2.20–2.21: Nucleic acids store information on how to build and run a body.
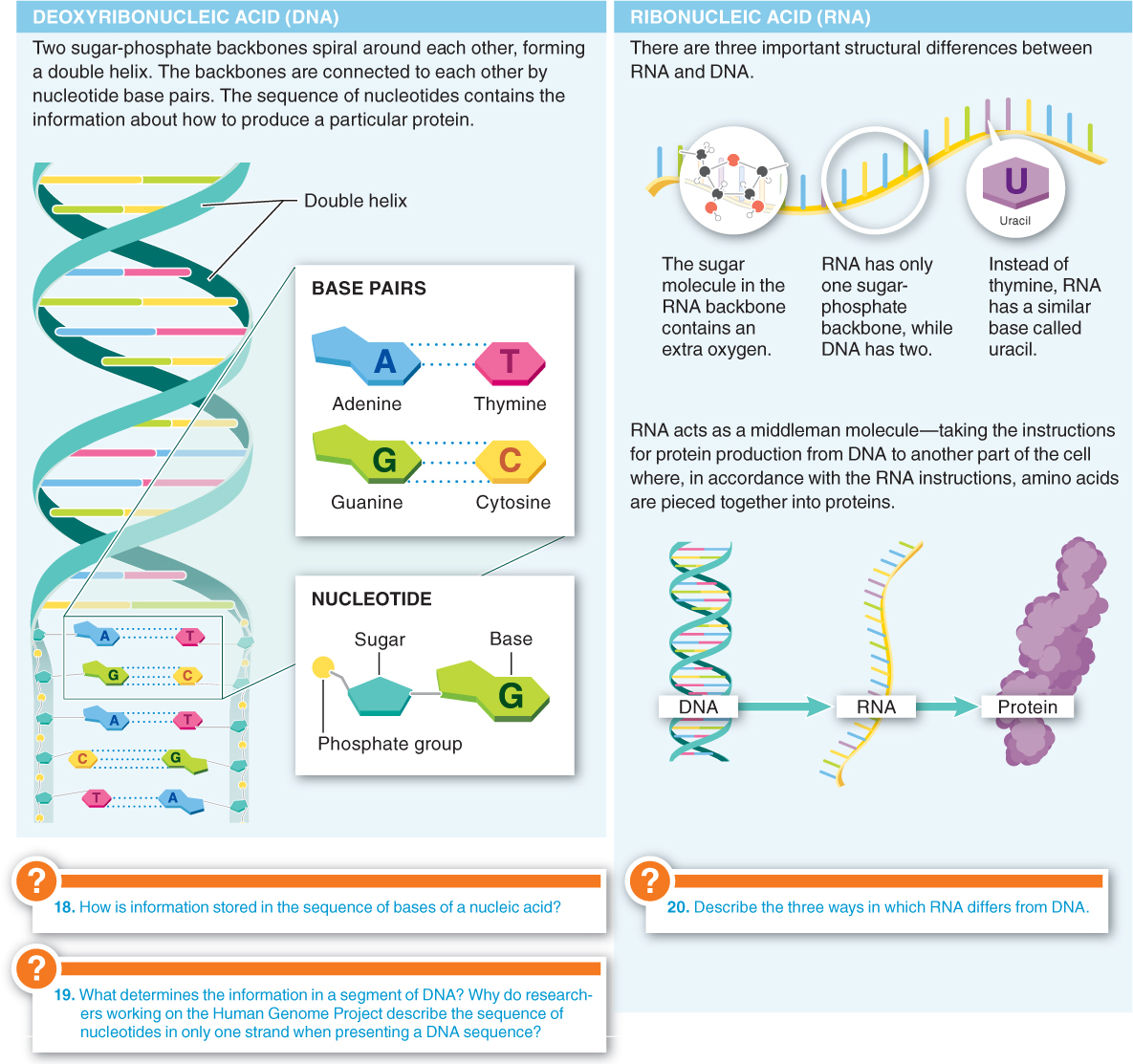
The nucleic acids DNA and RNA are macromolecules that store information by having unique sequences of nucleotides. Both play central roles in directing protein production in organisms. RNA acts as a translator of the genetic code into proteins. It reads DNA sequences and directs the production of a sequence of amino acids.
Question 2.31
Dietary proteins:
- a) are considered “complete” only if they contain the 8 essential amino acids required by humans.
- b) consist of all 20 amino acids required in the human body.
- c) are considered “complete” only if they contain the 12 non-
essential amino acids required by humans. - d) are nutritionally identical, since all are broken down into their constituent amino acids in the digestive system.
- e) can be obtained from animal sources but not plant sources.

Question 2.32
The primary structure of proteins is often described as amino acids connected like beads on a string. In this same vein, which of the following images best describes a protein’s quaternary structure?
- a) threads in a cloth
- b) needles in a haystack
- c) rungs on a ladder
- d) links on a chain
- e) coils in a spring

Question 2.33
Which of the following statements about enzymes is incorrect?
- a) Enzymes can initiate chemical reactions.
- b) Enzymes speed up chemical reactions.
- c) Enzymes are proteins.
- d) Enzymes contain an active site for binding of particular substrates.
- e) Enzymes undergo a permanent change during the reactions they promote.

Question 2.34
Which of the following nucleotide bases are present in equal amounts in DNA?
- a) adenine and cytosine
- b) thymine and guanine
- c) adenine and guanine
- d) thymine and cytosine
- e) adenine and thymine

Question 2.35
Which type of macromolecule contains an organism’s genetic information?
- a) polysaccharide
- b) monosaccharide
- c) fatty acid
- d) DNA
- e) phospholipid
