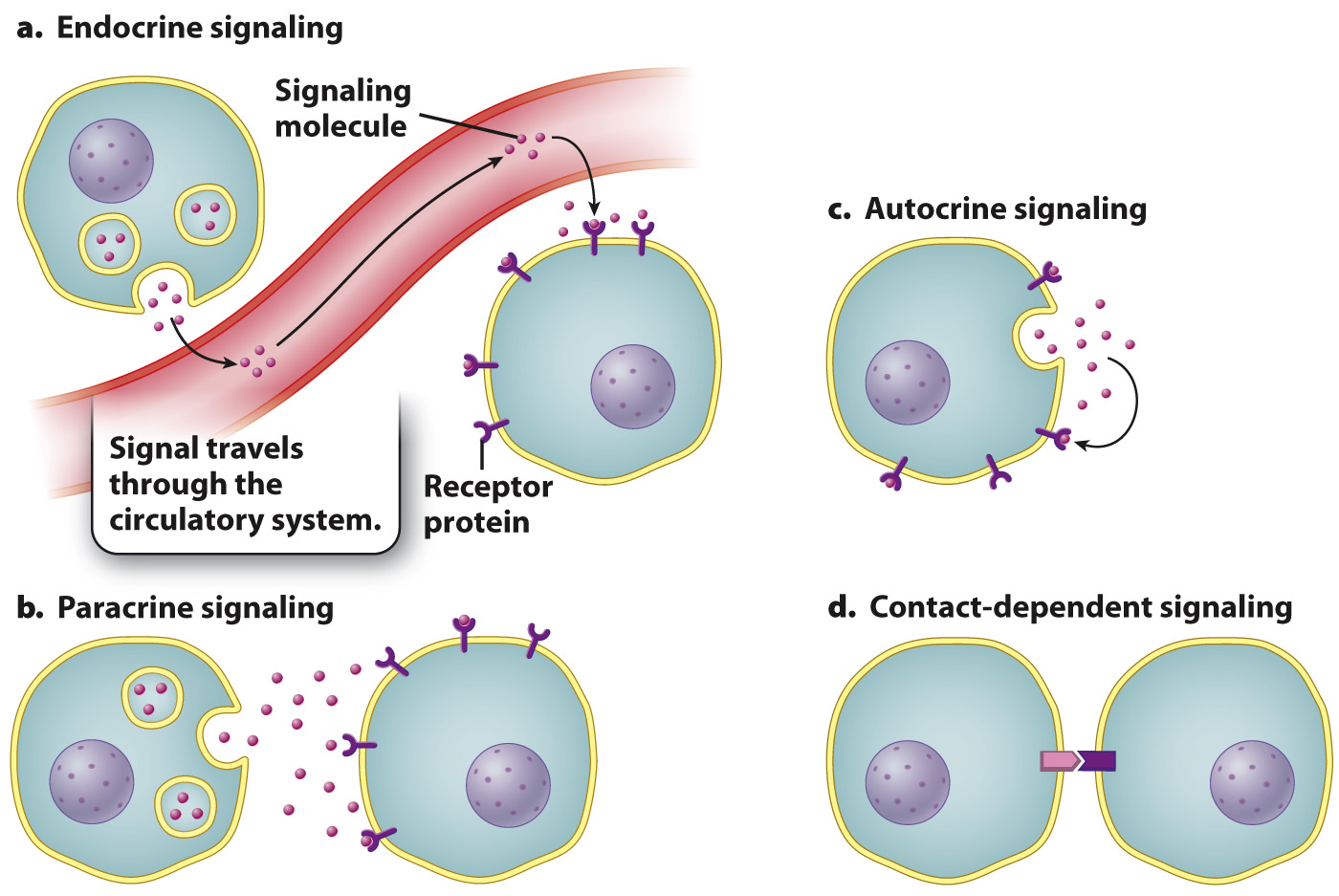
In prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes, cell communication occurs between individual organisms. In complex multicellular eukaryotes, cell signaling involves communication between cells within the same organism. The same principles apply in both instances, but there are important differences. In multicellular organisms, the distance between communicating cells varies considerably (Fig. 9.4). When the two cells are far apart, the signaling molecule is transported by the circulatory system. When they are close, the signaling molecule simply moves by diffusion. In addition, many cells in multicellular organisms are physically attached to one another; in this case, the signaling molecule is not released from the signaling cell at all. In this section, we explore communication over long and short distances, as well as communication between cells that are physically associated with one another.
183