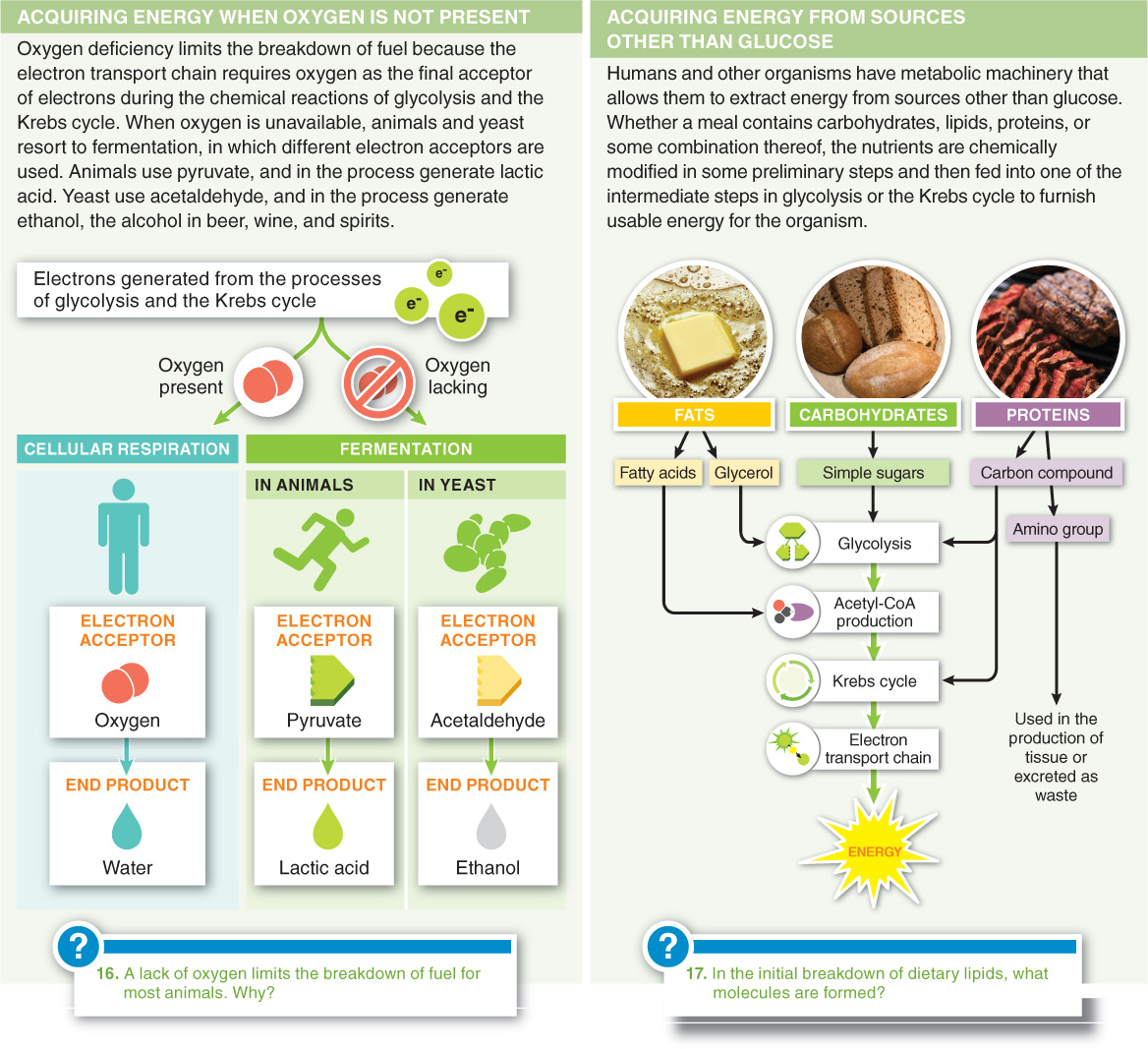
4.17–4.18: There are alternative pathways to energy acquisition
Organisms can generate ATP when oxygen is lacking or when organic molecules other than glucose, such as lipids, proteins, and polysaccharides, are consumed.
Question 4.30
Which of the following energy-
- a) the Krebs cycle
- b) glycolysis
- c) combustion
- d) photosynthesis
- e) None of the above. There are no energy-
generating processes that occur in all living organisms.

Question 4.31
During the Krebs cycle:
- a) the products of glycolysis are further broken down, generating additional ATP and the high-
energy electron carrier NADH. - b) high-
energy electron carriers pass their energy to molecules of sugar, which store the electrons as potential energy. - c) the products of glycolysis are broken down, generating ATP and ethanol.
- d) cellular respiration can continue even in the absence of oxygen.
- e) the products of glycolysis are converted to acetyl-
CoA.

Question 4.32
All alcoholic beverages are produced as the result of:
- a) cellular respiration by bacteria that occurs in the absence of oxygen.
- b) cellular respiration by bacteria that occurs in the absence of free electrons.
- c) cellular respiration by yeast that occurs in the absence of free electrons.
- d) cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of sugar.
- e) cellular respiration by yeast that occurs in the absence of oxygen.

Question 4.33
In harvesting the chemical energy of the molecules in food:
- a) all macromolecules must first be converted to glucose.
- b) all macromolecules must first be converted to hydrocarbon chains.
- c) all macromolecules must first be converted to simple sugars.
- d) organisms can use sugars, lipids, and proteins.
- e) all macromolecules must first be converted to free-
form amino acids.
